STREAK PLATE
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Aseptically transfer bacteria from one form of culture medium to another.
Perform streak plates resulting in isolated, individual colonies.
Describe bacterial colony morphology using the proper terminology.
MCCCD OFFICIAL COURSE COMPETENCIES
Utilize aseptic technique for safe handling of microorganisms.
Apply various laboratory techniques to identify types of microorganisms.
Identify structural characteristics of the major groups of microorganisms.
Compare and contrast prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell.
Compare and contrast the physiology and biochemistry of the various groups of microorganisms.
INCUBATION TIMES
Part One Subculturing Serratia marcesens AND Activating Escherichia coli 3 days
Part Two Streak plates and Escherichia coli stocks 3 days
PHOTO REQUIREMENTS
Take a photo with your photo ID during the lab exercises when you see this icon.

Paste these photos into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
INTRODUCTION
When microbiologists study microorganisms, they often work with pure cultures. A pure culture contains a single species of microorganism. When samples are taken from the environment or from a patient, they usually contain a variety of microorganisms. Mixed cultures contain more than one species of microorganism.
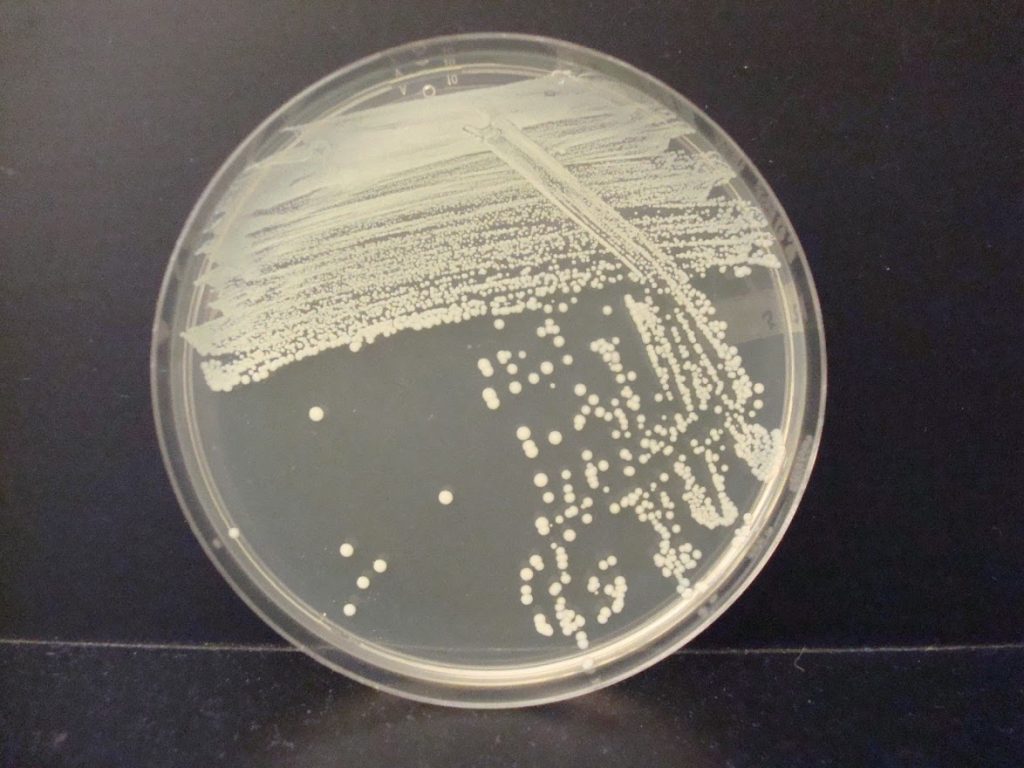
The streak plate is a common technique used to produce pure cultures from a mixed sample. The goal of the streak plate is to spread individual microorganisms so far apart on the surface of solid medium that they do not touch one another. When each microorganism divides, it gives rise to genetically identical progeny. With each generation of cell division, the number of progeny of each cell grows until discrete mounds of cells are visible to the naked eye. A colony is a visible mass of microorganisms all originating from a single cell. At least a million bacteria must be present in a colony for the unaided human eye to see the colony! Since all the cells in a colony are identical to each other, a colony is a pure culture.
