Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN)
In addition to using standard precautions and transmission-based precautions, aseptic technique (also called medical asepsis) is the purposeful reduction of pathogens to prevent the transfer of microorganisms from one person or object to another during a medical procedure. For example, a nurse administering parenteral medication or performing urinary catheterization uses aseptic technique. When performed properly, aseptic technique prevents contamination and transfer of pathogens to the patient from caregiver hands, surfaces, and equipment during routine care or procedures. The word “aseptic” literally means an absence of disease-causing microbes and pathogens. In the clinical setting, aseptic technique refers to the purposeful prevention of microbe contamination from one person or object to another. These potentially infectious, microscopic organisms can be present in the environment, on an instrument, in liquids, on skin surfaces, or within a wound.
There is often misunderstanding between the terms aseptic technique and sterile technique in the health care setting. Both asepsis and sterility are closely related, and the shared concept between the two terms is removal of harmful microorganisms that can cause infection. In the most simplistic terms, asepsis is creating a protective barrier from pathogens, whereas sterile technique is a purposeful attack on microorganisms. Sterile technique (also called surgical asepsis) seeks to eliminate every potential microorganism in and around a sterile field while also maintaining objects as free from microorganisms as possible. It is the standard of care for surgical procedures, invasive wound management, and central line care. Sterile technique requires a combination of meticulous hand washing, creation of a sterile field, using long-lasting antimicrobial cleansing agents such as betadine, donning sterile gloves, and using sterile devices and instruments.
Principles of Aseptic Non-Touch Technique
Aseptic non-touch technique (ANTT) is the most commonly used aseptic technique framework in the health care setting and is considered a global standard. There are two types of ANTT: surgical-ANTT (sterile technique) and standard-ANTT.
Aseptic non-touch technique starts with a few concepts that must be understood before it can be applied. For all invasive procedures, the “ANTT-approach” identifies key parts and key sites throughout the preparation and implementation of the procedure. A key part is any sterile part of equipment used during an aseptic procedure, such as needle hubs, syringe tips, needles, and dressings. A key site is any nonintact skin, potential insertion site, or access site used for medical devices connected to the patients. Examples of key sites include open wounds and insertion sites for intravenous (IV) devices and urinary catheters.
ANTT includes four underlying principles to keep in mind while performing invasive procedures:
- Always wash hands effectively.
- Never contaminate key parts.
- Touch non-key parts with confidence.
- Take appropriate infective precautions.
Preparing and Preventing Infections Using Aseptic Technique
When planning for any procedure, careful thought and preparation of many infection control factors must be considered beforehand. While keeping standard precautions in mind, identify anticipated key sites and key parts to the procedure. Consider the degree to which the environment must be managed to reduce the risk of infection, including the expected degree of contamination and hazardous exposure to the clinician. Finally, review the expected equipment needed to perform the procedure and the level of key part or key site handling. See Table 4.3 for an outline of infection control measures when performing a procedure.
