Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN)
The remainder of this chapter will focus on applying the nursing process to a specific type of wound called a pressure injury. Pressure injuries are defined as, “Localized damage to the skin or underlying soft tissue, usually over a bony prominence, as a result of intense and prolonged pressure in combination with shear.” (Note that the 2016 NPUAP Pressure Injury Staging System now uses the term “pressure injury” instead of the historic term “pressure ulcer” because a pressure injury can occur without an ulcer present.) Pressure injuries commonly occur on the sacrum, heels, ischia, and coccyx and form when the skin layer of tissue gets caught between an external hard surface, such as a bed or chair, and the internal hard surface of a bone.
Shear occurs when tissue layers move over the top of each other, causing blood vessels to stretch and break as they pass through the subcutaneous tissue. For example, when a client slides down in bed, the outer layer of skin remains immobile because it remains attached to the sheets due to friction. However, the deeper layer of tissue (attached to bone) moves as the client slides down. This opposing movement of the outer layer of skin and the underlying tissues causes the capillaries to stretch and tear, which then causes decreased blood flow and oxygenation of the surrounding tissues resulting in a pressure injury.[1]
Friction refers to rubbing the skin against a hard object, such as the bed or the arm of a wheelchair. This rubbing causes heat, which can remove the top layer of skin and often results in skin damage. See Figure 10.13[2] for an illustration of shear and friction forces in the development of pressure injuries.
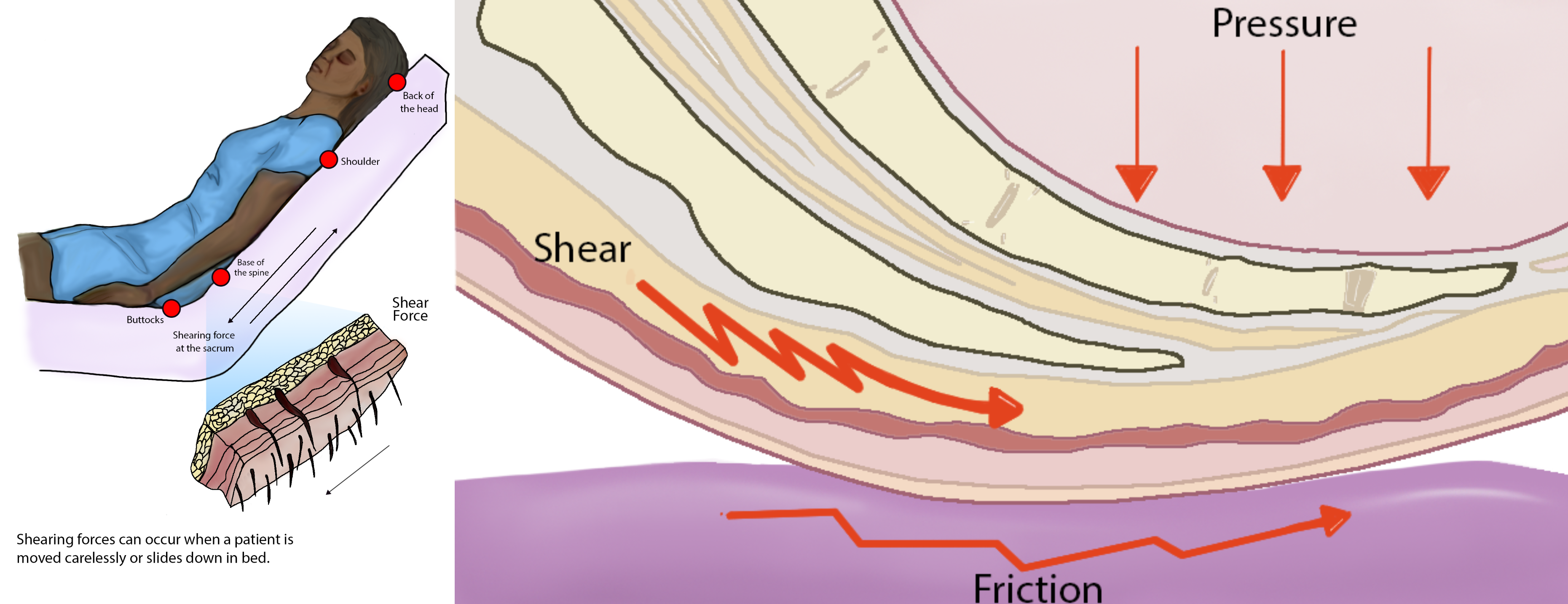
Hospital-acquired or worsening pressure injuries during hospitalization are considered “never events,” meaning they are a serious, preventable medical errors that should never occur and require reporting to The Joint Commission. Additionally, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and many private insurers will no longer pay for additional costs associated with “never events.”[3],[4] Pressure injuries can be prevented with diligent assessment and nursing interventions such as frequent repositioning and providing good skin care.
