GRAM NEGATIVE PATHOGENIC BACILLI
Escherichia coli (causative organism)
Ferments lactose and produces gas
Produces exotoxins (enterotoxins) release sodium, chlorine, potassium, and water from cells producing watery diarrhea that may be bloody, cramps, nausea, vomiting
Transmitted fecal-oral
Traveler’s diarrhea = Disease
80,000 cases per year of traveler’s in the U.S. (Africa, middle east, Latin America)
Signs and symptoms diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, bloating, malaise
90% cases resolve within one week
Urinary tract infection = Disease
80% urinary tract infections are caused by E. coli
Signs and symptoms persistent urge to urinate but pass only small amount of urine
Burning sensation when urinating
Foul-smelling urine, cloudy urine
Food poisoning = Disease
Escherichia coli 0157:H7
265,000 cases per yr. in U.S.
Signs and symptoms severe bloody diarrhea, severe cramps, vomiting, nausea
5-10% get hemolytic uremic syndrome
Under cooked beef, unpasteurized milk/juice, sprouts, lettuce, salami
Salmonella (causative organism)
Motile
Found in the intestine of birds, reptiles, mammals, so found in feces
200 different strains
Usually transmitted via contaminated food, eggs
Salmonellosis = Disease
Large Salmonella infection
1 million cases per year in U.S.; 19,000 hospitalized, 380 die
21.5 million per year worldwide
Signs and symptoms fever, diarrhea, abdominal cramps 12-72 hours after infection
Usually last 4-7 days
Salmonella typhi (causative organism)
Typhoid fever = Disease
5,700 cases per year in the U.S.; 75% traveled abroad (India, SE Asia, Africa, South America)
21.5 million cases per year worldwide; over 200,000 deaths/year
Positive glucose fermentation, positive H2S, positive motility, negative lactose fermentation
Only lives in humans
Contaminated food/water (flies, fingers, food, feces, fomites); able to live outside body for long periods
Carriers can be asymptomatic
5-21 day incubation period
Signs and symptoms 1-2 weeks fever, weakness, stomach pain, headache, decreased appetite
Signs and symptoms 3-4 weeks
Without treatment, 15% of infected people die
5% recover are carriers, shed organism 1 year (typhoid Mary shed her entire life and sickened 47, 3 dead)
Vaccine for international travel

Shigella sonnei and Shigella flexneri (causative organisms)
Non-motile
Urease negative
Does not produce H2S
Shigellosis = Disease
Shigella sonnei (causative organism 2/3 cases in U.S.) Shigella flexneri (causative organism, 1/3 cases in U.S.)
14,000 cases in U.S. per year; 90 million cases worldwide per year
Ingest contaminated food and water, eggs, veggies, shellfish, dairy
Transmitted fecal-oral
Incubation period 24-28 hours
Resolves in 5-7 days
Signs and symptoms often bloody diarrhea, fever, stomach cramps
Yersinia pestis (causative organism)
In the 6th century the plague killed 10 million people in less than 50 years
In the14th century the plague killed 25% of European population
3,000 cases per year worldwide; about 10-15 per year in U.S.
Rodents carry fleas, transmission via flea bites (flea is the vector), contact with contaminated fluid/tissue (hunter skinning infected rabbit), airborne infectious droplets
There are three types of plague:
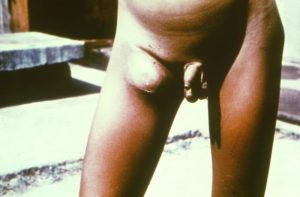
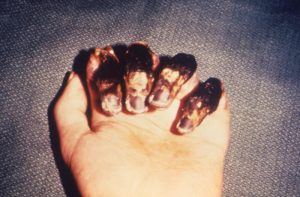
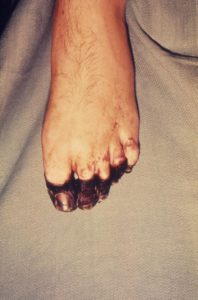
Bubonic plague = Disease
Signs and symptoms appear suddenly, usually after 2-7 days of exposure to the bacteria. High fever, headache, chills, weakness, smooth, painful lymph node swelling commonly found in the groin, but may occur in the armpits or neck, gangrene in extremities (black death), 40%-60% death rate if not treated.
Pneumonic plague = Disease
Signs and symptoms appear suddenly, typically 2-3 days after exposure. Headache, weakness, shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, respiratory failure, shock, 100% fatal if not treated in first 24 hours.
Septicemic plague = Disease
Signs and symptoms fever, chills, extreme weakness, abdominal pain, shock, bleeding into skin and other organs.
Haemophilus influenzae type b (causative organism)
Coccobacilli
Commonly found in the noses and throats of 75% of healthy individuals living in regions where vaccination is not carried out
Transmitted by respiratory droplets
Meningitis = Disease
Signs and symptoms fever, headache, stiff neck, nausea with or without vomiting, sensitivity to light, confusion
Leaves 30% of survivors with permanent disabilities such as mental impairment or deafness.
3-6% cases are fatal
Vaccine available
Bordetella pertussis (causative organism)
Aerobe
Non-motile
Very small bacilli
Under age 1 about half hospitalized (23% pneumonia, 1.1% convulsions, 61% apnea, 0.3% encephalopathy, 1% die)
Survives within phagocytes
Produces an exotoxin (cytotoxin) kills cilia, impairs mucus movement
Whooping cough = Disease
Pediatric disease, 30-50 million cases per year worldwide with 300,000 deaths; over 48,000 cases per year in the U.S.
Transmitted via respiratory droplets
7-14 days until signs and symptoms may be up to 6 weeks
Signs and symptoms rapid coughing fits followed by high pitched whoop, throwing up, exhaustion
1-2 weeks common cold signs and symptoms most infectious
2-4 weeks coughing spells with whoop
3-4 weeks convalescence
Vaccine (Tdap=tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (causative organism)
Opportunistic pathogen
Aerobe
Ubiquitous in soil, decaying organic matter, moist environments
Fimbrae and other adhesins for attachment
Glycocalyx (capsule)
Resistant to many drugs, soaps, disinfectants
Forms biofilms, drugs more difficult time
Causes diseases including urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, dermatitis, bacteremia, bone and joint infections
10% nosocomial infections are caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, common infection in burn patients
Cystic fibrosis patients often suffer from Pseudomonas aeruginosa, biofilm formation, decrease phagocytosis
Bacteroides fragilis (causative organism)
Normal flora of intestinal tract (commensal)
Makes up 30%-50% of the bacteria in fecal matter
Obligate anaerobe
Fimbrae
Glycocalyx (capsule)
Survives inside phagocytes
Causes diseases including intra-abdominal and pelvic abscesses (local accumulation of pus anywhere in the body), bacteremia.
