Cardiovascular System – Heart (SC)
Topic: Cardiovascular System – Heart
Text Reference: Chapter 6. Cardiovascular System – Heart
Objectives: Students should be able to…
Identify meanings of key word components of the cardiovascular system
Prefixes
a- (absence of, without)
bi- (two)
brady- (slow)
dys- (bad, abnormal, painful, difficult)
endo- (within, in)
epi- (on, upon, over)
hypo- (below, deficient)
hyper- (above, excessive)
inter- (between)
pan- (all, total)
peri- (surrounding, around)
poly- (excessive, over, many)
tachy- (fast, rapid)
tri- (three)
Combining Forms
angi/o (vessel)
ather/o (yellowish, fatty plaque)
arteri/o (artery)
atri/o (atrium)
cardi/o/ (heart)
coron/o (crown or circle, heart)
ech/o (sound)
electr/o (electricity)
isch/o (deficiency, blockage)
my/o (muscle)
myos/o (muscle)
symptomat/o (symptom)
thromb/o (clot)
valv/o (valve)
valvul/o (valve)
vas/o (vessel)
ven/o (vein)
ventricul/o (ventricle)
Suffixes
-ac (pertaining to)
-ade (process of)
-al (pertaining to)
-apheresis (removal)
-ar (pertaining to)
-centesis (surgical puncture to aspirate fluid)
-dynia (pain)
-ectomy (excision, surgical removal)
-emia (condition of blood)
-genic (producing, originating, causing)
-gia (pain)
-gram (record, radiographic image)
-graph (instrument used to record)
-graphy (process of recording, radiographic imaging)
-ia (condition of, diseased state, abnormal state)
-ic (pertaining to)
-ion (process)
-itis (inflammation)
-lysis (loosening, dissolution, separating)
-megaly (enlarged, enlargement)
-logist (specialist, physician who studies and treats)
-oma (tumor)
-osis (abnormal condition)
-ous (pertaining to)
-pathy (disease)
-penia (abnormal reduction in number)
-pexy (surgical fixation, suspension)
-plasty (surgical repair)
-poiesis (formation)
-sclerosis (hardening)
-scope (instrument used to view)
-scopy (process of viewing)
-stasis (stop, stopping, controlling)
-stenosis (narrowing, constriction)
-tomy (cut into, incision)
Apply the rules of medical language to pronounce, break into word parts, and define the following terms.
Label each word part by using the following abbreviations:
P = Prefix
WR = Word Root
CV = Combining Vowel
S = Suffix
CF = Combining Form
Example: osteoarthropathy (ä-stē-ō-är-THROP-ă-thē) – disease of bone and joint
WR CV WR CV S
oste / o / arthr / o /pathy
CF CF
Use terms related to the cardiovascular system.
Label the following heart anatomy in the diagram below.
aorta | aortic valve | interventricular septum | left atrium | left pulmonary artery | left pulmonary veins | left ventricle | mitral (bicuspid) valve | pulmonary trunk | pulmonary valve | right pulmonary artery | right pulmonary veins | right ventricle | tricuspid valve
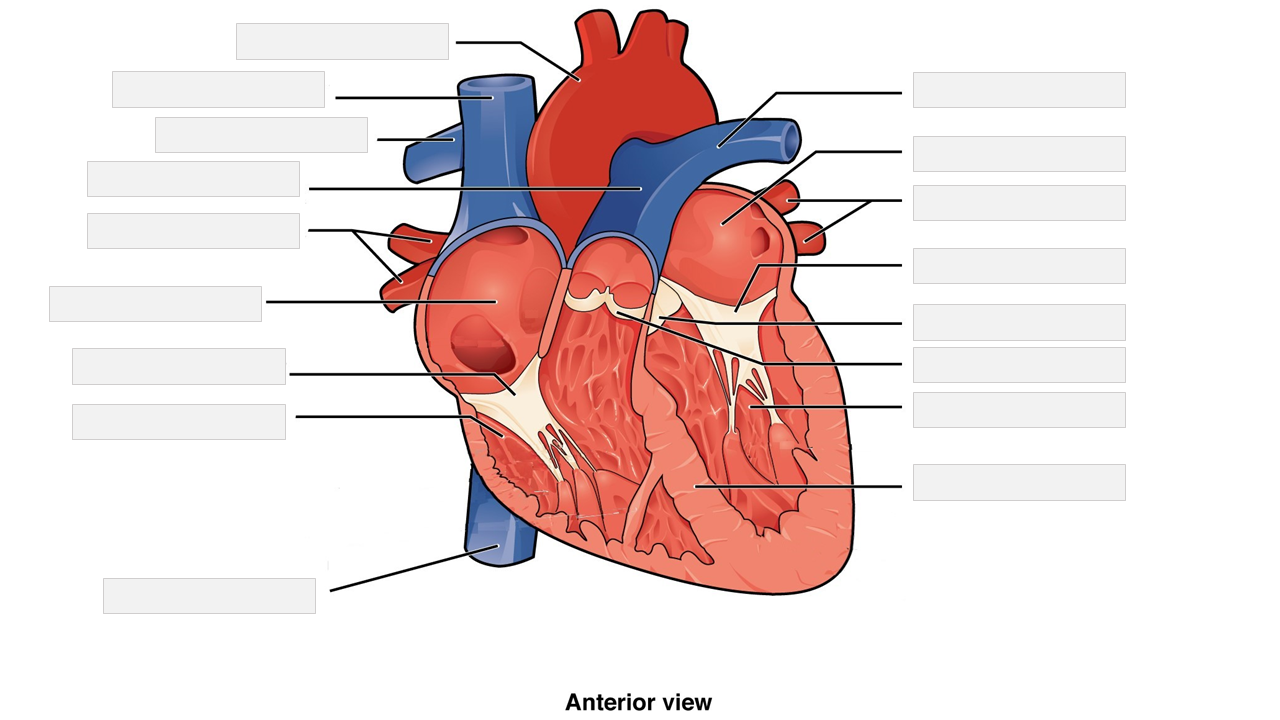
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below.
The ability of the blood vessels to dilate and constrict as needed…
- LDL
- Syncope
- Compliance
Difficult breathing
- Roots of the Great Vessels
- Dyspnea
- Pacemaker
A condition in which cells receive insufficient amounts of blood and oxygen
- Serous
- Ischemic
- Diaphoresis
Using extreme heat or extreme cold to destroy cells in part of the heart which were causing abnormal rhythms…
- Ablation
- Congenital
- Cyanosis
Chapter Attributions
This chapter was adapted by Jerry Casteel from “Cardiovascular System – Heart” in Medical Terminology Student Companion by Stacey Grimm; Colleen Allee; Heidi Belitz; Traci Gotz; Micheal Randolph; Elaine Strachota; and Laurie Zielinski. Licensed under a CC BY 4.0 license.