Staging
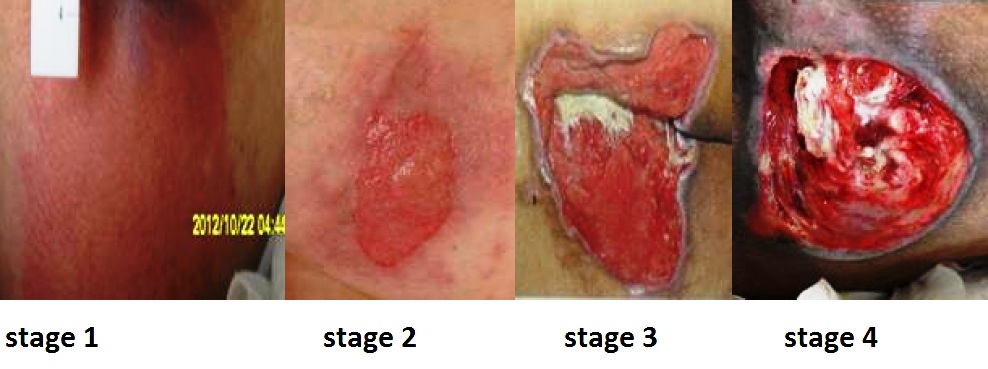
When assessed, pressure injuries are staged from 1 through 4 based on the extent of tissue damage. For example, Stage 1 pressure injuries have the least amount of tissue damage as evidenced by reddened, intact skin, whereas Stage 4 pressure injuries have the greatest amount of damage with deep, open ulcers affecting underlying tissue, muscle, ligaments, or tendons. See Figure 10.14[5] for images of four stages of pressure injuries.[6] Each stage is further described in the following subsections.
Stage 1 Pressure Injuries
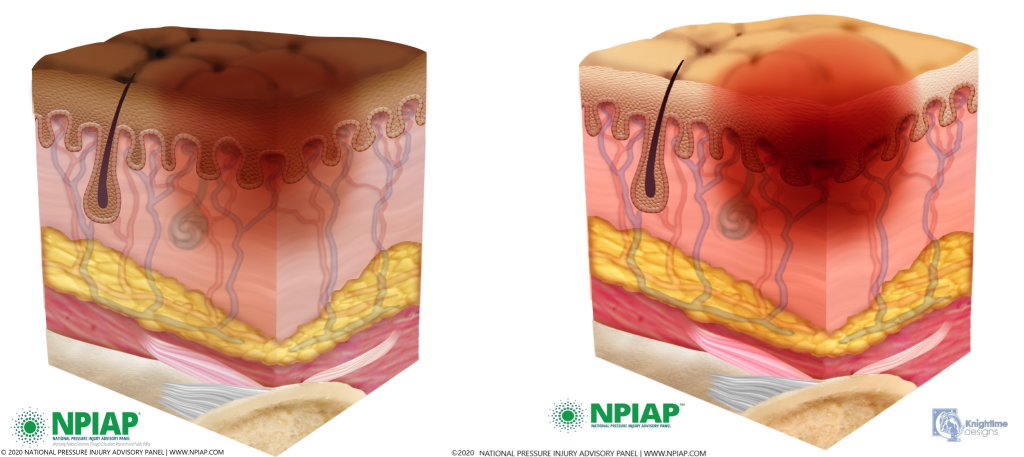
Stage 1 pressure injuries are intact skin with a localized area of nonblanchable erythema where prolonged pressure has occurred. Nonblanchable erythema is a medical term used to describe an area of reddened skin that does not turn white when pressed. Nonblanchable erythema is an early sign of damage to underlying tissue caused by poor blood flow, ischemia, and damage to blood vessels in the area. Because damage is already present, there is a greater risk for Stage 1 pressure injuries to develop into worse pressure injuries if interventions to relieve pressure and not implemented. Skin with dark pigmentation may not demonstrate visible blanching, so it can be challenging to detect Stage 1 pressure injuries. For clients with dark pigmentation, nurses should assess for pain, firmness, softness, changes in temperature, or changes in color compared to surrounding areas.[7],[8]
See Figure 10.15[9] for an illustration of a Stage 1 pressure injury.
