GRAM POSITIVE PATHOGENIC BACILLI
Bacillus anthracis (causative organism)
Normally found in soil
Endospore former; inhale, ingest, inoculate endospores
2001 terrorist attacks on U.S. 17 people sickened 5 dead (inhalation anthrax)
Glycocalyx (capsule)
Exotoxin (cytotoxin)
Incubation period about 7 days; inhalation 7-42 days
Inhalation anthrax = Disease
People who work with sheep or sheep products (inhale endospore)
Signs and symptoms fatigue, sore throat, malaise, fever, aches, chest pain, cough (exotoxin via vegetative cell). Later high fever, labored breathing, shock, death.
No treatment 10-15% survive, with aggressive treatment 55% survive
Intestinal anthrax = Disease
Consume contaminated/under cooked meat (ingest endospore)
Signs and symptoms nausea, decrease appetite, fever, bloody diarrhea
No treatment more than 50% die, with treatment 40% die
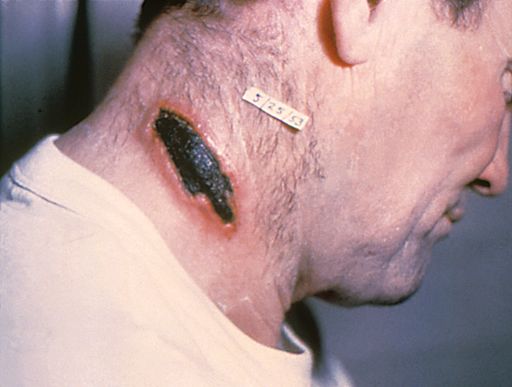
Cutaneous anthrax = Disease
Skin contact with endospore
Wool or hide worker, veterinarian, livestock handler
Signs and symptoms painless swollen black crusty ulcers (eschar), breathing issues, cough
95% of anthrax cases
Less than 1% die if treated
clostridium
Obligate anaerobes
Endospore former
Found in soil, water, sewage, GI tracts animals and humans
Produces exotoxins (neurotoxin and enterotoxin)
Clostridium perfringens (causative organism)
Bacteria need anaerobic environment, produces enterotoxin
Food poisoning = Disease
Raw meat/poultry; 1 million cases per yr. in U.S. Intense abdominal cramps and watery diarrhea. 8-12 incubation period. Usually resolves in 24 hours.
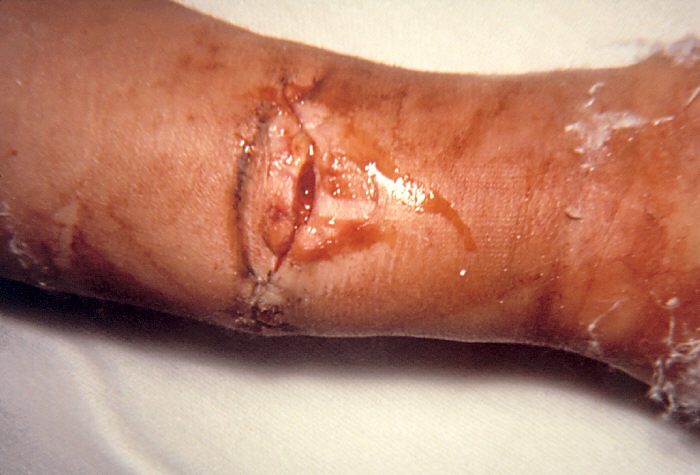
Gangrene= Disease
Endospore can enter anaerobic wound. Bacteria produce cytotoxin and may ferment and produce gas (gaseous gangrene). Toxin causes decrease blood flow; leads to tissue death.
Clostridium difficile (causative organism)
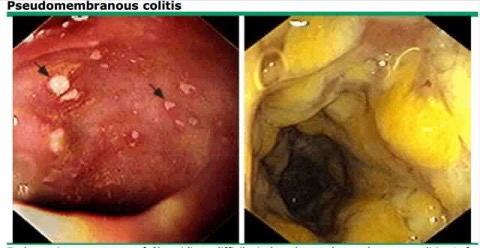
Pseudomembrane colitis = Disease
Large sections of the colon wall slough off
500,000 cases per year in the U.S.
Anaerobic intestinal bacteria (opportunist)
Antibiotic associated diarrhea which can lead to severe infection of the colon. Antibiotic killed normal flora; C. difficile over grows.
