GRAM NEGATIVE PATHOGENIC COCCI
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (causative organism)
Diplococci
Gonorrhea = Disease
583,405 cases per year in U.S.
Transmitted by unprotected oral, anal, vaginal intercourse; childbirth
Infection can be oral, anal, vaginal
Men 2-5 days until signs and symptoms pus discharge, painful urination, scar epididymis shut can lead to infertility, joint infection leading to gonococcal arthiritis, can go systemic via blood stream
Anal for men and women signs and symptoms rectal discharge, anal itching, anal bleeding, painful bowel movements
Throat may be asymptomatic or sore throat
Women 50% asymptomatic, signs and symptoms pain/burning urination, vaginal discharge, bleeding between periods, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, joint infection leading to gonococcal arthritis, can go systemic via blood stream
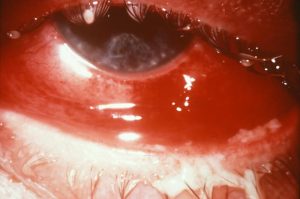
Eye infection in newborns (antibiotic drops after birth to prevent infection)
Diagnose via diplococci in pus discharge, genetic probe

Neisseria meningitidis (causative organism)
Part of normal flora in 10% of people (asymptomatic carrier)
Diplococci
Meningococcal meningitis = Disease
Transmitted via respiratory droplets
Signs and symptoms sudden onset fever, stiff neck, headache, vomiting, nausea, photophobia, confusion
Usually 3-7-day incubation period
Death can occur within hours of signs and symptoms
Diagnose via diplococci in cerebral spinal fluid
Vaccine available