Stage 2 Pressure Injuries
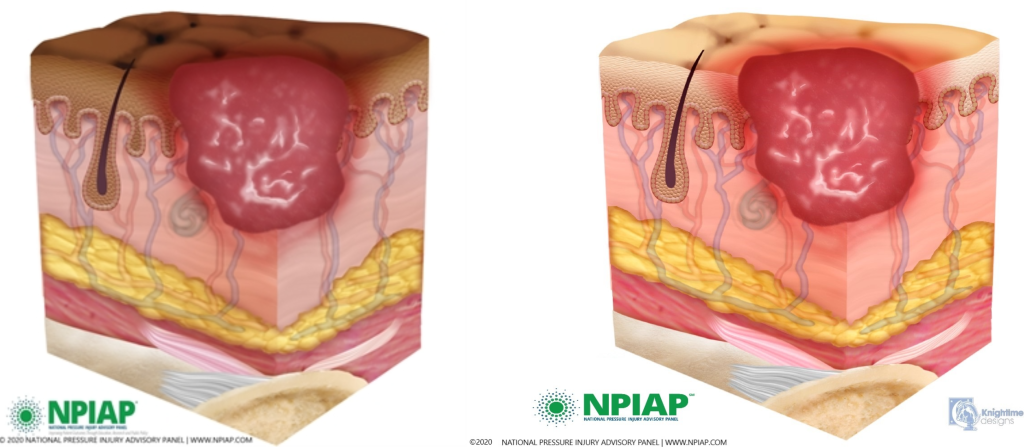
Stage 2 pressure injuries are partial-thickness loss of skin with exposed dermis. The wound has completely broken through the top layer of skin, and partly through the second layer, resulting in a shallow wound. The wound is shallow and generally open. The wound bed is viable and may appear like an intact or ruptured blister.[10] The wound area may be painful and the surrounding tissue may be swollen or discolored.[11] See Figure 10.16[12] for an illustration of a Stage 2 pressure injury.
Stage 3 Pressure Injuries
Stage 3 pressure injuries are full-thickness tissue loss in which fat is visible, but cartilage, tendon, ligament, muscle, and bone are not exposed. The depth of tissue damage varies by anatomical location. Because the wound extends through all skin layers, there is increased risk of infection in Stage 3 pressure injuries. There may be pus draining from the wound, tissue necrosis, pain, or fever, especially in the presence of an infection.[13] See Figure 10.17[14] for an illustration of a Stage 3 pressure injury.
Undermining and tunneling may occur in Stage 3 and 4 pressure injuries. Undermining occurs when the tissue under the wound edge becomes eroded, resulting in a pocket beneath the skin. Tunneling refers to passageways underneath the skin surface that extend from a wound and can take twists and turns.
Slough and eschar may also be present in Stage 3 and 4 pressure injuries. Slough is inflammatory exudate that is usually light yellow, soft, and moist. Eschar is dark brown/black, dry, thick, and leathery dead tissue. If slough or eschar obscures the wound so that tissue loss cannot be assessed, the pressure injury is referred to as unstageable.[15] In most wounds, slough and eschar must be removed by debridement for accurate wound staging and for healing to occur. Removed of slough or eschar is surgically performed by specially trained health care providers. Nurses may apply prescribed chemical debridement agents or wet-to-dry dressings for mechanical debridement per provider orders.