Colonies have different characteristics or morphologies such as elevation, margin, size, pigment, etc. It is important to observe a well-isolated colony when studying the morphology of a colony. Crowded colonies rapidly deplete the nutrients available in the media and thus do not grow as large or exhibit the typical morphological characteristics of those unencumbered by dense growth.
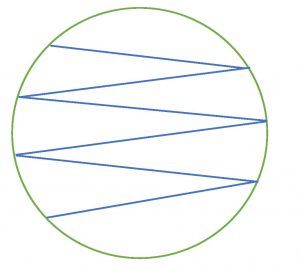
In a streak plate, an agar plate is divided into three sections. An inoculum from a pure culture is inoculated with a sterile swab in a zigzag pattern onto the first (and largest section) section of the agar plate. Then a sterile inoculating loop is used to pull a small amount of the inoculum from the first section into the second section of the streak plate. Then a fresh, sterile, inoculating loop is used to pull a small amount of inoculum from the second section into the third section of the streak plate. The plate is then incubated. When growth appears, the first section of the streak plate often has thick, continuous growth with no colonies. The second and/or third sections of the streak plate will have less growth and isolated, individual colonies.
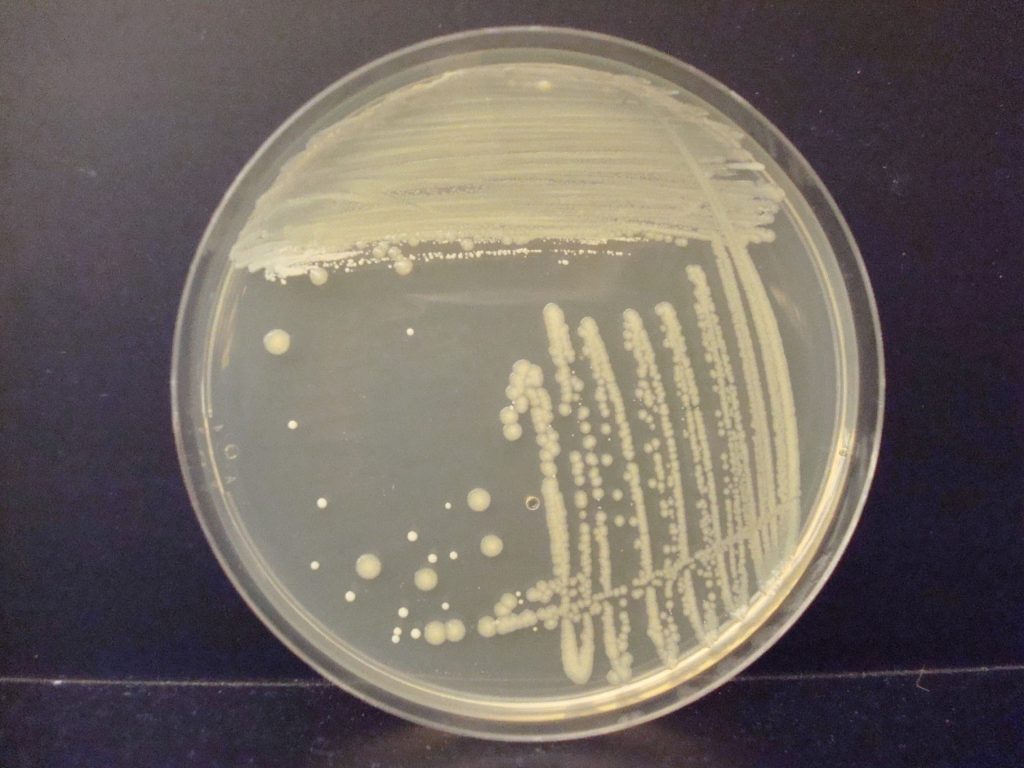
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a normal inhabitant of the colon of warm-blooded animals and is a Gram negative bacilli. Although E. coli is normally non-pathogenic, some strains cause urinary tract infections, food poisoning, and diarrheal infections.
In this lab exercise, you will perform a streak plate of two pure cultures resulting in isolated, individual colonies.
