GRAM POSITIVE PATHOGENIC COCCI
Staphylococcus aureus (causative organism)
Gram positive cocci in clusters
Non-motile
Opportunist
Salt-tolerant (must tolerate sweat on skin)
Glycocalyx (slime layer)
Coated with protein A, decreases IgG binding (decreases phagocytosis and complement)
Beta hemolytic
Produces extra cellular enzymes: catalase, coagulase, kinase , hyaluronidase , beta-lactamase (90% produce beta-lactamase)
Found on skin and in noses of 25-33% of healthy people; 2% of these people carry methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Produces seven exotoxins
Impetigo = Disease
A common and highly contagious skin infection that mainly affects infants and young children. It usually appears as reddish sores on the face, especially around the nose and mouth and on the hands and feet. Over about a week, the sores burst and develop honey-colored crusts.
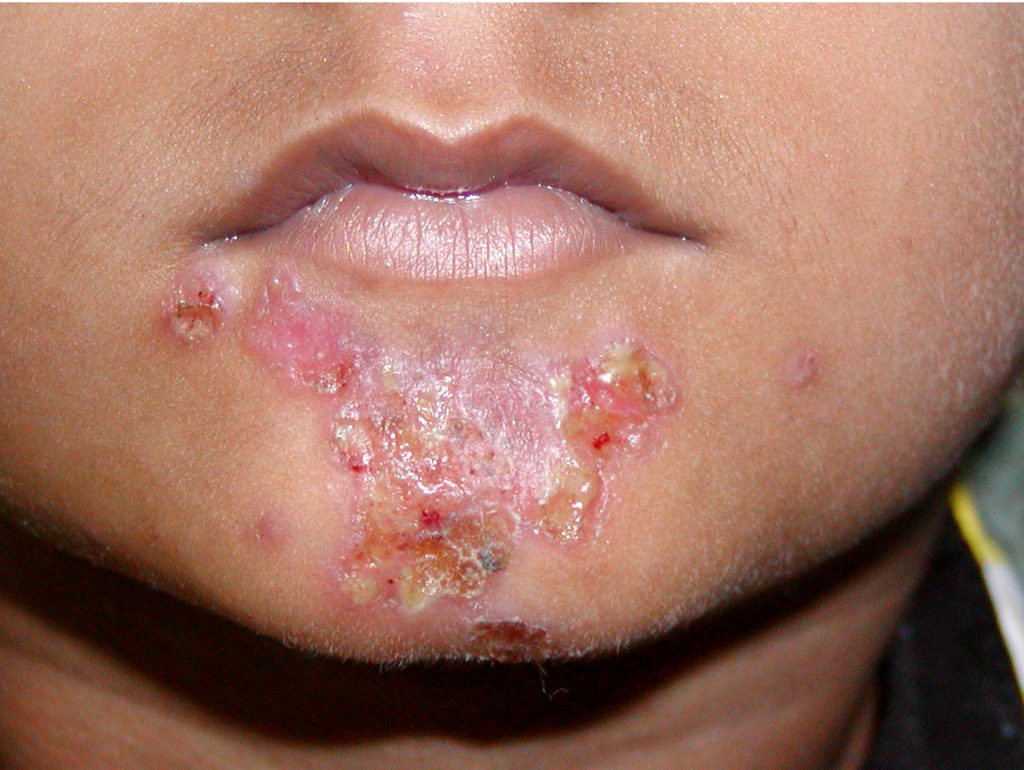
Folliculitis = Disease
A common skin condition when a hair follicle becomes infected.
