MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
Membrane transport is defined as passage of a substance across a membrane. The cell membrane is selectively permeable, the phospholipid bilayer allows some molecules to easily pass across the membrane and does not allow other molecules to easily pass across the membrane. There are two types of membrane transport; active transport and passive transport. Passive transport is movement of a substance across a membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. There is no energy or ATP required. The goal of passive transport is equilibrium across the membrane.
There are three types of passive transport; diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis.
diffusion
Diffusion is movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration across a membrane. No energy or ATP is required and the goal of diffusion is equilibrium across the membrane. Oxygen and carbon dioxide use diffusion to cross a membrane. Facilitated diffusion is movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration across a membrane using a protein transport channel. The protein transport channel can be specific or non-specific. No energy or ATP is required and the goal of facilitated diffusion is equilibrium across the membrane. Glucose and fructose use facilitated diffusion to cross a membrane.
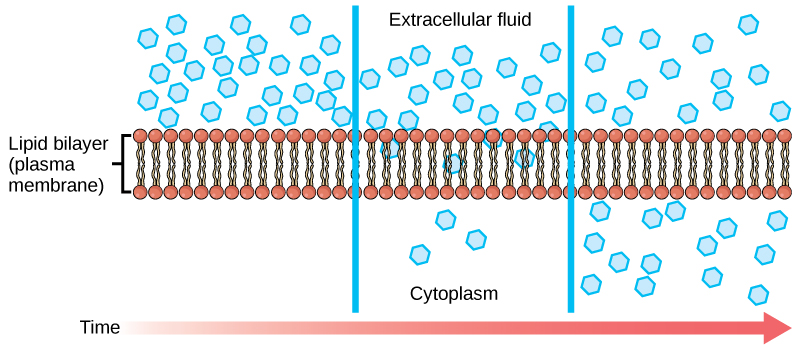
Image from openstax Biology 2e
osmosis
Osmosis is movement of water from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration. There is no energy or ATP required. The goal of osmosis is equilibrium across the membrane.
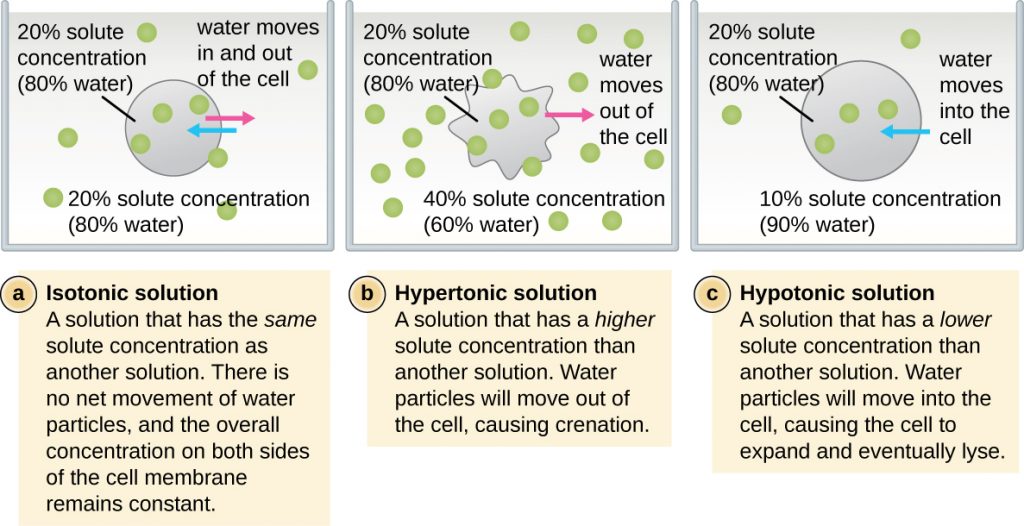
If there is not equilibrium across the membrane in what direction will water osmose? That depends on the solution the cell is in. An isotonic solution has the same water concentration inside and outside the cell. Equilibrium has already been achieved, no osmosis is required. A hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration outside the cell. Water will osmose out of the cell to achieve equilibrium and the cell will shrivel. This is why jelly and pickles last so long in the refrigerator; they are hypertonic solutions of sugar (jelly) or salt (pickles). A hypotonic solution has a lower solute concentration outside the cell. Water will osmose into the cell to achieve equilibrium and the cell will lyse.
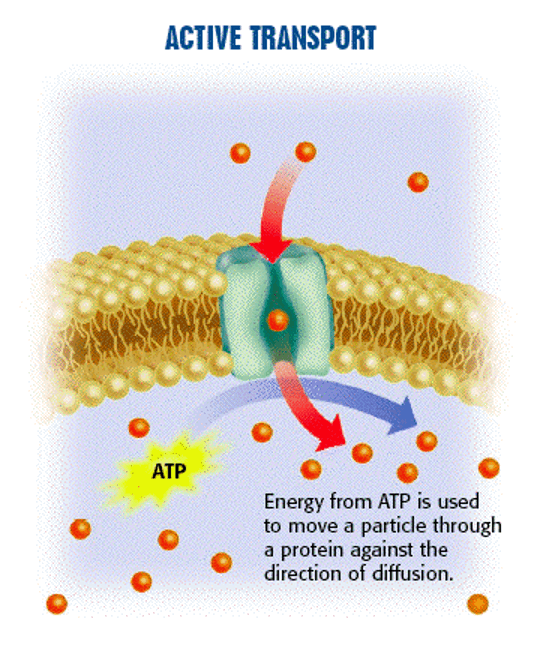
active transport
Active transport is movement of a substance across a membrane from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration using a protein transport channel. Energy or ATP is required for active transport. Ions like sodium and potassium use active transport to cross a membrane.