8 Chirality and R/S Naming System
Chapter 8 Learning Objectives
- Be able to distinguish between chiral and achiral molecules.
- Be able to identify stereogenic carbon atoms.
- Be able to determine R and S configuration from a Newman formula
- Be able to draw enantiomers.
- Be able to assign R or S configuration to stereogenic carbons.
8.1 Introduction
Other than geometric isomers, there is another type of stereoisomer that is related to a special property called chirality.
8.2 Chiral Molecules and Chirality
Take a closer look at your hands, left hand and right hand. The left hand can be regarded as the mirror image of the right hand, and vice versa. Now let’s try to superimpose (overlay) the left hand on right hand, can you do that?
No! No matter how hard you try, the left hand can not be superimposed on the right hand. This is because of the special property of hand, that is called chirality. Both left and right hand are chiral (ky-ral), and show chirality. Chiral derived from the Greek word cheir, that means “hand”, and chirality means “handedness”.
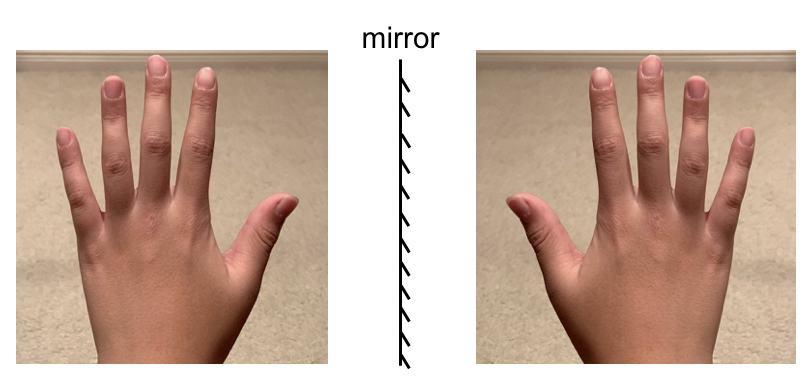
The definition of the chirality is the property of any object (molecule) of being non-superimposable on its mirror image. The left and right hand are mirror image to each other, and they are not superimposable, so both left hand and right hand are chiral. Other than that, you can also find lots other objects in daily life that show chirality as well.
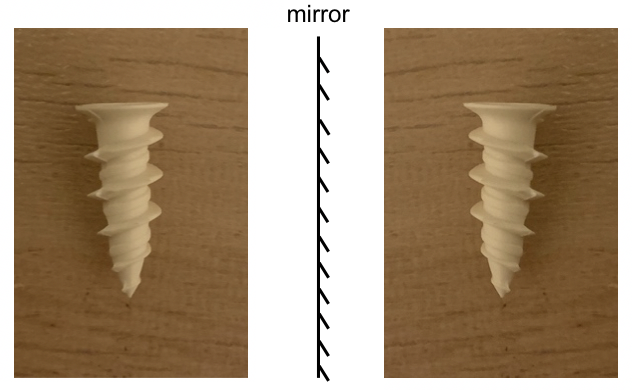
If an object is superimposable on its mirror image (for such case the object and its mirror image are exact identical), then this object is not chiral, that can be said as achiral.

In organic chemistry, we are interested in organic molecules that are chiral. Let’s see the following molecular models that represent a molecule and its mirror image.

In the models here, the four balls with different colors represent four different substituents, and the two structures are mirror image to each other. The effort of trying to superimpose one structure to the other does not work. Therefore, according to the definition of chiral/chirality, both molecules are non-superimposable on the mirror image, so they both chiral and show chirality.
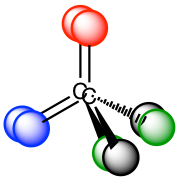
The chirality of the molecule results from the structure of the central carbon. When the central carbon is sp3 carbon, and bonded with four different groups (represented by four different colors in the model), the molecule is chiral. The central carbon is called chirality center (or asymmetric center or stereogenic carbon). The molecule with one chirality center must be chiral.
Exercise 8.1: Watch this video and answer the questions asked in the video.
As a summary, a chirality (asymmetric, stereogenic) center should meet two requirements:
- sp3 carbon;
- bonded with four different groups.