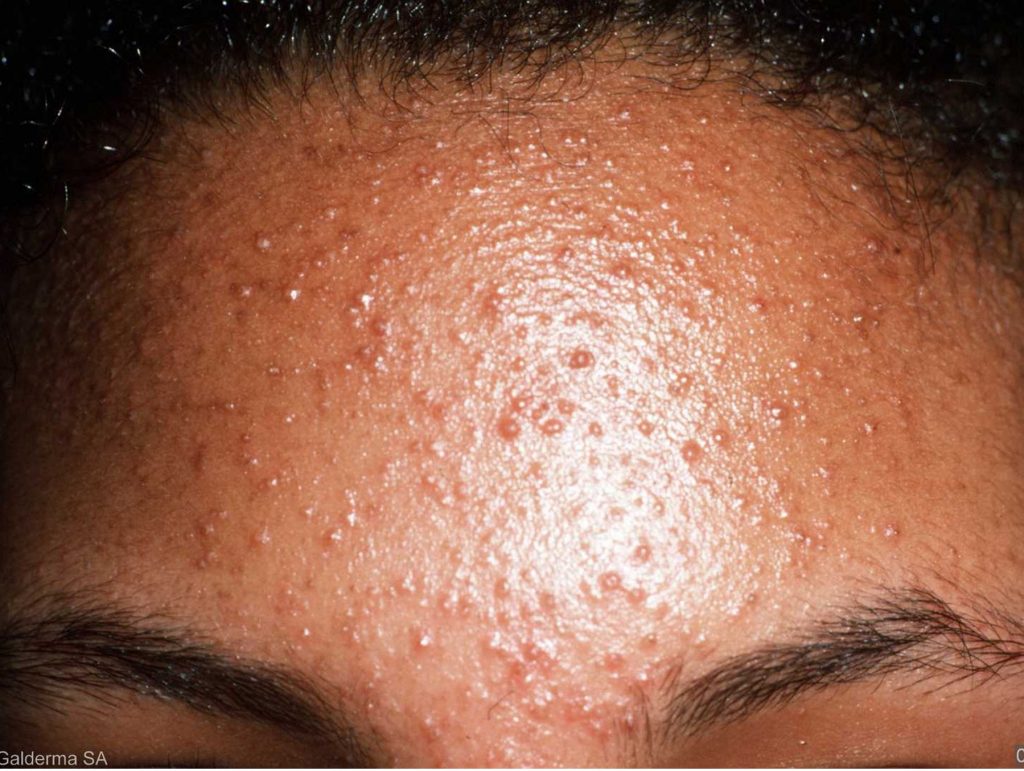
Cellulitis = Disease
A common, potentially serious bacterial skin infection. The affected skin is swollen and inflamed and is typically painful and warm to the touch. Cellulitis usually affects the lower legs, but it can occur on the face, arms and other areas. The infection happens when a break in the skin allows bacteria to enter. Left untreated, the infection can spread to the lymph nodes and bloodstream and rapidly become life-threatening.
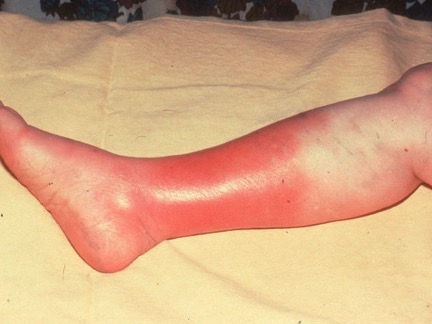
Food poisoning = Disease
Staphylococcus auerus food poisoning is the second most reported food borne illness. This is a food intoxication, ingestion of toxin (enterotoxin) via contaminated food. Brief incubation period, as little as 30 minutes; 1-6 hours. Sliced meat (ham salty), mayo salads, éclairs are common vehicles of the infection. Food service worker carries the bacteria and the toxin ends up in your food.
Signs and symptoms nausea, vomiting, cramps, diarrhea, headache, recover 1-3 days. Antibiotics won’t help with the toxin. The immune system must deal with the toxin.