Endospores on surfaces or hands of healthcare worker
Motile
Produces an exotoxin (cytotoxin causes necrosis of colon wall) and hyaluronidase
Watery diarrhea, fever, decreased appetite, nausea, abdominal pain/tenderness
29,000 die within 30 days of initial diagnosis
Decrease antibiotic use, hand washing, aseptic technique
Clostridium botulinum (causative organism)
Intoxication, produces an exotoxin (neurotoxin)
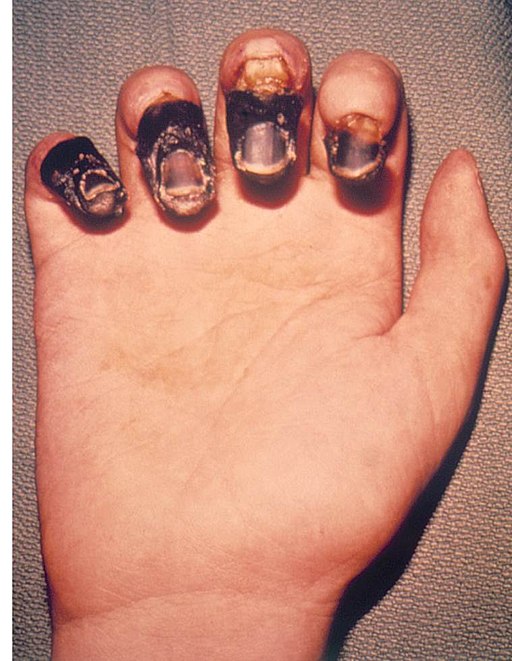
Endospore former, manure, organic fertilizer, sewage (soil and water)
Endospores enter anaerobic environment and germinate to bacteria
18-36-hour incubation period (as little as 6 hours as late as 10 days)
145 cases of botulism per year in the U.S
Botulism general signs and symptoms = double/blurred vision, slurred speech, drooping eyelids, difficulty swallowing and chewing, labored breathing, muscle weakness, flaccid paralysis (no acetylcholine released)
Antitoxins to neutralize toxin
1 ounce aerosolized botulism neurotoxin would kill all people in U.S.
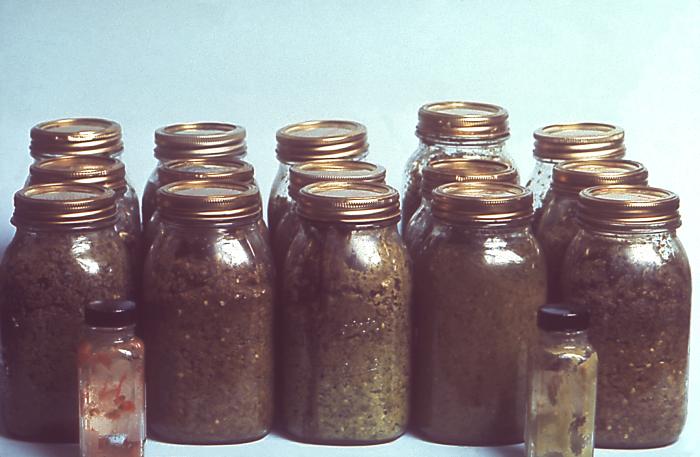
Food-borne botulism= Disease
15% of botulism cases
Severe type of food poisoning
Home canned foods, ingest food containing neurotoxin
Destroy neurotoxin if heat to 80◦C for 10 minutes

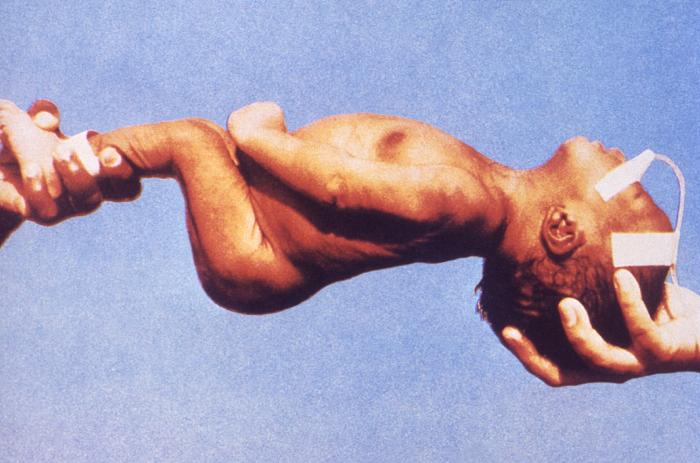
Infant botulism = Disease
65% of botulism cases
Ingestion of endospore by infant (honey); germinate in intestine
3-24 months of age; not enough normal flora to compete it out
Lethargy, poor muscle tone = floppy baby syndrome; failure to thrive

Wound botulism= Disease
20% of botulism cases
Deep wound contaminated with endospore; will germinate to bacteria
Clostridium tetani (causative organism)