Table 4.3 Infection Control Measures When Performing Procedures
| Infection Control Measure | Key Considerations | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental control |
|
|
| Hand hygiene |
|
|
| Personal protective equipment (PPE) |
|
|
| Aseptic field management | Determine level of aseptic field needed and how it will be managed before the procedure begins:
|
General aseptic field:
IV irrigation Dry dressing changes Critical aseptic field: Urinary catheter placement Central line dressing change Sterile dressing change |
| Non-touch technique |
|
|
| Sequencing |
|
|
Use of Gloves and Sterile Gloves
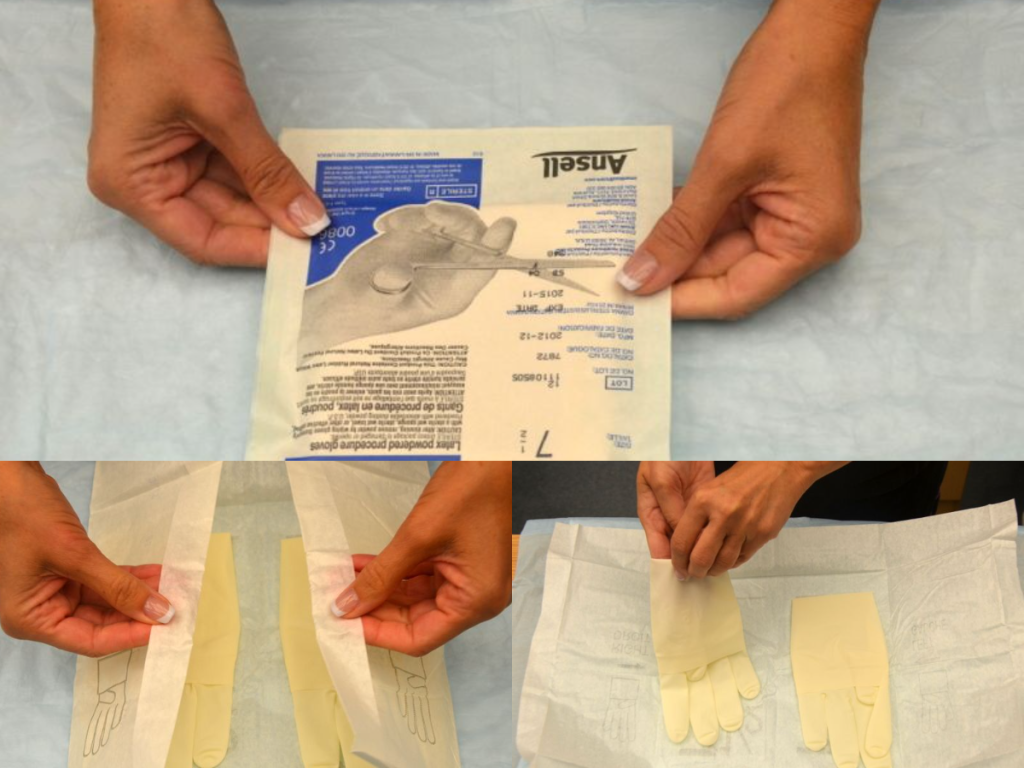
There are two different levels of medical-grade gloves available to health care providers: clean (exam) gloves and sterile (surgical) gloves. Generally speaking, clean gloves are used whenever there is a risk of contact with body fluids or contaminated surfaces or objects. Examples include starting an intravenous access device or emptying a urinary catheter collection bag. Alternatively, sterile gloves meet FDA requirements for sterilization and are used for invasive procedures or when contact with a sterile site, tissue, or body cavity is anticipated. Sterile gloves are used in these instances to prevent transient flora and reduce resident flora contamination during a procedure, thus preventing the introduction of pathogens. For example, sterile gloves are required when performing central line dressing changes, insertion of urinary catheters, and during invasive surgical procedures. See Figure 4.15[1] for images of a nurse opening and removing sterile gloves from packaging.
See the “Checklist for Applying and Removing Sterile Gloves” for details on how to apply sterile gloves.
Applying Sterile Gloves on YouTube[2]
- “Book-pictures-2015-199-001-300x241.jpg,” “Book-pictures-2015-215.jpg,” and “Book-pictures-2015-219.jpg” by British Columbia Institute of Technology are licensed under CC BY 4.0. Access for free at https://opentextbc.ca/clinicalskills/chapter/sterile-gloving/ ↵
- RegisteredNurseRN. (2017, April 28). Sterile gloving nursing technique | Don/donning sterile gloves tips. [Video]. YouTube. All rights reserved. Video used with permission. https://youtu.be/lumZOF-METc ↵
Assessment
Subjective Assessment
During a subjective assessment of a client’s integumentary system, begin by asking about current symptoms such as itching, rashes, or wounds. If a client has a wound, it is important to determine if a client has pain associated with the wound so that pain management can be implemented. For clients with chronic wounds, it is also important to identify factors that delay wound healing, such as nutrition, decreased oxygenation, infection, stress, diabetes, obesity, medications, alcohol use, and smoking.[1] See Table 10.6a for a list of suggested interview questions to use when assessing a client with a wound.
If a client has a chronic wound or is experiencing delayed wound healing, it is important for the nurse to assess the impact of the wound on their quality of life. Reasons for this may include the frequency and regularity of dressing changes, which affect daily routine; a feeling of continued fatigue due to lack of sleep; restricted mobility; pain; odor; and the side effects of multiple medications. The loss of independence associated with functional decline can also lead to changes in overall health and well-being. These changes include altered eating habits, depression, social isolation, and a gradual reduction in activity levels.
Table 10.6a Interview Questions Related to Integumentary Disorders
| Symptoms | Questions | Follow-up Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Current Symptoms | Are you currently experiencing any skin symptoms such as itching, rashes, or an unusual mole? | Please describe. |
| Wounds | Do you have any current wounds such as a surgical incision, skin tear, arterial ulcer, venous ulcer, diabetic or neuropathic ulcer, or a pressure injury?
If a wound is present:
|
Please describe.
Use the PQRSTU method to comprehensively assess pain. Read more about the PQRSTU method in the "Pain Assessment Methods" section of the "Comfort" chapter. |
| Medical History | Have you ever been diagnosed with a wound related to diabetes, heart disease, or peripheral vascular disease? | Please describe. |
| If chronic wounds or wounds with delayed healing are present: | ||
| Medications | Are you taking any medications that can affect wound healing, such as oral steroids to treat inflammation or help you breathe? | Please describe. |
| Treatments | What have you used to try to treat this wound? | What was successful? Unsuccessful? |
| Symptoms of Infection (pain, purulent drainage, etc.) | Are you experiencing any symptoms of infection related to this wound such as increased pain or yellow/green drainage? | Please describe. |
| Stress | Have you experienced any recent stressors such as surgery, hospitalization, or a change in life circumstances? | How do you cope with stress in your life? |
| Smoking | Do you smoke? | How many cigarettes do you smoke a day? How long have you smoked? Have you considered quitting smoking? |
| Quality of Life | Has this wound impacted your quality of life? | Have you had any changes in eating habits, feelings of depression or social isolation, or a reduction in your usual activity levels? |
Objective Assessment
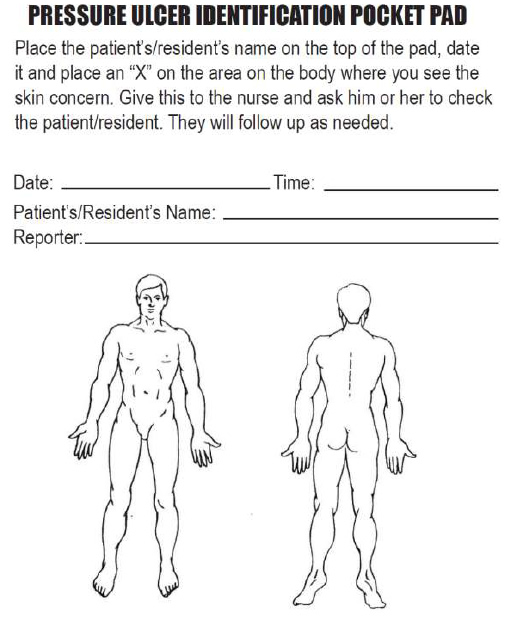
When performing an objective integumentary assessment on a client receiving inpatient care, it is important to perform a thorough exam on admission to check for existing wounds, as well as to evaluate their risk of skin breakdown using the Braden Scale. Agencies are not reimbursed for care of pressure injuries received during a client’s stay, so existing wounds on admission must be well-documented. Routine skin assessment should continue throughout a client’s stay, usually on a daily or shift-by-shift basis based on the client’s condition. If a wound is present, it is assessed during every dressing change for signs of healing. See Table 10.6b for components to include in a wound assessment. See Figure 10.22[2] for an image of a common tool used to document the location of a skin concern found during assessment.
Read more information about performing an overall integumentary assessment in the “Integumentary Assessment” chapter in Open RN Nursing Skills, 2e.
For additional discussion regarding assessing wounds, go to the “Assessing Wounds” section of the “Wound Care” chapter in Open RN Nursing Skills, 2e.
There are many common skin disorders that a nurse may find during assessment. Read more about common skin disorders in the “Common Integumentary Conditions” section of the “Integumentary Assessment” chapter in Open RN Nursing Skills, 2e.
Table 10.6b Wound Assessment
| Wound Assessment | |
|---|---|
| Type | Types of wounds may include abrasions, lacerations, burns, surgical incisions, pressure injuries, skin tears, arterial ulcers, or venous ulcers. It is important to understand the type of wound present to select appropriate interventions. |
| Location | The location of the wound should be documented precisely. A body diagram template is helpful to demonstrate exactly where the wound is located. |
| Size | Wound size should be measured regularly to determine if the wound is increasing or decreasing in size. Length is measured using the head-to-toe axis, and width is measured laterally. If tunneling or undermining is present, their depth should be assessed using a sterile, cotton-tipped applicator and documented using the clock method. |
| Degree of Tissue Injury | Wounds are classified as partial-thickness (meaning the epidermis and dermis are affected) or full-thickness (meaning the subcutaneous and deeper layers are affected). See Figure 10.1 in the “Basic Concepts” section for an image of the layers of skin.
For pressure injuries, it is important to assess the stage of the injury (see information on staging in the “Pressure Injuries” section). |
| Color of Wound Base | Assess the base of the wound for the presence of healthy, pink/red granulation tissue. Note the unhealthy appearance of dark red granulation tissue, white or yellow slough, or brown or black necrotic tissue. |
| Drainage | The color, consistency, and amount of exudate (drainage) should be assessed and documented at every dressing change. Drainage from wounds is often described as scant, small/minimal, moderate, and large/copious amounts. Use the following descriptions to select the appropriate terms:[3]
The type of wound drainage should be described using medical terms such as serosanguinous, sanguineous, serous, or purulent:
|
| Tubes or Drains | Check for patency and if they are attached correctly. |
| Signs and Symptoms of Infection | Assess for signs and symptoms of infection, which include the following:
|
| Wound Edges and Periwound | Assess the surrounding skin for maceration or signs of infection. |
| Pain | Assess for pain in the wound or during dressing changes. If pain is present, use the PQRSTU or OLDCARTES method to obtain a comprehensive pain assessment. |

See Table 10.6c for a comparison of expected versus unexpected findings on integumentary assessment.
Table 10.6c Expected Versus Unexpected Findings
| Assessment | Expected Findings | Unexpected Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Skin | Color: appropriate for ethnicity
Temperature: warm to touch Texture: smooth, soft, and supple Turgor: resilient Integrity: no wounds or lesions noted Sensory: no pain or itching noted |
Color: pale, white, red, yellow, purple, black and blue
Temperature: cool or hot to touch Texture: rough, scaly or thick; thin and easily torn; dry and cracked Turgor: tenting noted Integrity: rashes, lesions, abrasions, burns, lacerations, surgical wounds, pressure injuries noted Pain or pruritus (itching) present |
| Hair | Full distribution of hair on the head, axilla, and genitalia | Alopecia (hair loss), hirsutism (excessive hair growth over body), lice and/or nits, or lesions under hair |
| Nails | Smooth, well-shaped, and firm but flexible | Cracked, chipped, or splitting nail; excessively thick; presence of clubbing; ingrown nails |
| Skin Integrity | Skin intact with no wounds or pressure injuries. Braden Scale is 23 | A wound or pressure injury is present, or there is risk of developing a pressure injury with a Braden scale score of less than 23 |
Diagnostic and Lab Work
When a chronic wound is not healing as expected, laboratory test results can provide additional clues for the delayed healing. See Table 10.6d for a summary of lab results that offer clues to systemic issues causing delayed wound healing.
Table 10.6d Lab Values Associated with Delayed Wound Healing[9]
| Abnormal Lab Value | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Low hemoglobin | Low hemoglobin indicates less oxygen is transported to the wound site. |
| Elevated white blood cells (WBC) | Increased WBC indicates infection is occurring. |
| Low platelets | Platelets have an important role in the creation of granulation tissue. |
| Low albumin | Low albumin indicates decreased protein levels. Protein is required for effective wound healing. |
| Elevated blood glucose or hemoglobin A1C | Elevated blood glucose and hemoglobin A1C levels indicate poor management of diabetes mellitus, a disease that negatively impacts wound healing. |
| Elevated serum BUN and creatinine | BUN and creatinine levels are indicators of kidney function, with elevated levels indicating worsening kidney function. Elevated BUN (blood urea nitrogen) levels impact wound healing because it can indicate increased breakdown of the body's protein stores due to deficient protein in the diet. |
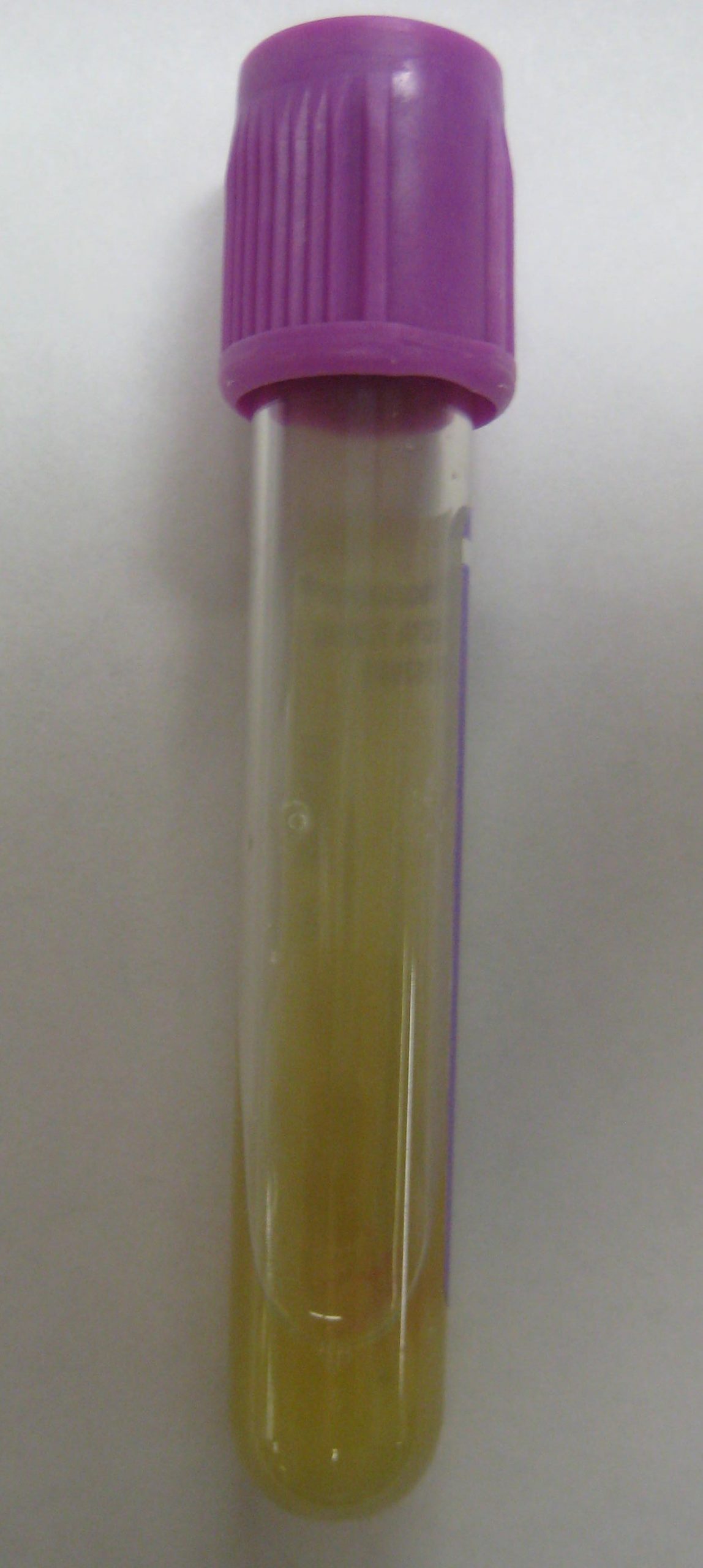
| Positive wound culture | Positive wound cultures indicate an infection is present and provide additional information including the type and number of bacteria present, as well as identifying antibiotics the bacteria is susceptible to. The nurse reviews this information when administering antibiotics to ensure the prescribed therapy is effective for the type of bacteria present. |
Life Span and Cultural Considerations
Newborns and Infants
Newborn skin is thin and sensitive. It tends to be easy to scratch and bruise and is susceptible to rashes and irritation. Common rashes seen in newborns and infants include diaper rash (contact dermatitis), cradle cap (seborrheic dermatitis), newborn acne, and prickly heat.
