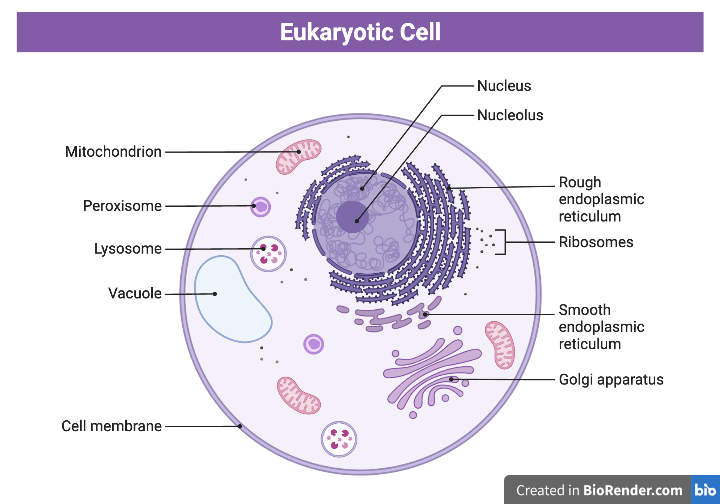
MEMBRANE-BOUND ORGANELLES
Bacteria are prokaryotes and viruses are not cells. Many microorganisms are eukaryotes, so a review of eukaryotic organelles is necessary. Unlike prokaryotic cells (bacteria), eukaryotic cells have numerous membrane-bound organelles. Organelles have specialized cellular functions, just as your body’s organs have specialized functions.
| ORGANELLE | FUNCTION(S) | PRESENT IN PROKARYOTES |
PRESENT IN EUKARYOTES |
| Nucleus | Contains DNA, directs synthesis of proteins and ribosomes | No | Yes |
| Nucleolus | Ribosome subunit synthesis | No | Yes |
| Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (no ribosomes) | Lipid synthesis | No | Yes |
| Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (studded with ribosomes) | Protein synthesis | No |
Yes |
| Golgi Apparatus | Where proteins and lipids coming from the rough ER are processed, sorted, and packaged for transport | No | Yes |
| Lysosomes | Sacs containing digestive enzymes break down captured food materials | No | Yes |
| Mitochondria | Cellular respiration (aerobic ATP production) | No | Yes |
| Vacuole | Storage | No | Yes |
| Peroxisome | Contain a variety of enzymes. These enzymes function together to rid the cell of toxic substances including hydrogen peroxide a common by-product of cellular respiration. | No | Yes |
| Chloroplast (plant cells, algae, some protozoa) | Photosynthesis | No | Yes |