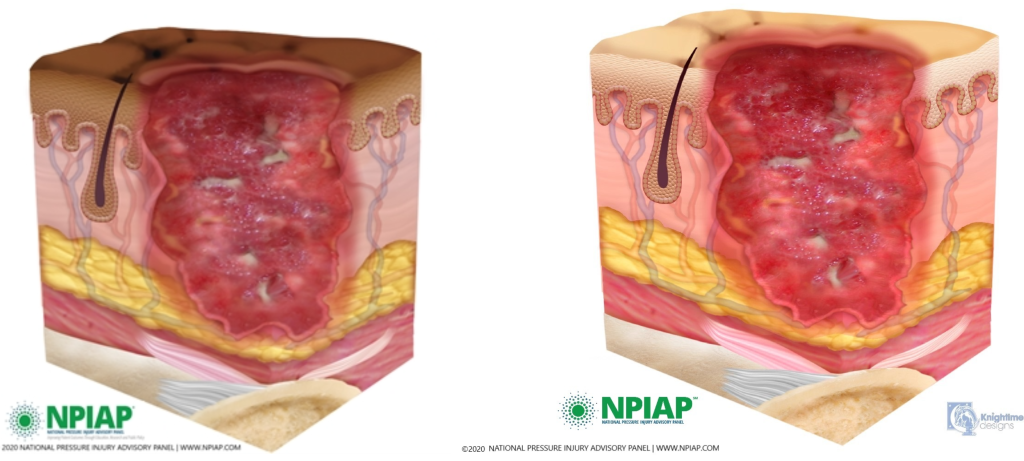
Stage 4 Pressure Injuries
Stage 4 pressure injuries are full-thickness tissue loss, like in Stage 3 pressure injuries, but also have exposed cartilage, tendon, ligament, muscle, or bone. Stage 4 pressure injuries are at an increased risk of infection because their depth goes through all skin layers. There may be pain associated with Stage 4 pressure ulcers, although they are often less painful because the wound damages nerve endings. There also at be firm or mushy texture at the site, discoloration, or necrosis to the wound. Because the wound often extends to the bone, thus exposing the bone to infectious agents in the environment, osteomyelitis (bone infection) may also be present. Osteomyelitis is a serious bone infection that may require amputation or cause death if not promptly treated aggressively with antibiotics.[16],[17]
See Figure 10.18[18] for an illustration of a Stage 4 pressure injury.
View images of different stages of pressure injuries on people with dark skin tones on the PPPIA Pressure Ulcers in People With Dark Skin Tones poster.
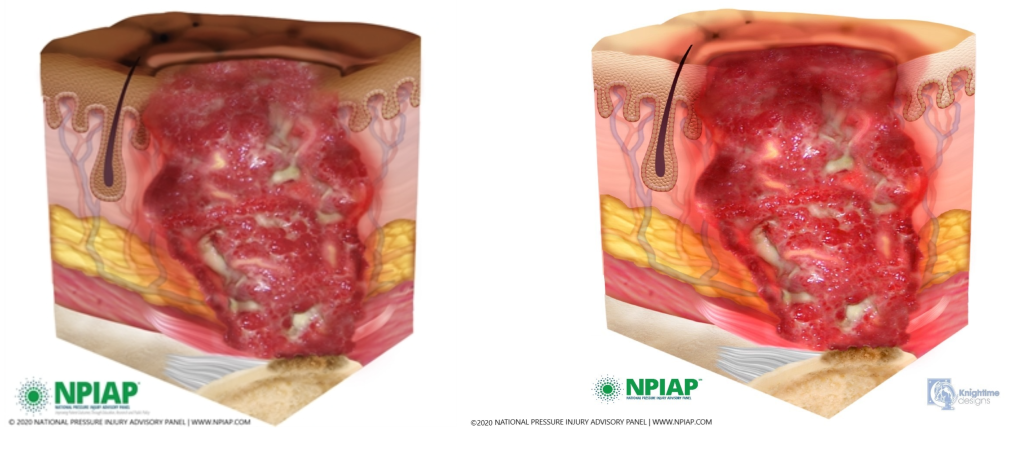
Unstageable Pressure Injuries
Unstageable pressure injuries are full-thickness skin and tissue loss in which the extent of tissue damage within the ulcer cannot be confirmed because it is obscured by slough or eschar. If slough or eschar were to be removed, a Stage 3 or Stage 4 pressure injury would likely be revealed. However, dry and adherent eschar on the heel or ischemic limb is not typically removed.[19] See Figure 10.19[20] for an illustration of an unstageable pressure ulcer due to the presence of eschar (on the left side of the wound) and slough (on the right side of the wound).