Toddlers and Preschoolers
Because of high levels of activity and increasing mobility, this age group is more prone to accidents. Issues like lacerations, abrasions, burns, and sunburns can occur frequently. It is important to be highly aware of the potential for accidents and implement safety precautions as needed.
School-Aged Children and Adolescents
Skin rashes tend to affect skin within this age group. Impetigo, scabies, and head lice are commonly seen and may keep children home from school. Acne vulgaris typically begins during adolescence and can alter physical appearance, which can be very upsetting to this age group. Another change during adolescence is the appearance of axillary, pubic, and other body hair. Also, as these children spend more time out of doors, sunburns are more common, and care should be given to encourage sunscreen and discourage the use of tanning beds.
Adults and Older Adults
As skin ages, many changes take place. Because aging increases the loss of subcutaneous fat and collagen breakdown, skin becomes thinner and wrinkles deepen. Decreased sweat gland activity leads to drier skin and pruritus (itching). Wound healing is slowed because of reduced circulation and the inability of proteins and proper nutrients to arrive at injury sites. Hair loses pigmentation and turns gray or white. Nails become thicker and are more difficult to cut. Age or liver spots become darker and more noticeable. The number of skin growths increases and includes skin tags and keratoses.
Diagnoses
There are several NANDA-I nursing diagnoses related to clients experiencing skin alterations or those at risk of developing a skin injury. See Table 10.6e for common NANDA-I nursing diagnoses and their definitions.[10]
Table 10.6e Common NANDA-I Nursing Diagnoses Related to Integumentary Disorders[11]
| Risk for Pressure Injury: “Susceptible to localized injury to the skin and/or underlying tissue usually over a bony prominence as a result of pressure, or pressure in combination with shear.” |
| Impaired Skin Integrity: “Altered epidermis and/or dermis.” |
| Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity: “Susceptible to alteration in epidermis and/or dermis, which may compromise health.” |
| Impaired Tissue Integrity: “Damage to the mucous membrane, cornea, integumentary system, muscular fascia, muscle, tendon, bone, cartilage, joint capsule, and/or ligament.” |
| Risk for Impaired Tissue Integrity: “Susceptible to damage to the mucous membrane, cornea, integumentary system, muscular fascia, muscle, tendon, bone, cartilage, joint capsule, and/or ligament, which may compromise health.” |
A commonly used NANDA-I nursing diagnosis for clients experiencing alterations in the integumentary system is Impaired Tissue Integrity, defined as, “Damage to the mucous membrane, cornea, integumentary system, muscular fascia, muscle, tendon, bone, cartilage, joint capsule, and/or ligament.”
To verify accuracy of this diagnosis for a client, the nurse compares assessment findings with defining characteristics of that diagnosis. Defining characteristics for Impaired Tissue Integrity include the following:
- Acute pain
- Bleeding
- Destroyed tissue
- Hematoma
- Localized area hot to touch
- Redness
- Tissue damage
A sample NANDA-I diagnosis in current PES format would be: “Impaired Tissue Integrity related to insufficient knowledge about protecting tissue integrity as evidenced by redness and tissue damage.”