Endospore former, obligate anaerobe
Ubiquitous in soil, dust, gastrointestinal tract of animals and humans
Vegetative needs anaerobic environment; enters via wound
Produces exotoxin (neurotoxin); intoxication
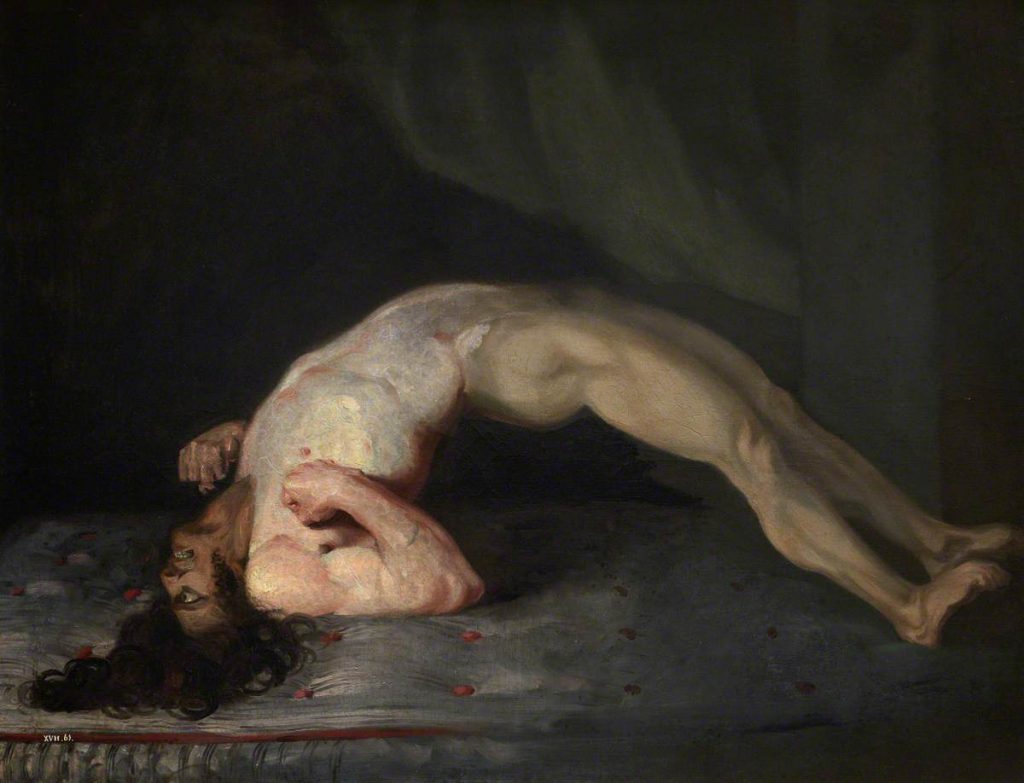
Tetanus= Disease
Early signs and symptoms = tight jaw/neck/abdomen, difficulty swallowing
Late signs and symptoms = severe muscle spasms, affects breathing (can’t exhale)
10-20% mortality rate
Vaccine available (toxoid vaccine)

Listeria monocytogenes (causative organism)
Motile, small
Intracellular pathogen (goes inside human cells once inside the body)
Facultative anaerobe
1-10% of humans, 37 mammalian species, 17 species of birds, some fish and shellfish carry in intestine so found in soil and human and animal feces
Grows in refrigerator
Listeriosis = Disease
1600 cases per year in the U.S.
Unpasteurized milk and cheese
Third leading cause of death from food poisoning
Incubation period 3-70 days but usually about 30 days
Signs and symptoms fever, muscle aches, stiff neck, headache, confusion, loss of balance, convulsions
Newborns, pregnant women, elderly, immunocompromised (healthy no signs and symptoms)
Pregnant woman (miscarry, still birth, premature delivery
Corynebacterium diphtheriae (causative organism)
Aerobe
Non-motile
Produces an exotoxin (cytotoxin)
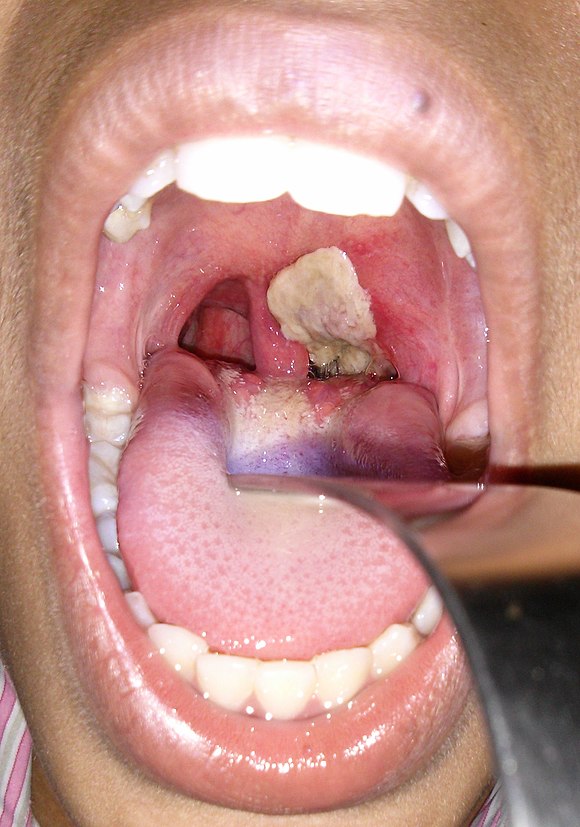
Diphtheria = Disease
Transmitted by respiratory droplet
Sore throat, fever, pseudomembrane in throat
Demyelination decreases motor control and causes loss of sensation
1 in 10 infected die, under 5 years of age 1 in 5 infected die
Vaccine (diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus); toxoid vaccine