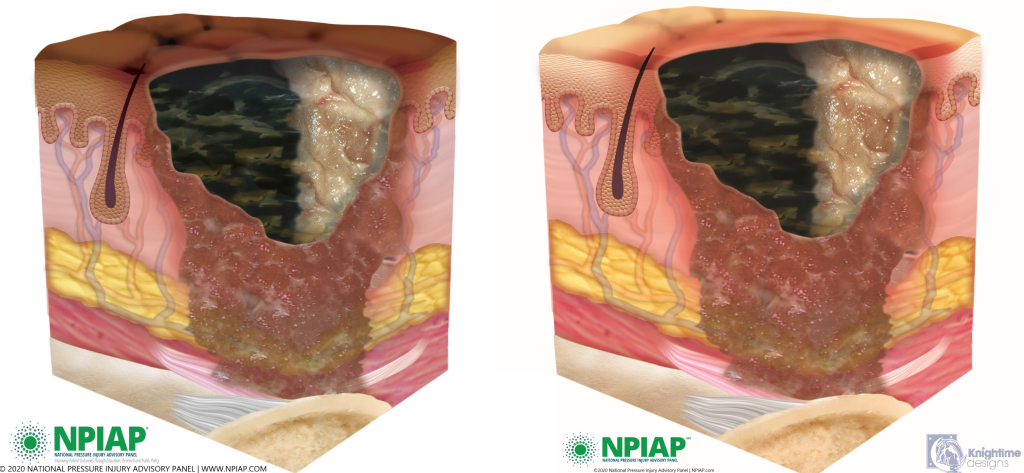
Deep Tissue Pressure Injuries
Deep tissue pressure injuries consist of persistent nonblanchable and deep red, maroon, or purple discoloration of an area. These discolorations typically reveal a dark wound bed or blood-filled blister. Be aware that the discoloration may appear differently in darkly pigmented skin. Deep tissue injury results from intense and/or prolonged pressure, as well as shear forces at the bone-muscle interface. The wound may evolve rapidly to reveal the actual extent of tissue injury, or it may resolve without tissue loss.[21],[22] See Figure 10.20 for an illustration of a deep tissue injury.
Video Review of Assessing Pressure Injuries[23]
- Edsberg, L. E., Black, J. M., Goldberg, M., McNichol, L., Moore, L., & Sieggreen, M. (2016). Revised national pressure ulcer advisory panel pressure injury staging system: Revised pressure injury staging system. Journal of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nursing: Official Publication of The Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nurses Society, 43(6), 585–597. https://doi.org/10.1097/WON.0000000000000281 ↵
- “Shear Force” and “Shear Force Closeup” by Meredith Pomietlo at Chippewa Valley Technical College are licensed under CC BY 4.0 ↵
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2019, September). Never events. psnet.ahrq.gov/primer/never-events ↵
- AMN Healthcare Education Services. (2020). Pressure injury: Never event. rn.com/clinical-insight-pressure-injury/ ↵
- “Wound stage.jpg” by Babagolzadeh is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 ↵
- Edsberg, L. E., Black, J. M., Goldberg, M., McNichol, L., Moore, L., & Sieggreen, M. (2016). Revised national pressure ulcer advisory panel pressure injury staging system: Revised pressure injury staging system. Journal of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nursing: Official Publication of The Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nurses Society, 43(6), 585–597. https://doi.org/10.1097/WON.0000000000000281 ↵
- Lindgren, M., Malmqvist, L. A., Sjöberg, F., & Ek, A.C. (2006) Altered skin blood perfusion in areas with non blanchable erythema: An explorative study. International Wound Journal, (3), 215-23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-481X.2006.00238.x. ↵
- Talley Group Limited. (2020. PPPIA pressure ulcers in People with dark skin tones. https://www.talleygroup.com/medias/documents/PPPIA-Pressure-Ulcers-in-People-with-Dark-Skin-Tones-Poster-A3L-0-1604484440.pdf ↵
- “Stage1-Darkly_Pigmented” and “Skin_01__healthy_skin_-_l_pigmen.jpg” provided by National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel are used with permission for educational purposes. Access for free at https://npiap.com/page/PressureInjuryStages ↵
- Edsberg, L. E., Black, J. M., Goldberg, M., McNichol, L., Moore, L., & Sieggreen, M. (2016). Revised national pressure ulcer advisory panel pressure injury staging system: Revised pressure injury staging system. Journal of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nursing: Official Publication of The Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nurses Society, 43(6), 585–597. https://doi.org/10.1097/WON.0000000000000281 ↵
- Richardson, C. (2023). Stage 2 pressure ulcer: Symptoms and treatment. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/stage-2-pressure-ulcer-symptoms-and-treatment ↵
- “20201202_114031_31850.jpg” and “stage_2_april_2020.jpg” provided by National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel are used with permission for educational purposes. Access for free at https://npiap.com/page/PressureInjuryStages. ↵
- Richardson, C. (2023). Stage 2 pressure ulcer: Symptoms and treatment. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/stage-2-pressure-ulcer-symptoms-and-treatment ↵
- “20201202_114132_23541.jpg” and “stage_3_april_2020.jpg” provided by National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel are used with permission for educational purposes. Access for free at https://npiap.com/page/PressureInjuryStages ↵