Outcome Identification
An example of a broad goal for a client experiencing alterations in tissue integrity is:
- The client will experience tissue healing.
A sample SMART expected outcome for a client with a wound is:
- The client’s wound will decrease in size and have increased granulation tissue within two weeks.
Planning Interventions
In addition to the interventions outlined under the “Braden Scale” section to prevent and treat pressure injury, see the following box for a list of interventions to prevent and treat impaired skin integrity. As always, consult a current, evidence-based nurse care planning resource for additional interventions when planning client care.
Selected Interventions to Prevent and Treat Impaired Skin Integrity [12],[13],[14]
- Assess and document the client’s skin status routinely. (Frequency is determined based on the client’s status.)
- Use the Braden Scale to identify clients at risk for skin breakdown. Customize interventions to prevent and treat skin breakdown according to client needs.
- If a wound is present, evaluate the healing process at every dressing change. Note and document characteristics of the wound, including size, appearance, staging (if applicable), and drainage. Notify the provider of new signs of infection or lack of progress in healing.
- Provide wound care treatments, as prescribed by the provider or wound care specialist, and monitor the client's response toward expected outcomes.
- Cleanse the wound per facility protocol or as ordered.
- Maintain non-touch or aseptic technique when performing wound dressing changes, as indicated. (Read more details about using aseptic technique and the non-touch method in the "Aseptic Technique" chapter of the Open RN Nursing Skills,2e textbook.)
- Change wound dressings as needed to keep them clean and dry and prevent bacterial reservoir.
- Monitor for signs of infection in an existing wound (as indicated by redness, warmth, edema, increased pain, reddened appearance of surrounding skin, fever, increased white blood cell count, changes in wound drainage, or sudden change in client’s level of consciousness).
- Apply lotion to dry areas to prevent cracking.
- Apply lubricant to moisten lips and oral mucosa, as needed.
- Keep skin free of excess moisture. Use moisture barrier ointments (protective skin barriers) or incontinence products in skin areas subject to increased moisture and risk of skin breakdown.
- Educate the client and/or family caregivers on caring for the wound and request return demonstrations, as appropriate.
- Administer medications, as prescribed, and monitor for expected effects.
- Consult with a wound specialist, as needed.
- Obtain specimens of wound drainage for wound culture, as indicated, and monitor results.
- Advocate for pressure-relieving devices in clients at risk for pressure injuries, such as elbow protectors, heel protectors, chair cushions, and specialized mattresses and monitor the client's response.
- Promote adequate nutrition and hydration intake, unless contraindicated.
- Use a minimum of two-person assistance and a draw sheet to pull a client up in bed to minimize shear and friction.
- Reposition the client frequently to prevent skin breakdown and to promote healing. Turn the immobilized client at least every two hours, according to a specific schedule.
- Maintain a client’s position at 30 degrees or less, as appropriate, to prevent shear.
- Keep bed linens clean, dry, and wrinkle free.
Implementation
Before implementing interventions, it is important to assess the current status of the skin and risk factors present for skin breakdown and modify interventions based on the client’s current status. For example, if a client's rash has resolved, some interventions may no longer be appropriate (such as applying topical creams). However, if a wound is showing signs of worsening or delayed healing, additional interventions may be required. As always, if the client demonstrates new signs of localized or systemic infection, the provider should be notified.
Evaluation
It is important to evaluate for healing when performing wound care. Use the following expected outcomes when evaluating wound healing:
- Resolution of periwound redness in 1 week
- 50% reduction in wound dimensions in 2 weeks
- Reduction in volume of exudate
- 25% reduction in amount of necrotic tissue/eschar in 1 week
- Decreased pain intensity during dressing changes[15]
If a client is experiencing delayed wound healing or has a chronic wound, it is helpful to advocate for a referral to a wound care nurse specialist.
Read a sample nursing care plan for a client with impaired skin integrity.