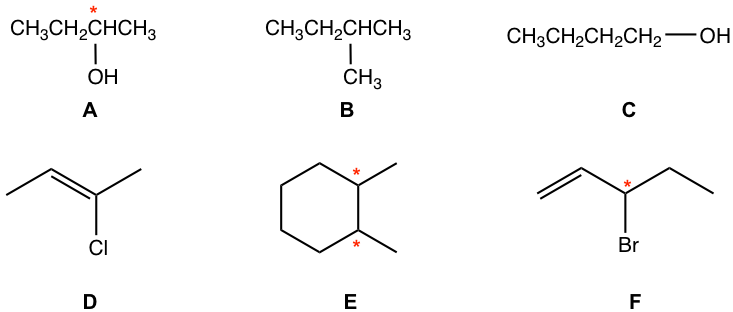
Examples
For following compounds, label each of the chirality center with a star.
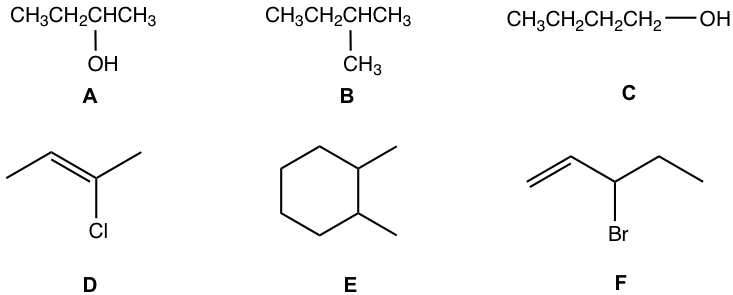
Approach:
- The carbons in CH3 or CH2 are NEVER chirality centers. The chirality center must be the carbon bonded with a branch (or branches).
- sp2 double bond carbon is NEVER a chirality center.
- Carbon in a ring can also be chirality center as long as it meet the two requirements.
- Not all the above compounds have a chirality center.
Solution:
Exercise 8.2
- Draw the structure of following compounds, determine which one has an chirality center and label it with a star.
a) 1-bromobutane,
b) 1-pentanol,
c) 2-pentanol,
d) 3-pentanol,
e) 2-bromopropanoic acid
f) 2-methyl cyclohexanone
2. Label all the chirality centers in the following molecules.
8.3 Determining R/S configuration from a Newman projection formula
2.3.4 Stereoisomer with One Chirality Center — Enantiomers
For 2-butanol, we are able to recognize that C2 is the chirality center.

The perspective formula show the 3D structure of 2-butanol in two different ways, and they are non-superimposable mirror images to each other.
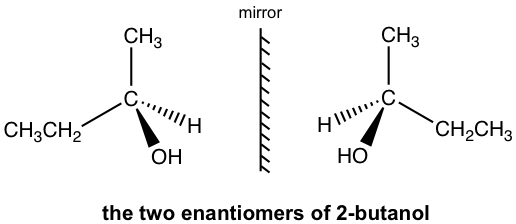
The two mirror images are different molecules. They have the same bonding, but differ in the way that the atoms arranged in space. So the two molecules are stereoisomers. This specific type of stereoisomer here is defined as enantiomers. Molecules that are a pair of non-superimposable mirror images of each other are called enantiomers.
Important Properties about Enantiomers:
- Enantiomers are a pair of non-superimposable mirror images.
- Enantiomers are a pair of molecules, they both chiral and show chirality. (Enantiomer must be chiral).
- For any chiral molecule, it must has its enantiomer, that is the mirror image to the molecule.
- Achiral molecule does not have enantiomer. The mirror image of an achiral molecule is the identical molecule to itself.
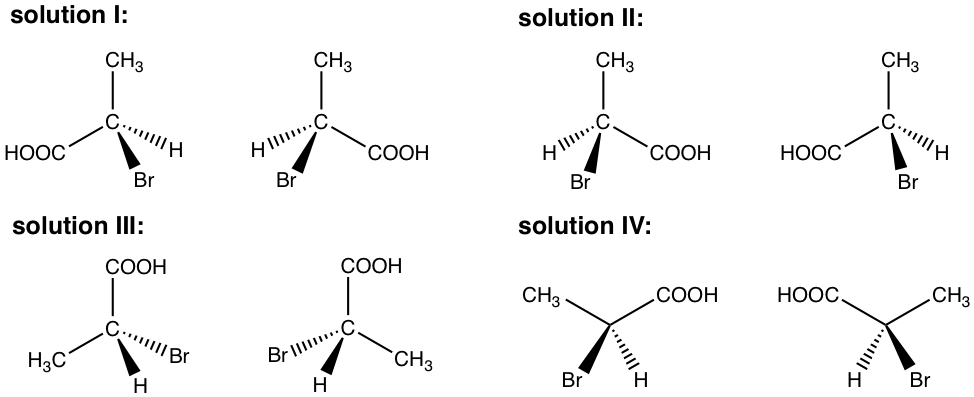
Examples: Draw the pair of enantiomers of 2-bromopropanoic acid.
