Homeostasis
Overview
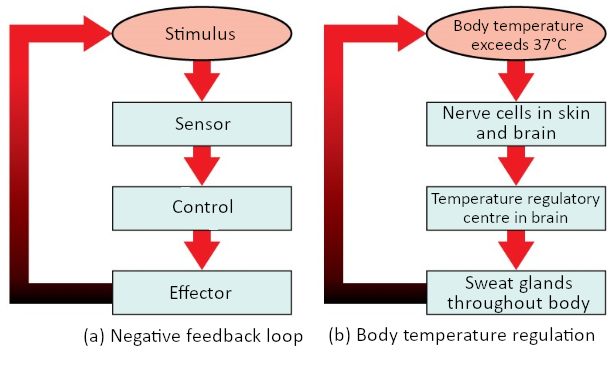
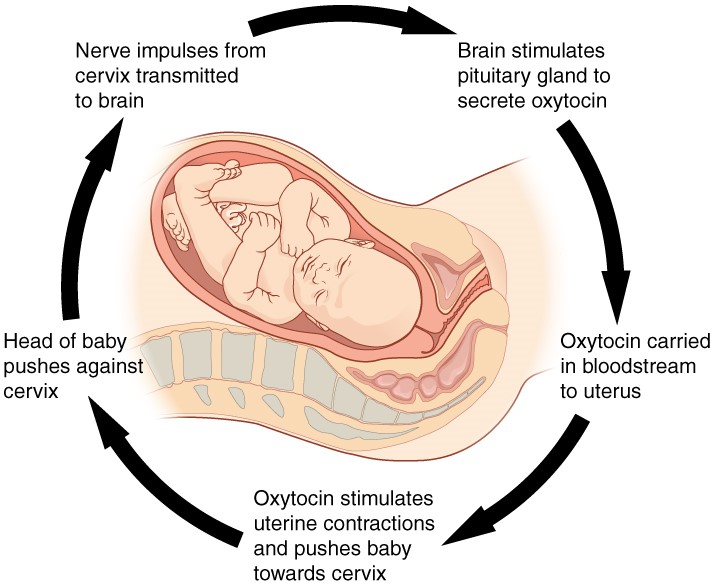
Homeostasis is the body’s ability to maintain internal stability despite external changes. One key mechanism that helps achieve this balance is through feedback loops. There are two main types of feedback loops: negative feedback and positive feedback. Negative feedback loops work to maintain a stable state by reversing any deviations from the set point. On the other hand, positive feedback loops amplify and reinforce changes, often leading to an increase in the deviation from the set point. Understanding these feedback loops is crucial in comprehending how our bodies regulate and maintain balance to ensure optimal functioning.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, students will be able to:
- identify the four components of a homeostatic feedback control loop.
- explain how a negative feedback loop works and give specific examples.
- explain how a positive feedback loop works and give specific examples.
Video Review
Watch the video: Positive And Negative Feedback Loops – Negative Feedback Loops – Positive Feedback Loops (2 minutes)
Activities
These infographics will be helpful as you work through the activities.
Flash Cards
Question Sets
Chapter Attributions
This chapter by Elisabeth Kehrli and Anil Kapoor is licensed under a CC BY 4.0 license.
Media Attributions
Positive And Negative Feedback Loops – Negative Feedback Loops – Positive Feedback Loops by Whats Up Dude is licensed under the Standard YouTube license.
Interactive Activity Attributions
The interactive activities in this chapter are from Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology by University of Southern Queensland, and are licensed under a CC BY SA 4.0 license.

