DNA AND RNA STRUCTURE
nucleic acids
Nucleic acids are one of the macromolecules of life along with carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are nucleic acids. Like all macromolecules nucleic acids are made of building blocks or monomers. The monomer of nucleic acids is nucleotides. Nucleotides are composed of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
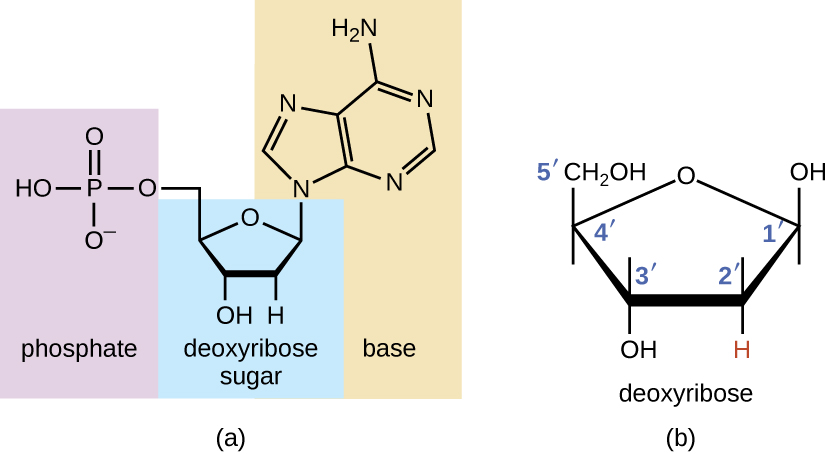
Image from openstax Microbiology
DNA
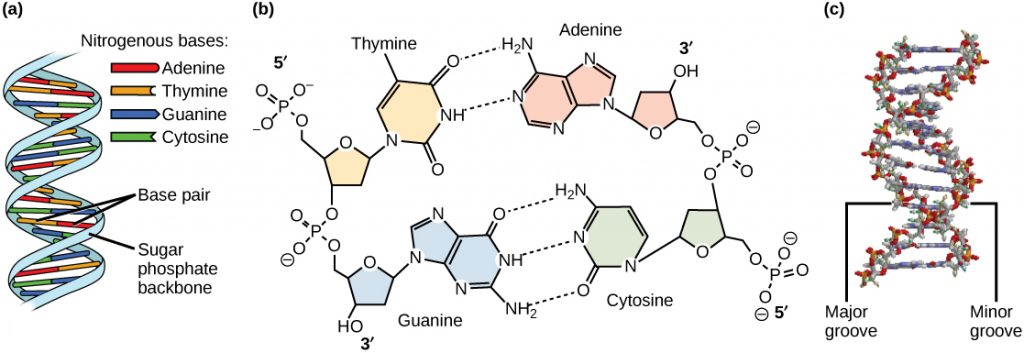
Let’s start our conversation about nucleic acids with DNA. The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose. The nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The specificity in DNA is in the order of the nucleotides. DNA is a double-stranded molecule. DNA contains the hereditary information, it is the genetic blueprint. DNA is a cell basic, all cells have DNA. DNA is a double helix; it looks like a spiral staircase. The sides of the staircase are composed of deoxyribose and phosphate groups. Each step of the spiral staircase is made of two nitrogenous bases; A pairs with T and C pairs with G. The two DNA strands run anti-parallel to each other. One strand (the 5’ or five prime strand) has a terminal phosphate group, the other strand (the 3’ or three prime strand) has a terminal hydroxyl group. The two DNA strands running anti-parallel will come into play during DNA replication.
QuIZ TIME!
RNA
Now let’s discuss the other nucleic acid RNA. The sugar in RNA is ribose. The nitrogenous bases in RNA are A, uracil (U), C, and G. In RNA A pairs with U and C pairs with G. RNA is a single-stranded molecule. There are three types of RNA. Messenger RNA or mRNA is a go between. Ribosomal RNA or rRNA along with some proteins is what ribosomes are made of. Transfer or tRNA transfers in amino acids.
| NUCLEIC ACID | SUGAR | NITROGENOUS BASES | NUMBER OF STRANDS |
| DNA | Deoxyribose | A, T, C. G | 2 |
| RNA | Ribose | A, U, C, G | 1 |
Genome is the entire genetic complement of a cell or virus. A gene is a specific sequence of nucleotides that codes for a protein or RNA. Escherichia coli has approximately 4, 300 genes; humans have approximately 20,000 genes.