Approach:
To draw the 3D structure of any enantiomer, we need to use perspective formula with solid and dashed wedges to show the tetrahedral arrangements of groups around the sp3 carbon (refer to section 2.11). Out of the four bonds on tetrahedral carbon, two bonds lie within the paper plane are shown as ordinary lines, the solid wedge represent a bond that point out of the paper plane, and the dashed wedge represent a bond that point behind the paper plane. For the first enantiomer, you can draw the four groups with any arrangement, then draw the other enantiomer by drawing the mirror image of the first one. Please note, although it seems there are different ways to show the enantiomers, there are only total two enantiomers, we will learn in next section how to identify and designate each of them.
Several possible ways to show the structures are included in the answer here. However, your answer can be different to any of them, as long as a pair of mirror images are shown.
Exercise 8.3
Draw the pair of enantiomers of 2-chloro-1-propanol.
8.4 Number of stereoisomers
The number of stereoisomers is determined by the number of stereogenic carbon atoms. If 'n' is the number of stereogenic carbon atoms, then 2n is the number of possible stereoisomers.
Exercise 8.4
Erythronolide B is the biological precursor of erythromycin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic. How many chirality centers does erythronolide B have? Identify them. What are the possible number of stereoisomers for this precursor?
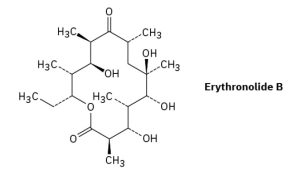
Answer:
Total chirality centers: 9
Each of these carbon atoms is bonded to four different groups, satisfying the condition for chirality.
The general formula to calculate the maximum number of stereoisomers is:
Where n = number of chiral centers.
For erythronolide B:
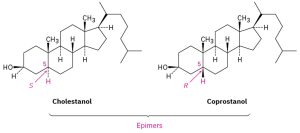
In the special case where two diastereomers differ at only one chirality center but are the same at all others, we say that the compounds are epimers. Cholestanol and coprostanol, for instance, are both found in human feces, and both have nine chirality centers. Eight of the nine are identical, but the one at C5 is different. Thus, cholestanol and coprostanol are epimeric at C5.
8.5 R/S Naming System of Chirality Center
The two enantiomers are different compounds, although they are very similar. Therefore we need a nomenclature system to distinguish between them, to give each one a different designation so that we know which one we are talking about. That is the R/S naming system defined in IUPAC. The R/S designation can be determined by following the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rule, the rule devised by R. S Cahn, C. Ingold and V. Prelog.
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rule (Priority or Sequence Rules):
- Assign priorities of the groups (or atoms) bonded to the chirality center by following the same priority rules as for E/Z system. The highest priority group is labelled as #1, and lowest priority group labelled as #4. Do not change this.
-
Orient the molecule in the way that the lowest priority group (#4) pointing away from you.
-
Look at the direction in which the priority decrease for the other three groups, that is 1→2→3.
For counterclockwise direction, designation is S-, sinister, means “left” in Latin.
Let’s take the following molecule as an example to practice the rule:
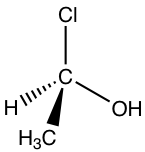
Step 1: The priorities are assigned.
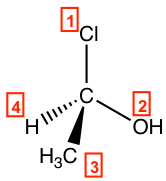
Step 2: Re-orient the molecule, so H (#4, lowest priority) is on the position away from us. Then the other three groups will be arranged in this way:
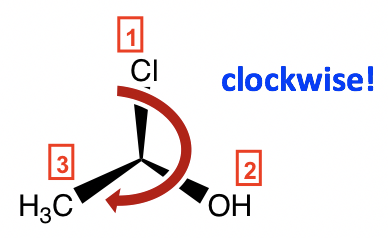
Step 3: Go along the direction from #1→#2→#3, it is in the clockwise direction, so this enantiomer is assigned R configuration, and the complete name of the molecule is (R)-1-chloroethanol.
