Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks
As previously discussed in section 3.9, a rock is a collection of consolidated minerals. Rocks are grouped into three main categories based on how they form:
- Igneous: formed from the cooling and crystallization of molten rock.
- Sedimentary: formed when weathered fragments of other rocks are buried, compressed, and cemented together, or when minerals precipitate directly from solution
- Metamorphic: formed by alteration (due to heat, pressure, and/or chemical action) of a pre-existing igneous or sedimentary rock
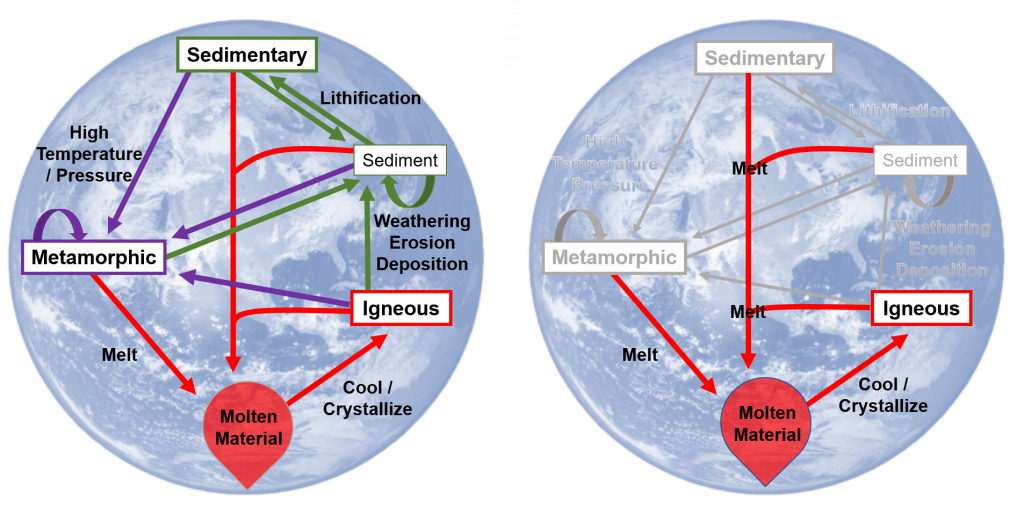
While we could start the rock cycle at any given point, it makes sense to focus on started with molten rocks. Initially, during early formation of Earth, these were the first rock types to form. In figure 4.0.1, the entire rock cycle is shown, as well as highlighting just the igneous rock portion of the cycle.
Learning Objectives
After carefully reading this chapter, completing the exercises within it, and answering the questions at the end, you should be able to:
- Describe the rock cycle and the types of processes that lead to the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, and explain why there is an active rock cycle on Earth.
- Explain the concept of partial melting and describe the geological processes that lead to melting.
- Describe, in general terms, the range of chemical compositions of magmas.
- Discuss the processes that take place during the cooling and crystallization of magma, and the typical order of crystallization according to the Bowen reaction series.
- Explain how magma composition can be changed by fractional crystallization and partial melting of the surrounding rocks.
- Apply the criteria for igneous rock classification based on mineral proportions.
- Describe the origins of phaneritic, porphyritic, and pegmatitic rock textures.
- Identify plutons on the basis of their morphology and their relationships to the surrounding rocks.
a substance that contains at least one mineral or mineraloid.