- Davis, C. P. Normal flora. (1996). In S. Baron (Ed.), Medical Microbiology (4th ed.). University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK7617/ ↵
- Edsberg, L. E., Black, J. M., Goldberg, M., McNichol, L., Moore, L., & Sieggreen, M. (2016). Revised national pressure ulcer advisory panel pressure injury staging system: Revised pressure injury staging system. Journal of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nursing: Official Publication of The Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nurses Society, 43(6), 585–597. https://doi.org/10.1097/WON.0000000000000281 ↵
- Momodu, I. I., & Savaliya, V. (2023). Osteomyelitis. [Updated 2023 May 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532250/ ↵
- “20201202_114459_31029.jpg” and “stage_4_april_2020.jpg” provided by National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel are used with permission for educational purposes. Access for free at https://npiap.com/page/PressureInjuryStages ↵
- A.D.A.M. Medical Encyclopedia [Internet]. Atlanta (GA): A.D.A.M., Inc.; c1997-2020. Stasis dermatitis and ulcers; [updated 2020, Dec 3; reviewed 2018, Oct 14; cited 2020, Dec 10]. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000834.htm ↵
- “Unstageable- Darkly Pigmented_Skin.jpg” and “unstageable-halfslough__1_.jpg” provided by National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel are used with permission for educational purposes. Access for free at https://npiap.com/page/PressureInjuryStages ↵
- Edsberg, L. E., Black, J. M., Goldberg, M., McNichol, L., Moore, L., & Sieggreen, M. (2016). Revised national pressure ulcer advisory panel pressure injury staging system: Revised pressure injury staging system. Journal of Wound, Ostomy, and Continence Nursing: Official Publication of The Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nurses Society, 43(6), 585–597. https://doi.org/10.1097/WON.0000000000000281 ↵
- “DTPI-Darkly Pigmented Skin” and “deep_tissue_pressure_injury_.jpg” provided by National Pressure Injury Advisory Panel are used with permission for educational purposes. Access for free at https://npiap.com/page/PressureInjuryStages ↵
- RegisteredNurseRN. (2018, March 7). Pressure ulcers (injuries) stages, prevention, assessment | Stage 1, 2, 3, 4 unstageable NCLEX [Video]. YouTube. All rights reserved. Video used with permission. https://youtu.be/MDtPik1UE6k ↵
Localized damage to the skin or underlying soft tissue, usually over a bony prominence, as a result of intense and prolonged pressure in combination with shear.
Damage that occurs when tissue layers move over the top of each other, causing blood vessels to stretch and break as they pass through the subcutaneous tissue.
The rubbing of skin against a hard object, such as the bed or the arm of a wheelchair. This rubbing causes heat that can remove the top layer of skin and often results in skin damage.
Intact skin with a localized area of nonblanchable erythema where prolonged pressure has occurred.
Skin redness that does not turn white when pressed.
Partial-thickness loss of skin with exposed dermis. The wound bed is viable and may appear like an intact or ruptured blister.
Full-thickness tissue loss in which fat is visible, but cartilage, tendon, ligament, muscle, and bone are not exposed.
A condition that occurs in wounds when the tissue under the wound edges becomes eroded, resulting in a pocket beneath the skin at the wound's edge.
Passageways underneath the surface of the skin that extend from a wound and can take twists and turns.
Inflammatory exudate in wounds that is usually light yellow, soft, and moist.
Dark brown/black, dry, thick, and leathery dead tissue in wounds.
Full-thickness tissue loss like Stage 3 pressure injuries but also have exposed cartilage, tendon, ligament, muscle, or bone.
Full-thickness skin and tissue loss in which the extent of tissue damage within the ulcer cannot be confirmed because it is obscured by slough or eschar.
Persistent; non-blanchable; deep red, maroon, or purple discoloration of intact or non-intact skin revealing a dark wound bed or blood filled blister.