Now let’s assign the configuration of the other enantiomer:
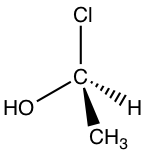
Following the same steps, put H away from us, and the arrangement of the other three groups is:
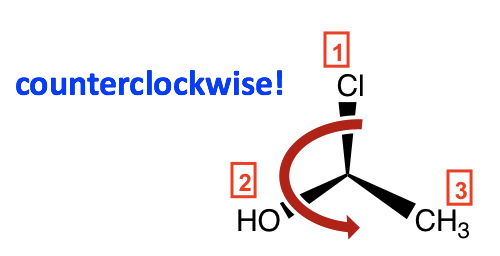
The counterclockwise direction gives the S configuration, and the complete name of the molecule is (S)-1-chloroethanol.
Examples: Assign R/S configuration of the chirality center.
1.
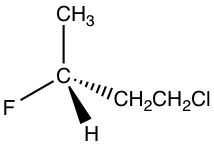
Solution:

2.
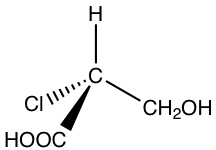
Solution:

More practical hints about R/S assignment with Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rule:
- Assigning priority is the first possible challenge for applying the C.I.P. rule. Review and practice the guidelines in section 5.2.
- The 2nd challenge is to re-orient the molecule (to arrange the #4 group away from you). The molecule model will be very helpful for this purpose. Assemble a molecular model with four different colors connected on the carbon. Compare your model to the given structure and match the assigned priority to each color, for example, red is #1, blue is #2, etc. Then rotate the model to arrange the lowest (#4) group away from you and see how the other groups locate to get the answer.
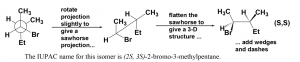
For the perspective formula of enantiomers, it is important to know the following properties:
- One (odd number of) switch (interchanging) for a pair of groups invert the configuration of the chirality centre;
- Two (even number of) switches get the original configuration back.
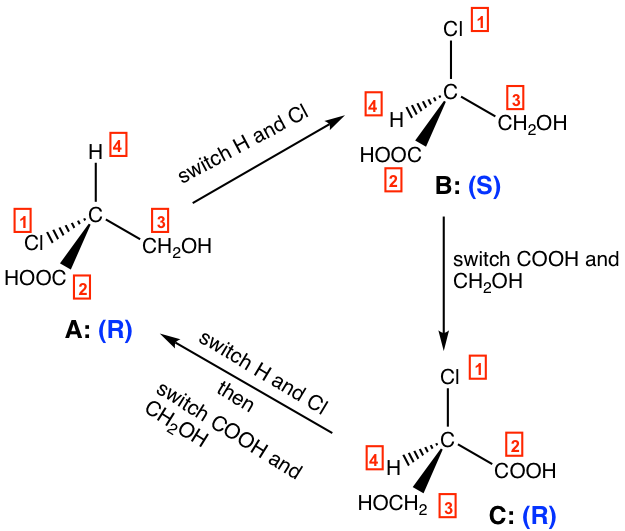
For the structures above:
- One switch of A leads to B, A is R and B is S, so A and B are enantiomers,
- One switch of B leads to C, B is S and C is R, so B and C are enantiomers,
- Two switches of C leads to A, both C and A are R, so C and A are identical.
Watch this video that shows tips and tricks for determining R and S configuration in molecules.
Exercise 8.5: R/S Configuration
Determine the R/S configuration for each chirality center in following compounds.
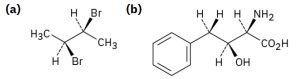
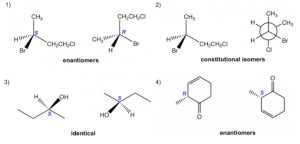
Exercise 8.6
Determine the relationship for each pair of molecules: enantiomers, identical, constitutional isomers, non-isomer:
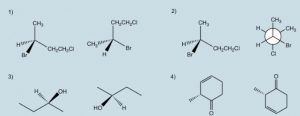
Answers: