Sensory Systems (SC)
Topic: Sensory Systems
Text Reference: Chapter 11. Sensory System
Objectives: Students should be able to…
Identify meanings of key word components of the sensory systems
Prefixes
bi- (two
bin- (two)
a- (absence of, without, no, not, negates meaning)
an- (absence of, without, no, not negates meaning)
endo- (within, in)
Combining Forms
acous/o (hearing)
audi/o (hearing)
audit/o (hearing)
aur/o (ear)
aur/i (ear)
blephar/o (eyelid)
cochle/o (cochlea)
conjunctiv/o (conjunctiva)
cor/o (pupil)
corne/o (cornea)
core/o (pupil)
cry/o (cold)
cyst/o (bladder, sac or cyst)
dacry/o (tear, tear duct)
dipl/o (two, double)
ir/o (iris)
irid/o (iris)
is/o (equal)
kerat/o (cornea)
labyrith/o (labyrinth, inner ear)
lacrim/o (tear, tear duct)
mastoid/o (mastoid bone)
myring/o (tympanic membrane, eardrum)
ocul/o (eye)
ophthalm/o (eye)
opt/o (vision)
ossicul/o (ossicle)
ot/o (ear)
phac/o (lens)
phak/o (lens)
phot/o (light)
pupill/o (pupil)
retin/o (retina)
salping/o (tube)
scler/o (sclera)
staped/o (stapes, middle ear)
ton/o (tension, pressure)
tympan/o (tympanic membrane, middle ear)
vestibul/o (vestibule)
Suffixes
–al (pertaining to)
-algia (pain)
-ar (pertaining to)
-ary (pertaining to)
-eal (pertaining to)
-ectomy (excision or surgical removal)
-gram (record, radiographic image)
-graphy (process of recording)
-ia (condition of, diseased or abnormal state)
-ic (pertaining to)
-itis (inflammation)
-logist (specialist or physician who studies and treats)
-logy (study of)
-malacia (softening)
-meter (instrument used to measure)
-metry (process of measuring)
-oma (tumor, swelling)
-opia (vision as it relates to condition)
-osis (abnormal condition)
-pathy (disease)
-pexy (surgical fixation)
-phobia (abnormal fear, aversion to specific things)
-plasty (surgical repair)
-plegia (paralysis)
-ptosis (prolapse, drooping, sagging)
-rrhea (flow, discharge)
-sclerosis (hardening)
-scope (instrument used to view)
-scopy (process of viewing)
-stomy (creation of artificial opening)
-tomy (incision, cut into)
Apply the rules of medical language to pronounce, break into word parts, and define the following terms.
Label each word part by using the following abbreviations:
P = Prefix
WR = Word Root
CV = Combining Vowel
S = Suffix
CF = Combining Form
Example: osteoarthropathy (ä-stē-ō-är-THROP-ă-thē) – disease of bone and joint
WR CV WR CV S
oste / o / arthr / o /pathy
CF CF
Practice pronouncing and defining these medical terms that are not easily broken into word parts.
amblyopia (am-blē-Ō-pē-ă)
anosmia (a-NOZ-mē-ă)
astigmatism (Ast) (ă-STIG-mă-tizm)
cataract (KAT-ă-rakt)
hyperopia (hī-pĕr-Ō-pē-ă)
myopia (mī-Ō-pē-ă)
nyctalopia (nik-ta-LŌ-pē-ă)
optician (ŏp-TĬSH-ăn)
optometrist (ŏp-TŎM-ĕ-trĭst)
presbycusis (prez-bĭ-KŪ-sĭs)
presbyopia (prez-bī-Ō-pē-ă)
sty (stī)
visual acuity (VA) (VIZH-u-ăl ă-KŪ-ĭt-ē)
Practice pronouncing and defining these commonly abbreviated sensory system terms.
AD (right ear)
AMD (age-related macular degeneration)
AS (left ear)
Ast (astigmatism)
Em (emmetropia)
IOL (intraocular lens)
IOP (intraocular pressure)
LASIK (laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis)
Ophth (ophthalmology)
PHACO (phacoemulsification)
PERRLA (pupils, equal, round, reactive, light, accommodation)
PRK (photorefractive keratectomy)
VA (visual acuity)
VF (visual field)
AOM (acute otitis media)
ENT (ears, nose, throat)
EENT (eyes, ears, nose and throat)
HOH (hard of hearing)
OM (otitis media)
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories.
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Use terms related to the sensory system.
