Learning Objectives
- Define self-disclosure.
- Explain the connection between social penetration theory, social comparison theory, and self-disclosure.
- Discuss the process of self-disclosure, including how we make decisions about what, where, when, and how to disclose.
- Explain how self-disclosure affects relationships.
Have you ever said too much on a first date? At a job interview? To a professor? Have you ever posted something on Facebook only to return later to remove it? When self-disclosure works out well, it can have positive effects for interpersonal relationships. Conversely, self-disclosure that does not work out well can lead to embarrassment, lower self-esteem, and relationship deterioration or even termination. As with all other types of communication, increasing your competence regarding self-disclosure can have many positive effects.
So what is self-disclosure? It could be argued that any verbal or nonverbal communication reveals something about the self. The clothes we wear, a laugh, or an order at the drive-through may offer glimpses into our personality or past, but they are not necessarily self-disclosure. Self-disclosure is purposeful disclosure of personal information to another person. If I purposefully wear the baseball cap of my favorite team to reveal my team loyalty to a new friend, then this clothing choice constitutes self-disclosure. Self-disclosure doesn’t always have to be deep to be useful or meaningful. Superficial self-disclosure, often in the form of “small talk,” is key in initiating relationships that then move onto more personal levels of self-disclosure. Telling a classmate your major or your hometown during the first week of school carries relatively little risk but can build into a friendship that lasts beyond the class.
Theories of Self-Disclosure
Social penetration theory states that as we get to know someone, we engage in a reciprocal process of self-disclosure that changes in breadth and depth and affects how a relationship develops. Depth refers to how personal or sensitive the information is, and breadth refers to the range of topics discussed (Greene, Derlega, & Mathews, 2006). You may recall Shrek’s declaration that ogres are like onions in the movie Shrek. While certain circumstances can lead to a rapid increase in the depth and/or breadth of self-disclosure, the theory states that in most relationships people gradually penetrate through the layers of each other’s personality like we peel the layers from an onion.

Social penetration theory compares the process of self-disclosure to peeling back the layers of an onion.
Helena Jacoba – Red Onion close up – CC BY 2.0.
The theory also argues that people in a relationship balance needs that are sometimes in tension, which is a dialectic. Balancing a dialectic is like walking a tightrope. You have to lean to one side and eventually lean to another side to keep yourself balanced and prevent falling. The constant back and forth allows you to stay balanced, even though you may not always be even, or standing straight up. One of the key dialectics that must be negotiated is the tension between openness and closedness (Greene, Derlega, & Mathews, 2006). We want to make ourselves open to others, through self-disclosure, but we also want to maintain a sense of privacy.
We may also engage in self-disclosure for the purposes of social comparison. Social comparison theory states that we evaluate ourselves based on how we compare with others (Hargie, 2011). We may disclose information about our intellectual aptitude or athletic abilities to see how we relate to others. This type of comparison helps us decide whether we are superior or inferior to others in a particular area. Disclosures about abilities or talents can also lead to self-validation if the person to whom we disclose reacts positively. By disclosing information about our beliefs and values, we can determine if they are the same as or different from others. Last, we may disclose fantasies or thoughts to another to determine whether they are acceptable or unacceptable. We can engage in social comparison as the discloser or the receiver of disclosures, which may allow us to determine whether or not we are interested in pursuing a relationship with another person.
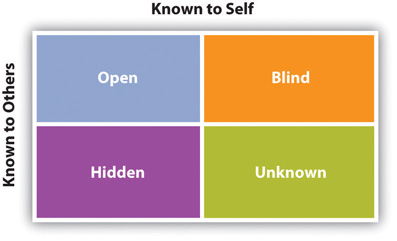
The final theory of self-disclosure that we will discuss is the Johari window, which is named after its creators Joseph Luft and Harrington Ingham (Luft, 1969). The Johari window can be applied to a variety of interpersonal interactions in order to help us understand what parts of ourselves are open, hidden, blind, and unknown. To help understand the concept, think of a window with four panes. As you can see in Figure 6.2 “Johari Window”, one axis of the window represents things that are known to us, and the other axis represents things that are known to others. The upper left pane contains open information that is known to us and to others. The amount of information that is openly known to others varies based on relational context. When you are with close friends, there is probably a lot of information already in the open pane, and when you are with close family, there is also probably a lot of information in the open pane. The information could differ, though, as your family might know much more about your past and your friends more about your present. Conversely, there isn’t much information in the open pane when we meet someone for the first time, aside from what the other person can guess based on our nonverbal communication and appearance.
The bottom left pane contains hidden information that is known to us but not to others. As we are getting to know someone, we engage in self-disclosure and move information from the “hidden” to the “open” pane. By doing this, we decrease the size of our hidden area and increase the size of our open area, which increases our shared reality. The reactions that we get from people as we open up to them help us form our self-concepts and also help determine the trajectory of the relationship. If the person reacts favorably to our disclosures and reciprocates disclosure, then the cycle of disclosure continues and a deeper relationship may be forged.
The upper right pane contains information that is known to others but not to us. For example, we may be unaware of the fact that others see us as pushy or as a leader. Looking back to self-discrepancy theory from Chapter 2 “Communication and Perception”, we can see that people who have a disconnect between how they see themselves and how others see them may have more information in their blind pane. Engaging in perception checking and soliciting feedback from others can help us learn more about our blind area.
The bottom right pane represents our unknown area, as it contains information not known to ourselves or others. To become more self-aware, we must solicit feedback from others to learn more about our blind pane, but we must also explore the unknown pane. To discover the unknown, we have to get out of our comfort zones and try new things. We have to pay attention to the things that excite or scare us and investigate them more to see if we can learn something new about ourselves. By being more aware of what is contained in each of these panes and how we can learn more about each one, we can more competently engage in self-disclosure and use this process to enhance our interpersonal relationships.
“Getting Plugged In”
Self-Disclosure and Social Media
Facebook and Twitter are undoubtedly dominating the world of online social networking, and the willingness of many users to self-disclose personal information ranging from moods to religious affiliation, relationship status, and personal contact information has led to an increase in privacy concerns. Facebook and Twitter offer convenient opportunities to stay in touch with friends, family, and coworkers, but are people using them responsibly? Some argue that there are fundamental differences between today’s digital natives, whose private and public selves are intertwined through these technologies, and older generations (Kornblum, 2007). Even though some colleges are offering seminars on managing privacy online, we still hear stories of self-disclosure gone wrong, such as the football player from the University of Texas who was kicked off the team for posting racist comments about the president or the student who was kicked out of his private, Christian college after a picture of him dressed in drag surfaced on Facebook. However, social media experts say these cases are rare and that most students are aware of who can see what they’re posting and the potential consequences (Nealy, 2009). The issue of privacy management on Facebook is affecting parent-child relationships, too, and as the website “Oh Crap. My Parents Joined Facebook.” shows, the results can sometimes be embarrassing for the college student and the parent as they balance the dialectic between openness and closedness once the child has moved away.
- How do you manage your privacy and self-disclosures online?
- Do you think it’s ethical for school officials or potential employers to make admission or hiring decisions based on what they can learn about you online? Why or why not?
- Are you or would you be friends with a parent on Facebook? Why or why not? If you already are friends with a parent, did you change your posting habits or privacy settings once they joined? Why or why not?
The Process of Self-Disclosure
There are many decisions that go into the process of self-disclosure. We have many types of information we can disclose, but we have to determine whether or not we will proceed with disclosure by considering the situation and the potential risks. Then we must decide when, where, and how to disclose. Since all these decisions will affect our relationships, we will examine each one in turn.
Four main categories for disclosure include observations, thoughts, feelings, and needs (Hargie, 2011). Observations include what we have done and experienced. For example, I could tell you that I live in a farmhouse in Illinois. If I told you that I think my move from the city to the country was a good decision, I would be sharing my thoughts, because I included a judgment about my experiences. Sharing feelings includes expressing an emotion—for example, “I’m happy to wake up every morning and look out at the corn fields. I feel lucky.” Last, we may communicate needs or wants by saying something like “My best friend is looking for a job, and I really want him to move here, too.” We usually begin disclosure with observations and thoughts and then move onto feelings and needs as the relationship progresses. There are some exceptions to this. For example, we are more likely to disclose deeply in crisis situations, and we may also disclose more than usual with a stranger if we do not think we’ll meet the person again or do not share social networks. Although we don’t often find ourselves in crisis situations, you may recall scenes from movies or television shows where people who are trapped in an elevator or stranded after a plane crash reveal their deepest feelings and desires. I imagine that we have all been in a situation where we said more about ourselves to a stranger than we normally would. To better understand why, let’s discuss some of the factors that influence our decision to disclose.
Generally speaking, some people are naturally more transparent and willing to self-disclose, while others are more opaque and hesitant to reveal personal information (Jourard, 1964). Interestingly, recent research suggests that the pervasiveness of reality television, much of which includes participants who are very willing to disclose personal information, has led to a general trend among reality television viewers to engage in self-disclosure through other mediated means such as blogging and video sharing (Stefanone & Lakaff, 2009). Whether it is online or face-to-face, there are other reasons for disclosing or not, including self-focused, other-focused, interpersonal, and situational reasons (Green, Derlega, & Mathews, 2006).
Self-focused reasons for disclosure include having a sense of relief or catharsis, clarifying or correcting information, or seeking support. Self-focused reasons for not disclosing include fear of rejection and loss of privacy. In other words, we may disclose to get something off our chest in hopes of finding relief, or we may not disclose out of fear that the other person may react negatively to our revelation. Other-focused reasons for disclosure include a sense of responsibility to inform or educate. Other-focused reasons for not disclosing include feeling like the other person will not protect the information. If someone mentions that their car wouldn’t start this morning and you disclose that you are good at working on cars, you’ve disclosed to help out the other person. On the other side, you may hold back disclosure about your new relationship from your coworker because he or she’s known to be loose-lipped with other people’s information. Interpersonal reasons for disclosure involve desires to maintain a trusting and intimate relationship. Interpersonal reasons for not disclosing include fear of losing the relationship or deeming the information irrelevant to the particular relationship. Your decision to disclose an affair in order to be open with your partner and hopefully work through the aftermath together or withhold that information out of fear he or she will leave you is based on interpersonal reasons. Finally, situational reasons may be the other person being available, directly asking a question, or being directly involved in or affected by the information being disclosed. Situational reasons for not disclosing include the person being unavailable, a lack of time to fully discuss the information, or the lack of a suitable (i.e., quiet, private) place to talk. For example, finding yourself in a quiet environment where neither person is busy could lead to disclosure, while a house full of company may not.
Deciding when to disclose something in a conversation may not seem as important as deciding whether or not to disclose at all. But deciding to disclose and then doing it at an awkward time in a conversation could lead to negative results. As far as timing goes, you should consider whether to disclose the information early, in the middle, or late in a conversation (Greene, Derlega, & Mathews, 2006). If you get something off your chest early in a conversation, you may ensure that there’s plenty of time to discuss the issue and that you don’t end up losing your nerve. If you wait until the middle of the conversation, you have some time to feel out the other person’s mood and set up the tone for your disclosure. For example, if you meet up with your roommate to tell her that you’re planning on moving out and she starts by saying, “I’ve had the most terrible day!” the tone of the conversation has now shifted, and you may not end up making your disclosure. If you start by asking her how she’s doing, and things seem to be going well, you may be more likely to follow through with the disclosure. You may choose to disclose late in a conversation if you’re worried about the person’s reaction. If you know they have an appointment or you have to go to class at a certain time, disclosing just before that time could limit your immediate exposure to any negative reaction. However, if the person doesn’t have a negative reaction, they could still become upset because they don’t have time to discuss the disclosure with you.
Sometimes self-disclosure is unplanned. Someone may ask you a direct question or disclose personal information, which leads you to reciprocate disclosure. In these instances you may not manage your privacy well because you haven’t had time to think through any potential risks. In the case of a direct question, you may feel comfortable answering, you may give an indirect or general answer, or you may feel enough pressure or uncertainty to give a dishonest answer. If someone unexpectedly discloses, you may feel the need to reciprocate by also disclosing something personal. If you’re uncomfortable doing this, you can still provide support for the other person by listening and giving advice or feedback.
Once you’ve decided when and where to disclose information to another person, you need to figure out the best channel to use. Face-to-face disclosures may feel more genuine or intimate given the shared physical presence and ability to receive verbal and nonverbal communication. There is also an opportunity for immediate verbal and nonverbal feedback, such as asking follow-up questions or demonstrating support or encouragement through a hug. The immediacy of a face-to-face encounter also means you have to deal with the uncertainty of the reaction you’ll get. If the person reacts negatively, you may feel uncomfortable, pressured to stay, or even fearful. If you choose a mediated channel such as an e-mail or a letter, text, note, or phone call, you may seem less genuine or personal, but you have more control over the situation in that you can take time to carefully choose your words, and you do not have to immediately face the reaction of the other person. This can be beneficial if you fear a negative or potentially violent reaction. Another disadvantage of choosing a mediated channel, however, is the loss of nonverbal communication that can add much context to a conversation. Although our discussion of the choices involved in self-disclosure so far have focused primarily on the discloser, self-disclosure is an interpersonal process that has much to do with the receiver of the disclosure.
Effects of Disclosure on the Relationship
The process of self-disclosure is circular. An individual self-discloses, the recipient of the disclosure reacts, and the original discloser processes the reaction. How the receiver interprets and responds to the disclosure are key elements of the process. Part of the response results from the receiver’s attribution of the cause of the disclosure, which may include dispositional, situational, and interpersonal attributions (Jiang, Bazarova, & Hancock, 2011). Let’s say your coworker discloses that she thinks the new boss got his promotion because of favoritism instead of merit. You may make a dispositional attribution that connects the cause of her disclosure to her personality by thinking, for example, that she is outgoing, inappropriate for the workplace, or fishing for information. If the personality trait to which you attribute the disclosure is positive, then your reaction to the disclosure is more likely to be positive. Situational attributions identify the cause of a disclosure with the context or surroundings in which it takes place. For example, you may attribute your coworker’s disclosure to the fact that you agreed to go to lunch with her. Interpersonal attributions identify the relationship between sender and receiver as the cause of the disclosure. So if you attribute your coworker’s comments to the fact that you are best friends at work, you think your unique relationship caused the disclosure. If the receiver’s primary attribution is interpersonal, relational intimacy and closeness will likely be reinforced more than if the attribution is dispositional or situational, because the receiver feels like they were specially chosen to receive the information.
The receiver’s role doesn’t end with attribution and response. There may be added burdens if the information shared with you is a secret. As was noted earlier, there are clear risks involved in self-disclosure of intimate or potentially stigmatizing information if the receiver of the disclosure fails to keep that information secure. As the receiver of a secret, you may feel the need to unburden yourself from the co-ownership of the information by sharing it with someone else (Derlega, Petronio, & Margulis, 1993). This is not always a bad thing. You may strategically tell someone who is removed from the social network of the person who told you the secret to keep the information secure. Although unburdening yourself can be a relief, sometimes people tell secrets they were entrusted to keep for less productive reasons. A research study of office workers found that 77 percent of workers that received a disclosure and were told not to tell anyone else told at least two other people by the end of the day (Hargie, 2011)! They reported doing so to receive attention for having inside information or to demonstrate their power or connection. Needless to say, spreading someone’s private disclosure without permission for personal gain does not demonstrate communication competence.
When the cycle of disclosure ends up going well for the discloser, there is likely to be a greater sense of relational intimacy and self-worth, and there are also positive psychological effects such as reduced stress and increased feelings of social support. Self-disclosure can also have effects on physical health. Spouses of suicide or accidental death victims who did not disclose information to their friends were more likely to have more health problems such as weight change and headaches and suffer from more intrusive thoughts about the death than those who did talk with friends (Greene, Derlega, & Mathews, 2006).
Key Takeaways
- Through the process of self-disclosure, we disclose personal information and learn about others.
- The social penetration theory argues that self-disclosure increases in breadth and depth as a relationship progresses, like peeling back the layers of an onion.
- We engage in social comparison through self-disclosure, which may determine whether or not we pursue a relationship.
- Getting integrated: The process of self-disclosure involves many decisions, including what, when, where, and how to disclose. All these decisions may vary by context, as we follow different patterns of self-disclosure in academic, professional, personal, and civic contexts.
- The receiver’s reaction to and interpretation of self-disclosure are important factors in how the disclosure will affect the relationship.
Exercises
- Answer the questions from the beginning of the section: Have you ever said too much on a first date? At a job interview? To a professor? Have you ever posted something on Facebook only to return later to remove it? If you answered yes to any of the questions, what have you learned in this chapter that may have led you to do something differently?
- Have you experienced negative results due to self-disclosure (as sender or receiver)? If so, what could have been altered in the decisions of what, where, when, or how to disclose that may have improved the situation?
- Under what circumstances is it OK to share information that someone has disclosed to you? Under what circumstances is to not OK to share the information?
References
Derlega, V. J., Sandra Metts, Sandra Petronio, and Stephen T. Margulis, Self-Disclosure (Newbury Park, CA: Sage, 1993).
Greene, K., Valerian J. Derlega, and Alicia Mathews, “Self-Disclosure in Personal Relationships,” in The Cambridge Handbook of Personal Relationships, eds. Anita L. Vangelisti and Daniel Perlman (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006), 412–13.
Hargie, O., Skilled Interpersonal Interaction: Research, Theory, and Practice (London: Routledge, 2011), 261.
Jiang, L. C., Natalie N. Bazarova, and Jeffrey T. Hancock, “The Disclosure-Intimacy Link in Computer-Mediated Communication: An Attributional Extension of the Hyperpersonal Model,” Human Communication Research 37 (2011): 63.
Jourard, S., The Transparent Self (New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1964).
Kornblum, J., “Privacy? That’s Old-School: Internet Generation Views Openness in a Different Way,” USA Today, 1D, October 23, 2007.
Luft, J., Of Human Interaction (Palo Alto, CA: National Press Books, 1969).
Nealy, M. J., “The New Rules of Engagement,” Diverse: Issues in Higher Education 26, no. 3 (2009): 13.
Stefanone, M. A. and Derek Lakaff, “Reality Television as a Model for Online Behavior: Blogging, Photo, and Video Sharing,” Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication 14 (2009): 964–87.