7 1.6 Geological Time
Steven Earle
In 1788, after many years of geological study, James Hutton, one of the great pioneers of geology, wrote the following about the age of Earth: The result, therefore, of our present enquiry is, that we find no vestige of a beginning — no prospect of an end.[1] Of course he wasn’t exactly correct, there was a beginning and there will be an end to Earth, but what he was trying to express is that geological time is so vast that we humans, who typically live for less than a century, have no means of appreciating how much geological time there is. Hutton didn’t even try to assign an age to Earth, but we now know that it is approximately 4,570 million years old. Using the scientific notation for geological time, that is 4,570 Ma (for mega annum or “millions of years”) or 4.57 Ga (for giga annum or billions of years). More recent dates can be expressed in ka (kilo annum); for example, the last cycle of glaciation ended at approximately 11.7 ka or 11,700 years ago. This notation will be used for geological dates throughout this book.
Exercises
| 2.75 ka |
| 0.93 Ga |
| 14.2 Ma |
We use this notation to describe times from the present, but not to express time differences in the past. For example, we could say that the dinosaurs lived from about 225 Ma to 65 Ma, which is 160 million years, but we would not say that they lived for 160 Ma.
Unfortunately, knowing how to express geological time doesn’t really help us understand or appreciate its extent. A version of the geological time scale is included as Figure 1.9. Unlike time scales you’ll see in other places, or even later in this book, this time scale is linear throughout its length, meaning that 50 Ma during the Cenozoic is the same thickness as 50 Ma during the Hadean—in each case about the height of the “M” in Ma. The Pleistocene glacial epoch began at about 2.6 Ma, which is equivalent to half the thickness of the thin grey line at the top of the yellow bar marked “Cenozoic.” Most other time scales have earlier parts of Earth’s history compressed so that more detail can be shown for the more recent parts. That makes it difficult to appreciate the extent of geological time.
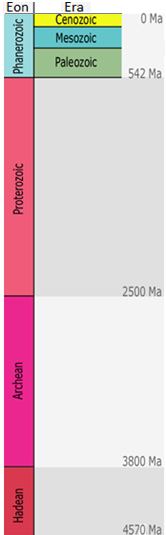
To create some context, the Phanerozoic Eon (the last 542 million years) is named for the time during which visible (phaneros) life (zoi) is present in the geological record. In fact, large organisms — those that leave fossils visible to the naked eye — have existed for a little longer than that, first appearing around 600 Ma, or a span of just over 13% of geological time. Animals have been on land for 360 million years, or 8% of geological time. Mammals have dominated since the demise of the dinosaurs around 65 Ma, or 1.5% of geological time, and the genus Homo has existed since approximately 2.2 Ma, or 0.05% (1/2,000th) of geological time.
Geologists (and geology students) need to understand geological time. That doesn’t mean simply memorizing the geological time scale; instead, it means getting your mind around the concept that although most geological processes are extremely slow, very large and important things can happen if such processes continue for enough time.
For example, the Atlantic Ocean between Nova Scotia and northwestern Africa has been getting wider at a rate of about 2.5 cm per year. Imagine yourself taking a journey at that rate — it would be impossibly and ridiculously slow. And yet, since it started to form around 200 Ma (just 4% of geological time), the Atlantic Ocean has grown to a width of over 5,000 km!
A useful mechanism for understanding geological time is to scale it all down into one year. The origin of the solar system and Earth at 4.57 Ga would be represented by January 1, and the present year would be represented by the last tiny fraction of a second on New Year’s Eve. At this scale, each day of the year represents 12.5 million years; each hour represents about 500,000 years; each minute represents 8,694 years; and each second represents 145 years. Some significant events in Earth’s history, as expressed on this time scale, are summarized on Table 1.1.
| Event | Approximate Date | Calendar Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| Formation of oceans and continents | 4.5 – 4.4 Ga | January |
| Evolution of the first primitive life forms | 3.8 Ga | early March |
| Formation of British Columbia’s oldest rocks | 2.0 Ga | July |
| Evolution of the first multi-celled animals | 0.6 Ga or 600 Ma | November 15 |
| Animals first crawled onto land | 360 Ma | December 1 |
| Vancouver Island reached North America and the Rocky Mountains were formed | 90 Ma | December 25 |
| Extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs | 65 Ma | December 26 |
| Beginning of the Pleistocene ice age | 2 Ma or 2000 ka | 8 p.m., December, 31 |
| Retreat of the most recent glacial ice from southern Canada | 14 ka | 11:58 p.m., December 31 |
| Arrival of the first people in British Columbia | 10 ka | 11:59 p.m., December 31 |
| Arrival of the first Europeans on the west coast of what is now Canada | 250 years ago | 2 seconds before midnight, December 31 |
Exercises
Exercise 1.4 Take a Trip through Geological Time
We’re going on a road trip! Pack some snacks and grab some of your favourite music. We’ll start in Tofino on Vancouver Island and head for the Royal Tyrrell Museum just outside of Drumheller, Alberta, 1,500 km away. Along the way, we’ll talk about some important geological sites that we pass by, and we’ll use the distance as a way of visualizing the extent of geological time. Of course it’s just a “virtual” road trip, but it will be fun anyway. To join in, go to: https://barabus.tru.ca/geol2051/road_trip/road_trip.html
Once you’ve had a chance to do the road trip, answer these questions:
1. We need oxygen to survive, and yet the first presence of free oxygen (O2 gas) in the atmosphere and the oceans was a “catastrophe” for some organisms. When did this happen and why was it a catastrophe?
2. Approximately how much time elapsed between the colonization of land by plants and animals?
3. Explain why the evolution of land plants was such a critical step in the evolution of life on Earth.
- Hutton, J, 1788. Theory of the Earth; or an investigation of the laws observable in the composition, dissolution, and restoration of land upon the Globe. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. ↵