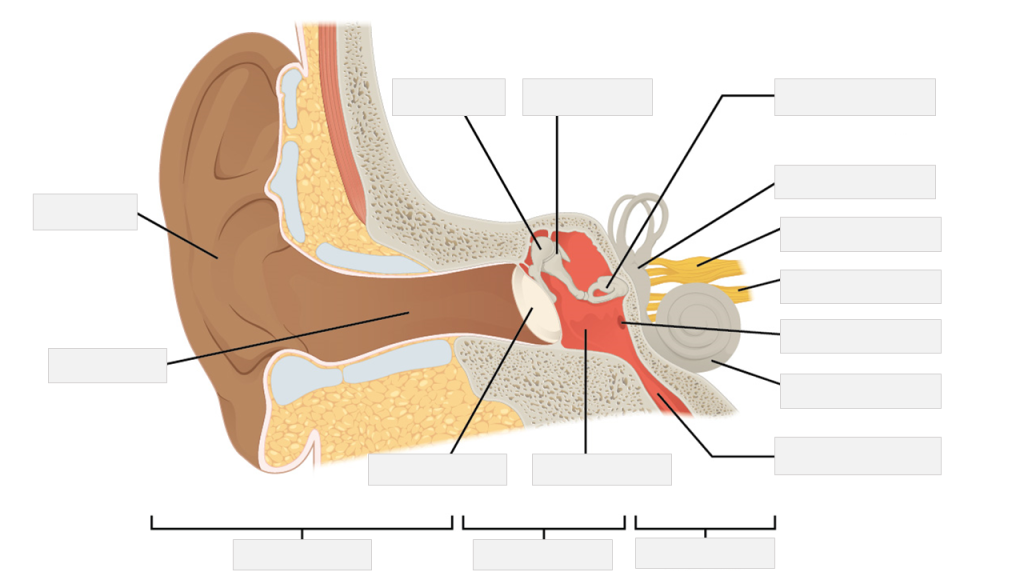
Label the following sensory system ear anatomy.
auricle | cochlea | cochlear nerve | ear canal | eustachian tube | external ear | incus | inner ear | malleus | middle ear | round window | stapes (attached to oval window) | tympanic cavity | tympanic membrane | vestibular nerve | vestibule
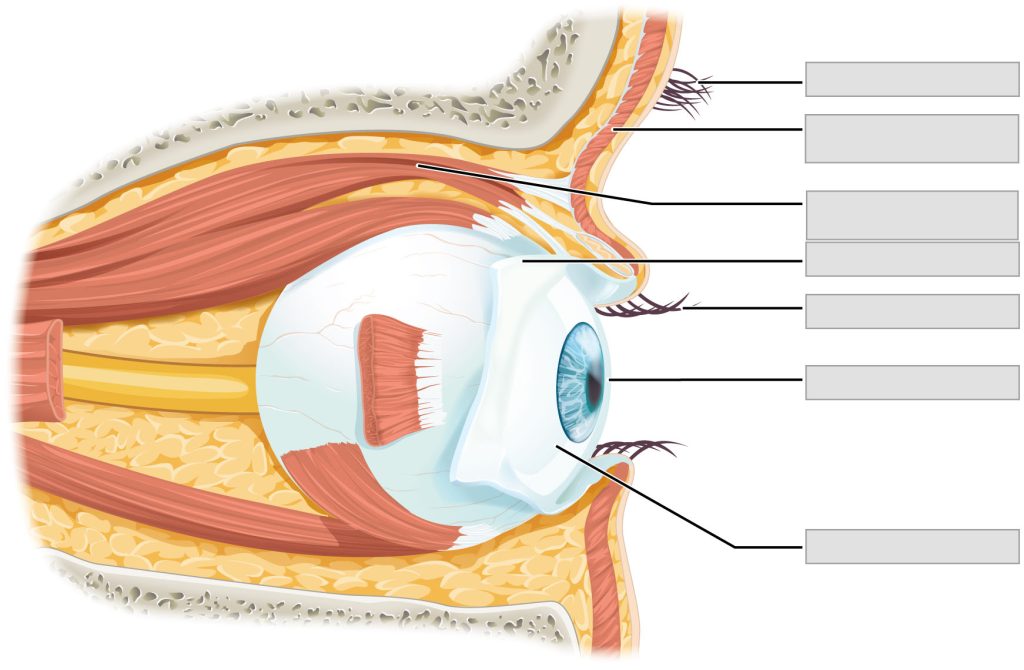
Label the following sensory system eye anatomy.
conjunctiva | cornea | eyebrow | eyelashes | levator palpebrae superioris muscle | orbicularis oculi muscle | palpebral conjunctiva
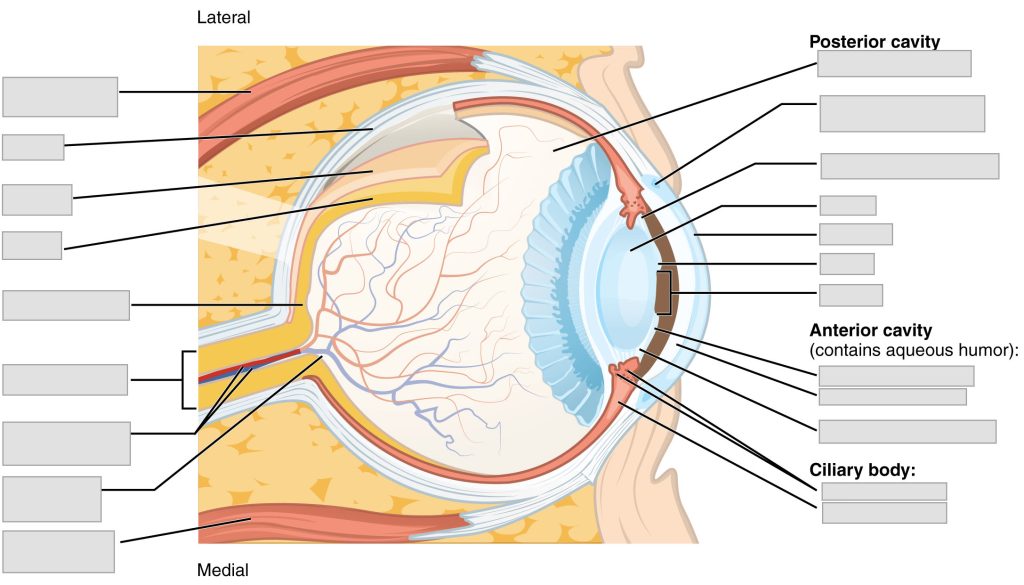
Label the following sensory system eye anatomy.
anterior chamber | central retinal artery and vein | choroid | ciliary muscle | ciliary process | cornea | fovea centralis | iris | lateral recus muscle | lens | medial rectus muscle | optic disc (blind spot) | optic (II) nerve | posterior chamber | pupil | retina | sclera | scleral venous sinus (canal of Schlemm) | suspensory ligaments | suspensory ligaments | vitreous chamber
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below.
acuity | cataracts | dilate | eye | halos | intraocular | iris | ophthalmoscope | subcapsular | surgery
SENSORY SYSTEM – CONSULTATION REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Betty FOX
AGE: 72
SEX: Female
DOB: October 2
DATE OF CONSULTATION: August 5
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Brian Gates, MD, Ophthalmology
REASON FOR CONSULTATION: Cataracts
HISTORY: I saw Mrs. Fox a 72-year-old for her regular ________ examination. She has been wearing reading glasses for several year now but has noticed that she has been having troubles reading and has been seeing ________ around lights while driving at night.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: A visual ________ test was performed. I used a slit lamp to view the cornea, ________, lens, and the space between the iris and cornea. I detected tiny abnormalities. I administered drops to ________ the pupils to examine the retina. Using an ________, I was able to examine the lenses for signs of ________. I was able to determine that Mrs. Fox has posterior ________ cataracts in both eyes.
PLAN: I explained to Mrs. Fox that she required cataract ________. I explained that her clouded lens would be replaced with an ________ lens – a clear artificial lens. She was in agreeance to having the surgery. I told her we would perform the surgery on her right eye first, then in about eight weeks we would do the left eye. Arrangements for her surgery will be made for next month.
_____________________________
Brian Gates, MD, Ophthalmology
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below.
abnormalities | anaesthetic | antihistamines | dacryocystitis | dacryocystorhinostomy | erythematous | masses | medication | nasolacrimal | ophthalmalgia | OS | puncta | thyroid | watering
SENSORY SYSTEM – CONSULTATION REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Rose MACKENZIE
AGE: 57
SEX: Female
DOB: November 25
DATE OF CONSULTATION: April 16
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Ashley Cook MD, Ophthalmology
REASON FOR CONSULTATION: Epiphora in left eye.
HISTORY: Patient is a 57-year-old female who reports epiphora in ________. Prior to the encounter, she attempted to cure the condition with various ________. She states that this has been an ongoing issue for the past 2 years, but the ________ has affected her ability to safely drive over the past 8 months. She denied any persistent ________, although noted that the surface of the eye was occasionally irritated and ________ due to rubbing away the tears. She has had no prior eye surgery and no relevant family or personal history of dermatitis or ________ pathologies.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: Patient is alert and oriented x 3, and in no acute distress. Examination of the eye surface revealed no ________ other than the erythema and tearing. The skin surrounding the eye appeared normal, with no ________ or swelling.
An irrigation test was then conducted. The eye was treated with ________ eye drops prior to the test. A syringe filled with saline was inserted into the left ________ using a hollow wire. The syringe was then pressed to assess the pressure of the left ________ duct. The fluid did not pass through the nose, indicating inflammation of the duct. No further diagnostic testing was required.
ASSESSMENT: Chronic ________ of the left nasolacrimal duct.
PLAN: Return for ________ in 3 months. Patient was instructed to remove tears using tissue instead of her hand to avoid the risk of infection. No ________ is required in the meantime.
_______________________________
Ashley Cook MD, Ophthalmology
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below.
Specialized neurons that respond to changes in temperature are called…
- Nociceptors
- Thermoreceptors
- Mechanoreceptors
Body movement is called…
- Proprioception
- Kinesthesia
- Visceral
Sharpness of vision is called…
- Proprioception
- Kinesthesia
- Visual acuity
Sensory neurons that respond to pain are called…
- Nociceptors
- Thermoreceptors
- Glossopharyngeal
The ear drum is also called…
- Tympanic membrane
- Glossopharyngeal
- Mechanoreceptors
Chapter Attributions
This chapter was adapted by Karen Hobbs from “Sensory Systems” in Medical Terminology Student Companion by Stacey Grimm; Colleen Allee; Heidi Belitz; Traci Gotz; Micheal Randolph; Elaine Strachota; and Laurie Zielinski. Licensed under a CC BY 4.0 license.