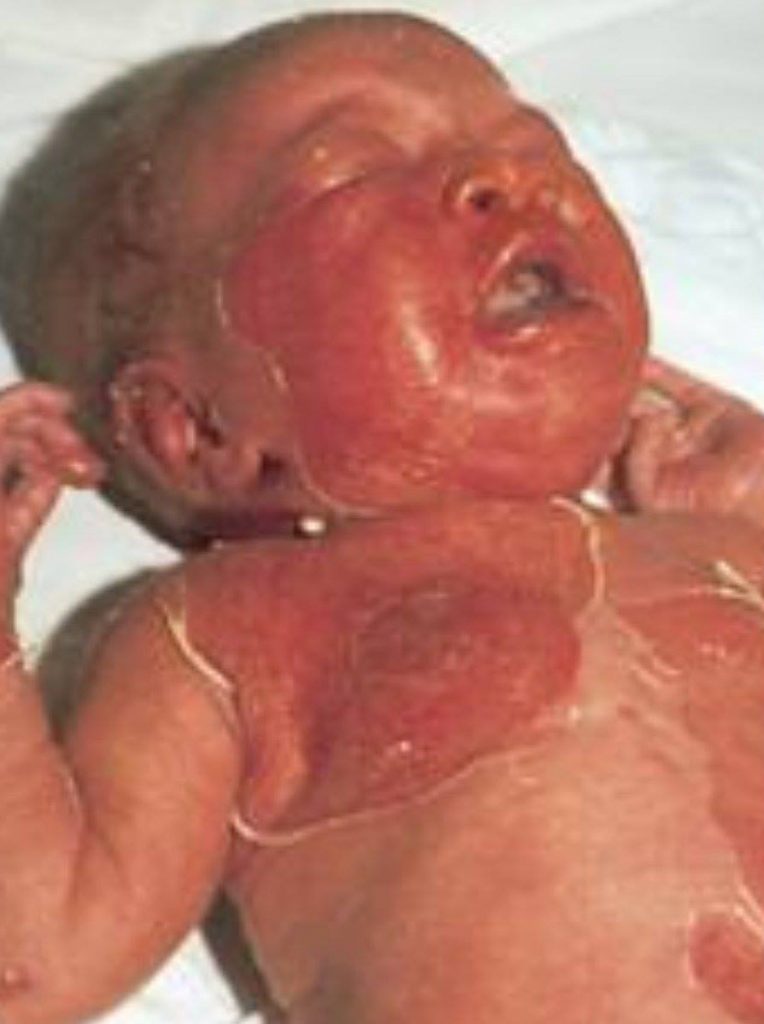
Scalded skin syndrome = Disease
Reddening of the skin, followed by large blisters. Within 2 days exotoxin (cytotoxin) causes epidermis to peel off. Secondary bacterial infection possible.
MRSA wound infections = Disease
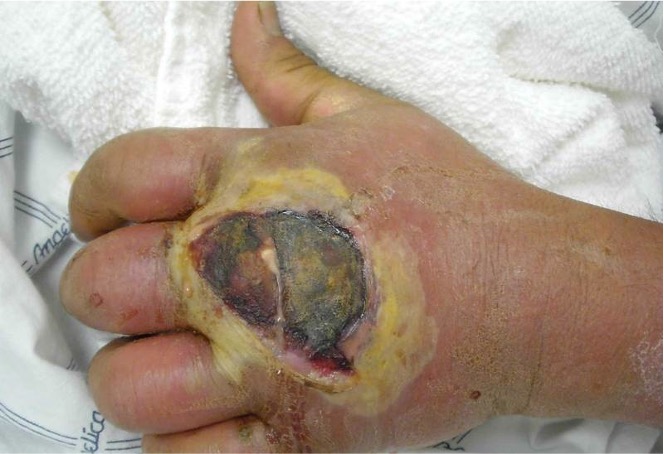
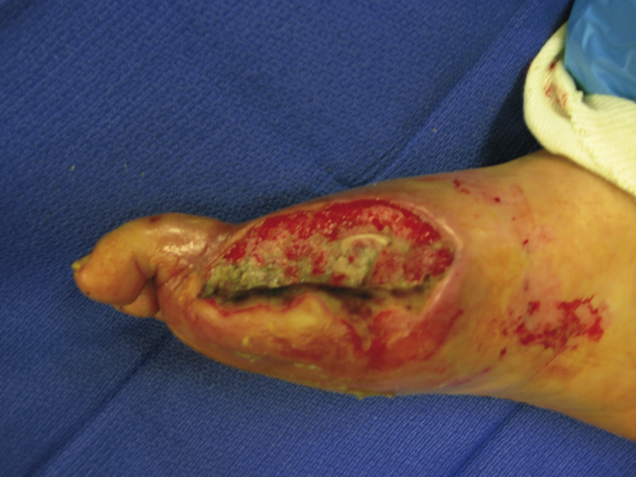
Streptococcus pyogenes (causative organism)
Pyogenic = pus formation
Lancefield group A organism
5-15% harbor in respiratory tract (asymptomatic)
Respiratory droplet transmission (cough/sneeze)
Exotoxin (cytotoxin) caps near surface dilate = rash
Extra cellular enzymes produced include kinase, hyaluronidase, c5a peptidase (breaks down complement)
Glycocalyx (capsule)
M protein destabilized complement and decreases phagocytosis
Strep throat = Disease
Signs and symptoms sore throat, fever, headache, swollen nodes and tonsils, red throat, pus on tonsils
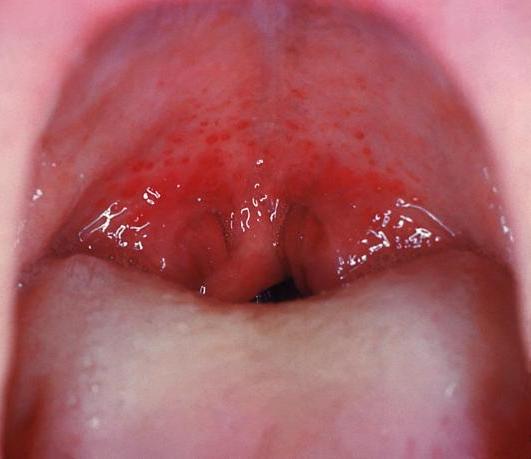
Complication = scarlet fever; high fever, rash that looks like sunburn and feels like sandpaper, strawberry appearance of tongue
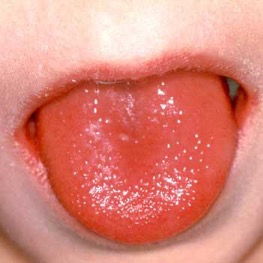
Complication = Rheumatic fever; serious. Autoimmune response antibodies against strep cross react with heart antigens. Heart valves damaged.
Impetigo, Cellulitis, Necrotizing fasciitis, Sepsis after Childbirth = Diseases
Streptococcus pyogenes can cause impetigo, cellulitis, and sepsis after child birth.
