2 When Eating Hurts
Heather Maher; Lourdes Vasquez; and Koffi Kouadio

What is IBS?
IBS stands for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. It is a large intestine disorder known as a gastrointestinal disorder, which causes stomach pain and discomfort. It is a common disorder, and the signs and symptoms include:
- Cramping
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Gas
- Vomiting and diarrhea or constipation (sometimes both)
The symptoms and severity can vary from person to person. However, what is the same for all is that the symptoms and signs are, for the most part, present for a long time. Meaning this is a chronic condition that needs to be treated long term. Having IBS can create a poor quality of life. This can lead to mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety, if not treated.
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
______________________________________________________________
What Causes It?
The causes of this disorder are still not very well known. Usually, unhealthy food and stressful situations trigger it, making it worse. Nonetheless, they do not cause it. What has been noted is that females under the age of 50, people with a family history of IBS, and a history of abuse or trauma tend to be more susceptible to the disorder. Other factors that may play a role are gut microbes changes due to a severe infection, antibiotics, or unhealthy eating habits. This diminishes your gastrointestinal flora, the healthy bacteria, which helps keep you healthy and increases the disease-causing bacteria. It is not easy to enjoy life with constant pain, discomfort, and such symptoms.
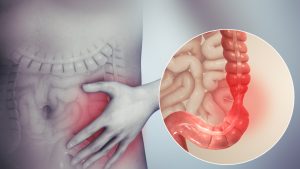
The pain might come from uncontrolled contractions in the muscles of the colon. And discomfort can be due to abnormalities in the nerves of your digestive system. Since the brain and the gut are interconnected, stress is a trigger for pain and discomfort. If not properly treated and kept under control, it can lead to more severe issues.
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
______________________________________________________________
Why is it Important that I treat it?
Chronic constipation or diarrhea can cause hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids are blood vessels within the lower rectum that become enlarged due to excessive pressure. This can be painful and cause bleeding, which can lead to more severe complications. Diarrhea and vomiting increase liquid and nutrient loss, which can lead to dehydration and nutrient deficiencies.
Being deficient in one or more nutrients results in your immune system being at risk and susceptible to infectious bacteria. IBS can also affect your body’s digestion and how you absorb nutrients from foods. This can lead to malnutrition, which can cause more severe diseases. At this point, your immune response and your immune system become weak, not able to fight off infectious or chronic diseases, heal wounds, or protect you from developing cancer.

Do you feel IBS symptoms creep up more during finals, exams, or stressful situations?
Luckily it can be managed with:
- Proper diet
- Lifestyle
- Keeping stress under control.
Focus on lowering your stress levels. Chronic high levels of stress are hard on your whole body, including your gut.
- Get enough sleep.
- Eat slowly and chew your food several times.
- Eat foods rich in prebiotics and probiotics.
- These can be foods high in fiber, kombucha, miso soup, kimchi yogurt, and sauerkraut.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- Stay hydrated.
- You can also follow a FODMAP diet. It is a temporary diet, which helps figure out which foods are causing your IBS.
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
______________________________________________________________
However, if you have kept a great diet, lifestyle, and stress under control, yet the symptoms persist or worsen, you should see a doctor. Especially if you experience:
- Rapid weight loss
- Rectal bleeding
- Difficulty swallowing
- A persistent change in bowel movements
- Unexplained vomiting
For further information and community support on IBS, visit https://www.ibspatient.org/.

Food Allergies and Intolerances
Sometimes the most delicious and nutritious foods can cause a range of physical problems from GI pain and discomfort to severe immune reactions that can be life-threatening. What do we do when faced with these issues? Can a healthy diet be maintained if someone is allergic to a whole grain like wheat or has a dairy intolerance? Let’s first begin by defining both food allergy and food intolerance.
Food Intolerances
Food intolerance is defined by Janice Thompson in The Science of Nutrition as “gastrointestinal discomfort caused by a digestive problem and not an immune system reaction.” When we eat certain foods, and our body does not make the proper digestive enzymes break down all the food item components, our GI tract can become inflamed or irritated. Food intolerances are also linked to recurring stress or psychological issues, irritable bowel syndrome, and sensitivity to food additives. Generally, food intolerances are less serious than a food allergy, and typically the pain and discomfort reside once the offending food has passed through the individuals’ system.
Lactose intolerance is very common and includes a range of GI problems:
- gas
- indigestion
- diarrhea
- cramping
- bloating
As we age, our bodies make less and less of the enzyme lactase, which is needed to breakdown lactose (the primary carbohydrate of dairy products), so it is typical to see more lactose intolerance as people make their way through the middle and later parts of their life. It is uncommon to see lactose intolerance in children.
Food Allergies
Food allergies are an immune hypersensitivity reaction to certain foods. Usually, a protein in the food causes the immune cells to respond by releasing chemicals that cause inflammation throughout the body or in certain areas. The inflammation can be life-threatening if it impacts your airway and causes the trachea or bronchioles to swell shut, a reaction known as anaphylaxis.
Anaphylaxis left untreated can lead to shock and maybe even death. Skin rashes, swelling of the tongue, lips, or face can occur in an allergic reaction to food. Wheezing and difficulty breathing are also signs of a food allergy and should be addressed with medical attention as soon as possible. Food allergies are less common than food intolerances but are often more problematic and typically require medication to recover fully. The eight most common food allergens in the United States are milk, egg, wheat, soy, peanut, tree nuts, fish, and shellfish.
Management of Intolerances and Allergies
Now that we know the differences between a food allergy and intolerance, how can we be sure we don’t consume the offending food items? What happens if we do so accidentally? The best way to avoid an allergic reaction or episode of GI distress is not to eat the food item, which may be easier said than done. While it may be easy to avoid cheese that causes lactose intolerance symptoms, it can be more challenging to avoid wheat or soy, common components of many food products. Become familiar with and used to reading food labels, sometimes a seemingly safe product may have a hidden ingredient. The Food Allergy Labeling and Consumer Protection Act of 2004 mandates that all packed foods produced in the US must identify easily to understand terms if there are any of the eight most common food allergens. Even if the allergen is only an incidental ingredient, such as in the flavoring, it must be listed. If you accidentally consume something you have a true allergy to, it is helpful to have medications like antihistamines on hand or an auto-injector of epinephrine for severe allergies that cause anaphylaxis. Severe reactions should be managed at the hospital, and the epinephrine shot will typically allow enough time to get to the emergency department. For accidental consumption of food intolerances, the symptoms should pass once the problematic food is out of the body.
Where Do These Problems Come From? How Do I Maintain A Healthy Diet?
It is important to be aware of your family history regarding food allergies and intolerances; allergies, in particular, can run in families. Monitor what children eat and gauge their physical reactions to new foods since most food allergies develop in childhood. If you suspect a food allergy, a visit to an allergist can help determine which particular foods you may have immune reactions to. A healthy diet can still be maintained if someone has a food intolerance or a limited number of allergies. Still, individuals with complex allergies and severe reactions should work with a registered dietician to ensure that they consume the macro and micronutrients they need while avoiding the allergens.
For further information about food allergies, visit https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition/food-allergies.
Resources for Phoenix-area families can be found at http://www.phoenixallergynetwork.org/.
Disordered Eating and Psychological Issues
What are Disordered Eating and Psychological Issues?
Disordered eating is a condition where one adopts unhealthy eating habits based on the outside world. This means that the obsession with size, weight, diet, and exercise is taken to an unhealthy level. Disordered eating manifests itself through many eating disorders.
All of it has a psychological aspect of its own. People suffering from an eating disorder are often exposed to much bigger pressure from society. The fear of gaining weight, constantly running through their minds, gets them to take drastic measures. Those people are often diagnosed with Anorexia Nervosa (AN) or Bulimia Nervosa (BN).
This chapter will discuss the two main eating disorders linked to disordered eating and their psychological impact on the person over time. We will also be discussing the symptoms and treatments of those conditions.
Anorexia Nervosa
Definition
Anorexia Nervosa or commonly called Anorexia, is an extremely uncommon fear of gaining weight. It is characterized as abnormally low body weight and a different perception of weight. It was a time when weight was associated with being in a good position in life. Not being rich but being happy and being able to provide enough food for oneself. Society changed to the point where eating is almost being prohibited. “Prohibited” is exactly the feeling that people suffering from Anorexia feel. They are trapped in this box where eating is almost seen as a sin. They could be bereaved themselves from food even though their weight is acceptable.
This is not really food-related; it is more of a coping mechanism. Coping is used differently depending on the person. Some people cope by isolating themselves; some people cope by partying more, some cope with eating, and some cope with not eating. It is most of the time to deal with trauma. People suffering from Anorexia have sometimes been bullied in their childhood about their weight. The only way they know to avoid being bullied is to lose weight, which is not bad, but this disorder turns it into an unhealthy habit. Its consequences can even be life-threatening.
Symptoms
Many symptoms can characterize anorexia Nervosa. Those symptoms can easily be divided into two categories: The physical symptoms and the behavioral symptoms. As there are plenty of those symptoms, we will show the six more frequent of each category.
The physical symptoms:
- Extreme weight loss
- Thin appearance
- Abnormal blood counts
- Dry or yellow skin
- Dehydration
The behavioral symptoms:
- Preoccupation with food
- Frequently skipping meals
- Denial of hunger
- Adopting eating rituals such as spitting food after chewing
- Lying about the quantity of food eaten
- Frequently checking in the mirror for perceived flaws.
Treatment
As mentioned above, Anorexia Nervosa can be life-threatening, and one might need a few trips to the hospital and even be hospitalized. There is no medication to treat this condition. The fastest way to fight against it is to get back to a healthy weight as soon as possible. This recovery may need to be supervised by your primary caregiver and a dietician to prevent any abnormal conditions throughout the process. Remember that psychological issues firstly trigger this condition; like the disorder itself, the recovery is also psychological. The family and a psychiatrist’s support plays a big role in the road back to a healthy life.
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia Nervosa is an eating disorder that might potentially be life-threatening. People who have bulimia will eat in substantial quantities (bingeing) and then go through unhealthy ways of getting rid of the extra calories. They will tend to make themselves vomit, use laxatives, or even abuse weight-loss supplements. They will tend to restrict themselves from food after eating an enormous quantity. They see themselves as overly big and try to get back to “normal” any way possible. They give a lot of importance to what society can think about them. This psychological pressure makes them “normal” sometimes and “abnormal” some other times. Like Anorexia Nervosa, this disorder is really not about food; it is about the perception and the need to belong.
Symptoms
Some symptoms of Bulimia Nervosa might seem similar to those of Anorexia Nervosa. Symptoms include:
- Being preoccupied with your body shape and weight
- Living in fear of gaining weight
- Repeated episodes of eating abnormally large amounts of food in one sitting
- Feeling a loss of control during bingeing.
- Using dietary supplements or herbal products excessively for weight loss
- Forcing yourself to vomit to keep from gaining weight after bingeing
Treatment
Contrary to Anorexia Nervosa, bulimia nervosa can actually be treated with some medication. Bulimia Nervosa is often linked to depression; thus, the most effective treatment would be to combine antidepressants with psychotherapy.
Sources
IBS:
Herndon J. Healthline. March 7/2019. Everything you want to know about IBS. Access 11/2020 https://www.healthline.com/health/irritable-bowel-syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome. Mayo Clinic. 1998-2020. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. Access 11/2020 https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/irritable-bowel-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20360016
Medical Express. Health. October, 7/2010. The University of Cincinnati. Access 11/2020
https://medicalxpress.com/news/2010-10-hemorrhoid-treatment-doesnt-involve-surgery.html
What’s causing your IBS. Harvard Health Publishing. 2010-2020 Harvard University. Healthbeat. Access 11/2020 https://www.health.harvard.edu/healthbeat/whats-causing-your-ibs
Allergies and Intolerances:
Li, James. Mayo Clinic. April 3, 2020. What’s The Difference Between A Food Intolerance and a Food Allergy? Accessed: 11/18/2020. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/food-allergy/expert-answers/food-allergy/faq-20058538#:~:text=A%20true%20food%20allergy%20causes,often%20limited%20to%20digestive%20problems.
West, Helen. Healthline. June 24, 2017. Lactose Intolerance 1010-Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment. Accessed: 11/20/2020. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/lactose-intolerance-101#TOC_TITLE_HDR_3
American College of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology. 2014. Food Allergy. Accessed: 11/16/2020. https://acaai.org/allergies/types/food-allergy
US Food & Drug Administration. November 10 2020. Food Allergies. Accessed: 11/22/2020. https://www.fda.gov/food/food-labeling-nutrition/food-allergies
Disordered Eating and Psychological Issues:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/anorexia-nervosa/symptoms-causes/syc-20353591
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/anorexia-nervosa/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353597
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bulimia/symptoms-causes/syc-20353615
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bulimia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353621
https://www.psypost.org/2017/07/young-women-suffering-anorexia-nervosa-tend-better-sense-smell-49378
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325874#raynauds-disease
https://www.steadfastnutrition.in/blogs/news/bulimia-nervosa-bn
https://www.hypnosisondemand.com/overcome-pocrescophobia-obesophobia-fear-gaining-weight/
Media Attributions
- stomach-3532098_1920 © Image by mohamed Hassan from Pixabay is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Irritable_bowel_syndrome © By http://www.scientificanimations.com - http://www.scientificanimations.com/wiki-images/, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=81575725 is licensed under a Public Domain license
- books-4118058_1920 © Image by silviarita from Pixabay is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Sad Vegetables © Viktoria Slowikowska is licensed under a Public Domain license

