2.5 Divergent Boundaries
Divergent boundaries are places where two or more plates move away from each other. These boundaries can be found on continental or oceanic lithosphere. Tensional stress operates between the tectonic plates at a divergent boundary, which causes the lithosphere at these locations to stretch and pull apart. Divergent boundaries slowly grow ocean basins along continental lithosphere.
The process of divergence is responsible for breaking up continental landmasses and supercontinents. This boundary type is the reason why the generations of scientists noticed the apparent fit between the coastlines of South America and Africa. Indeed, it is the reason that the world map appears the way it does today!
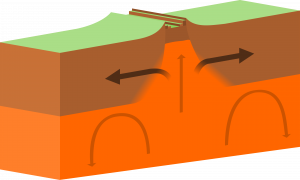
Continental Rift Valleys
How does a continent, or even a supercontinent, break apart? At first glance, such a task seems difficult considering continental lithosphere can be up to 20 times thicker than oceanic lithosphere due to billions of years of mountain-building. However, the insulation from that thick lithosphere will eventually allow a hot plume of magma from the mantle to rise toward the Earth’s surface. That mantle plume will weaken the continental lithosphere, and eventually the convection cells within the mantle will be able to push the continent apart.

A continental rift valley is a region where the continental lithosphere is weakening and stretching apart. It is an observable divergent boundary and a sign that a continent is breaking apart. Given enough time, the rifting will continue to a point in which the continental lithosphere will become so thin, it will become predominantly enriched in the mantle plume materials. At that point, the rift will have created brand new oceanic crust, and a newborn ocean basin will open between the continental fragments.
This process of continental rifting has taken place about 250 million years ago between South America and Africa, as well as North America and Eurasia during the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea. From a single landmass, the Earth saw many new continents form as well as a narrow sea that would one day widen to become our Atlantic Ocean.
PLATE TECTONICS IN ACTION: CONTINENTAL RIFT VALLEYS
Some of the world’s continents are breaking apart as we speak! Here are some examples of regions undergoing continental rifting:
- The East African Rift Valley (Djibouti, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania)
- The Red Sea (Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, Saudi Arabia, Yemen)
- Lake Baikal (Russia)
Mid-Ocean Ridges
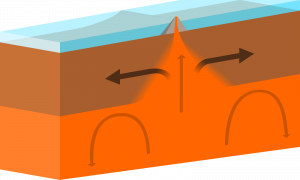
We have previously discussed the discovery of Mid-Ocean Ridges as a key piece of evidence for the theory of plate tectonics. The reason these spreading centers along the ocean floor are essential for plate tectonics is that they represent a clear example divergent boundary.
Mid-Ocean Ridges typically follow the long process of continental rifting. Once continental lithosphere has thinned and become mafic, upwelling magma begins to produce new oceanic lithosphere and a narrow ocean basin forms between the rifted continents (review video in previous section). As this process evolves, a Mid-Ocean Ridge forms above the rift on the floor of the new ocean because the cooling lava is hot and less dense (i.e., it takes up more space than cold material).
The places where we find Mid-Ocean Ridges are called spreading centers. These are sometimes characterized as “conveyer-belts” because they are the one site on the planet where new oceanic lithosphere is constantly created. These spreading centers are volcanoes; molten magma from the asthenosphere erupts underwater as lava and rapidly cools as new oceanic lithosphere. The material near the spreading centers is relatively hot and less dense, and therefore it has a higher elevation. Mid-Ocean Ridges often form long, high-elevation mountain chains because of their underwater volcanism.
Some Like It Boiling: Life at Hydrothermal Vents
Mid-ocean ridges also are home to some of the unique ecosystems discovered, found around hydrothermal vents that circulate ocean water through the shallow oceanic crust, and send it back out to rich chemical compounds and heat. While it was known for some time that hot fluids could be found on the ocean floor, it was only in 1977 when a team of scientists using the Diving Support Vehicle Alvin discovered a thriving community of organisms, including tubeworms bigger than people!
This group of organisms is dependent on the sun and photosynthesis but instead relies on chemical reactions with sulfur compounds and heat from within the Earth, a process known as chemosynthesis. Before this discovery, the thought in biology was that the sun was the ultimate source of energy in ecosystems; now, we know this to be false. Not only that, but some have also suggested it is from this that life could have started on Earth, and it now has become a target for extraterrestrial life (e.g., Jupiter’s moon Europa).