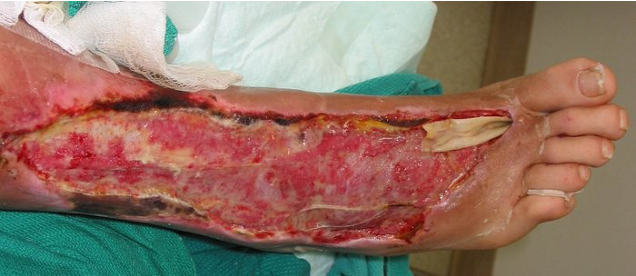
Streptococcus pyogenes is the most common cause of necrotizing fasciitis (Staphylococcus aureus and other bacteria are also capable). Bacteria enters the body via breaks in skin. Extracellular enzymes and exotoxins destroy tissue along fascia, 25% die.

Streptococcus pneumoniae (causative organism)
75% have as normal flora, issue if spreads to lungs (especially kids, elderly)
Cocci arrangement
Glycocalyx (capsule)
Alpha hemolytic on blood agar when grown aerobically; beta-hemolytic grown anaerobically
Optochin sensitive
Extracellular enzyme produced-secretory IgA protease destroys IgA
Pneumococcal pneumonia = Disease
85% of all cases of pneumonia
Droplet transmission (cough/sneeze)
Signs and symptoms high fever, severe shaking chills, productive cough, slightly bloody sputum, rapid pulse, and chest pain
Antibiotic resistance becoming an issue
Vaccine available for 50 and older, adult who is at increased risk for pneumococcal disease, kids under 5
30% of the cases invades bloodstream = bacteremia
Pneumococcal meningitis = Disease
Most common cause of meningitis in adults
Signs and symptoms high fever, sleepiness, confusion, nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, severe headache, stiff neck
20% die, 50% serious long-term complications (deaf, paralysis)
Vaccine available
