DERMATOPHYOSIS
DERMATOPHYOSIS = Disease
Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton (causative organisms, molds)
Tinea or ringworm is caused by the molds Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton. The infection tends to expand circularly, hence the name ringworm. Dermatophytosis is usually transmitted by fomites but it can be transmitted by direct contact with lesions. Ringworm is a zoonotic disease and it can be transmitted by dogs, cats, birds, rodents, rabbits, cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs.
Signs and Symptoms:
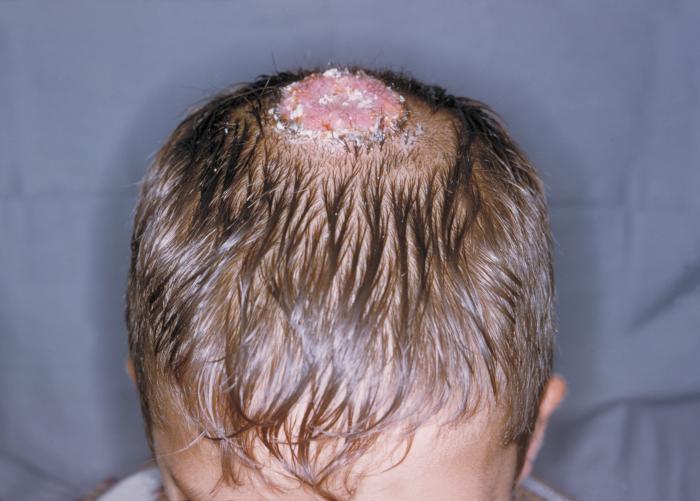
Tinea captis (scalp) itchy, red, circular bald spot. The bald spot can grow and multiple bald spots may develop. This is not a common infection in adults.
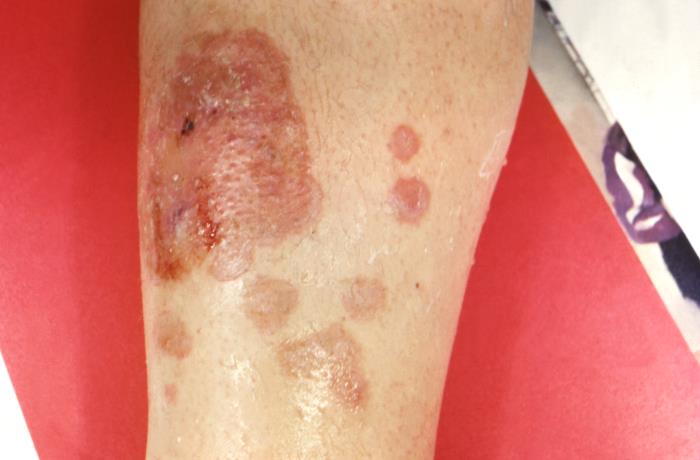
Tinea corporis (body) round, scaly, red lesions on the body.
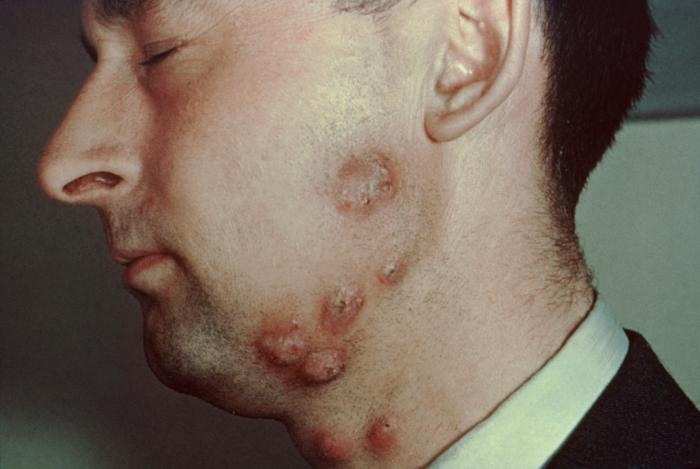
Tinea barbae (beard) scaly, itchy, red spots on the cheeks, chin, or upper neck. The spots may crust over or fill with pus, and the affected hair might fall out.
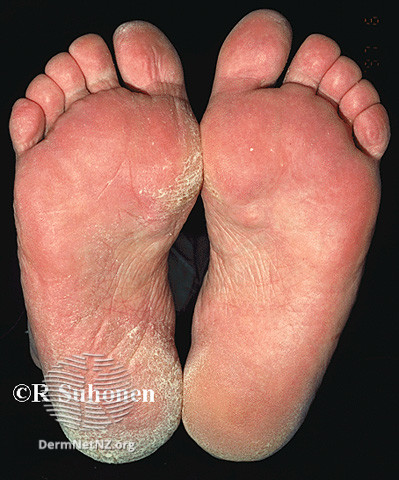
Tinea pedis (feet) red, raised lesions on and around the toes and soles and sides of the feet; webbing between the toes is heavily infected.
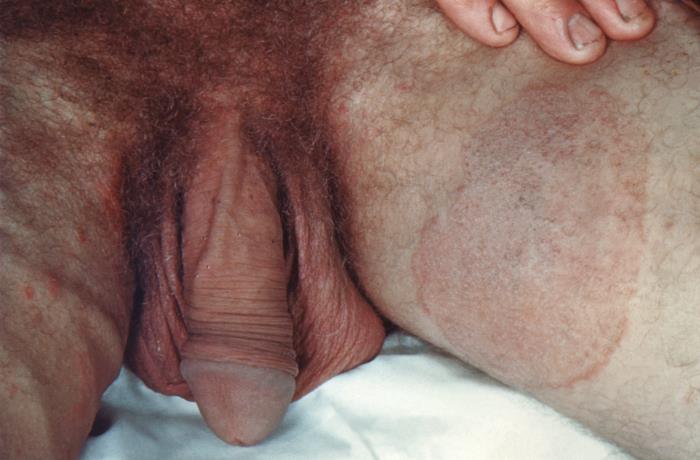
Tinea cruris (groin) red, raised lesions on and around the groin and buttocks. Also known as jock itch.
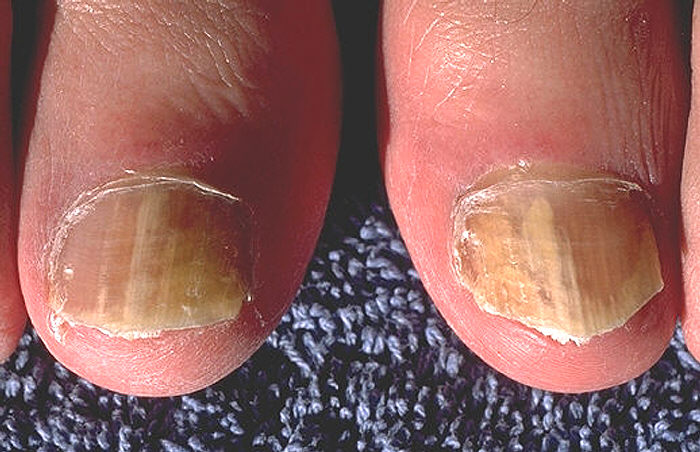
Tinea unguium (nails) white patches or pits on the nail surface. Yellowing and thickening of the nail plate.