Continued volcanism will cause the new oceanic lithosphere to move away from the Mid-Ocean Ridges, and that lithosphere will cool and sink deeper along the ocean floor. Because new oceanic lithosphere is always produced at a spreading center, the age of the seafloor is predictably younger near a Mid-Ocean Ridge and older as it moves farther away.
Divergent plate motion at a Mid-Ocean Ridge occurs at different rates, depending on the location. Spreading can be as fast as 20 cm/year or as slow as 1 cm/year. At these rates over hundreds of millions of years, it is not a surprise that the continents have moved so far apart.
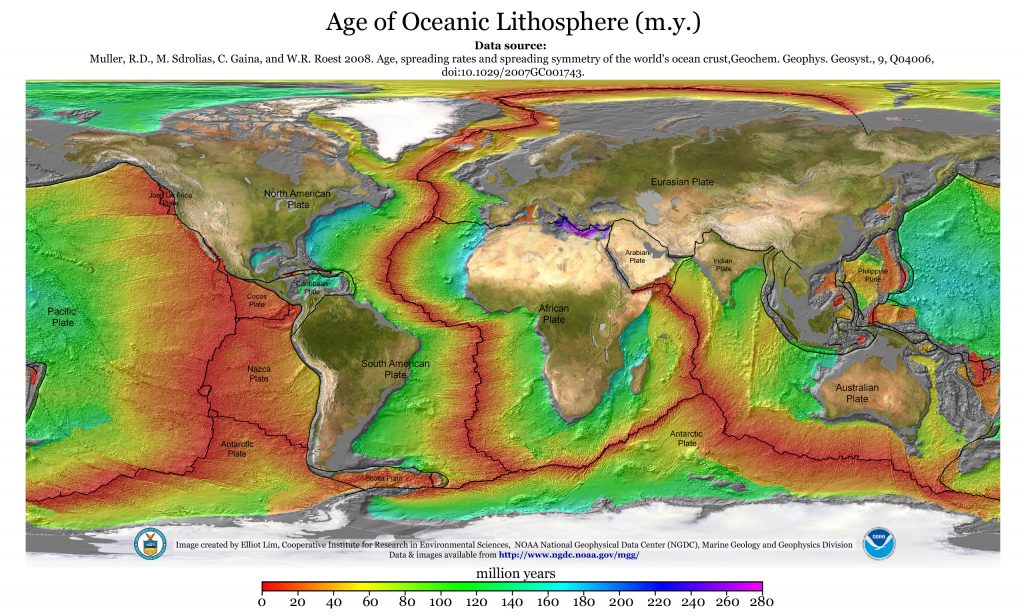
PLATE TECTONICS IN ACTION: MID-OCEAN RIDGES
Although they are sometimes deep underwater, we have known about mid-ocean ridges for decades! Here are some good examples of this type of divergent boundary:
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge
- The East Pacific Rise
- The Gakkel Ridge/ Mid-Arctic Ridge
***See 2.10 for Text and Media Attributions
A region along Earth's lithosphere where at least two tectonic plates move apart from one another.
The outer, relatively rigid layer of the Earth that responds to the emplacement of a load by flexural bending.
A type of force placed on an area of rock that pulls or moves it apart.
a massive landmass composed of multiple continents formed by the collision of tectonic plates with smaller continents.
molten rock that can be found beneath the Earth's surface.
A hot interior layer of solid rock between the crust and core that is capable of plastic flow. The mantle is the largest layer of Earth.
movement driven by density and heat in which low-density hot materials move upward and dense, cold materials sink downward.
an area on a continent where there is an active divergent boundary stretching and tearing the landmass apart.
A type of rigid, thin crust made of iron and magnesium rich minerals that is found beneath the planet's oceans.
also known as Pangea. A large, single landmass, or supercontinent, that existed on Earth from about 300 - 180 million years ago.
(sometimes abbreviated as "MORs" by scientists) an underwater mountain ridge in the middle of the ocean that is formed by seafloor spreading centers at divergent boundaries.
Originating from an iron and magnesium-rich magma/lava composition.
A region on the ocean floor where magma from an active divergent boundary is creating new oceanic lithosphere, thus pushing or spreading the older lithosphere outwards.
The process of using chemicals to form nutrients and organic molecules by microbes in the absence of sunlight.