SAFETY
This investigation requires safety goggles, gloves, a lab apron, and proper attire. Read all the instructions for this laboratory exercise before beginning. Follow the instructions closely and observe established laboratory safety practices as outlined in the Safety exercise. Email your instructor with any questions.
 Isopropyl alcohol is flammable. Keep containers of isopropyl alcohol away from any heat or flame sources.
Isopropyl alcohol is flammable. Keep containers of isopropyl alcohol away from any heat or flame sources.
 Chlorine bleach is a corrosive material. Use these materials near a source of running water that can be used as a safety eye wash or safety shower if any corrosive material comes in contact with skin or eyes. Do not use bleach in an area without proper ventilation.
Chlorine bleach is a corrosive material. Use these materials near a source of running water that can be used as a safety eye wash or safety shower if any corrosive material comes in contact with skin or eyes. Do not use bleach in an area without proper ventilation.
part one-activating escherichia coli and subculturing serratia marcescens (DO NOT just activate escherichia coli you must also subculture serratia marcescens)
| PROPER ATTIRE AND REQUIRED PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT (PPE) |
|---|
| Laboratory safety apron (from the lab kit). Wear a long-sleeve shirt under the lab apron.
|
| Safety goggles (from the lab kit)
|
| Disposable gloves (from the lab kit)
|
| Closed-toe shoes that are solid, not made of cloth, not perforated (no ballet flats). To reduce exposure of your body, wear long pants, no skin can be showing, so you may have to wear socks with your shoes. A skirt can be worn but it must fit close to the body and again no skin can be showing. Long hair should be fastened and dangling jewelry or loose hanging garments or sleeves should not be worn. They may contaminate microbial cultures. Avoid loose or dangling clothing or jewelry that could catch on objects or interfere with the lab exercise. |
| REQUIRED SUPPLIES FROM THE LAB KIT |
|---|
| Grease pencil
|
| Tube rack
|
| Lyophilized Escherichia coli culture (stored in the refrigerator)
|
| Tryptic soy broth (2) Do not remove the caps! (stored in the refrigerator)
Allow media that have been stored in the refrigerator to sit at room temperature in the tube rack for 60 minutes prior to use
|
| Sterile transfer pipette (2) Do not open the package!
|
| Sterile Inoculating Loop (1) Do not remove the loop from its package!
|
| REQUIRED SUPPLIES YOU PROVIDE |
|---|
| Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens) stock plate or slant stored in the refrigerator |
| Bleach |
| Isopropyl alcohol |
| Paper towels |
| Small disposable plastic container (plastic cup or empty water bottle) filled half way with isopropyl alcohol for disinfect inoculating tools (for lab use only)
|
| Large disposable plastic container filled half way with 10% bleach solution for disinfecting cultures (for lab use only)
|
| Resealable plastic bag (sandwich or quart size) |
| Timer or stopwatch, or resealable plastic bag to protect your cell phone if using it as a timer |
| Cell phone or digital camera to take digital photos |
| Fine tip permanent marker to be used instead of grease pencil (optional) |
ACTIVATING ESCHERICHIA COLI procedure (You will also subculture Serratia marcescens)
PLEASE NOTE THE CONTENTS OF THE LAB KIT HAVE CHANGED. IN THE DEMONSTRATION VIDEO BELOW NUTRIENT BROTH IS USED. YOU WILL USE TRYPTIC SOY BROTH INSTEAD OF NUTRIENT BROTH.
Read all instructions carefully before you start the experiment. Wear proper attire when performing laboratory experiments. Allow media that have been stored in the refrigerator to sit at room temperature for 60 minutes prior to use. Read each step carefully and watch any accompanying video. Think about what you are going to do before you do it. Once you begin, move with purpose and focus.
Step 1. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Dry your hands with paper towel. Put on your PPE (gloves, safety goggles, apron).
Step 2. Prepare your surface disinfectant. Add 180 ml of tap water to the 250 ml beaker. Now add 20 ml of bleach to the 250 ml beaker. Your surface disinfectant (10% bleach solution) is now ready to use.
Step 3. Disinfect the work surface, tube rack, and grease pencil or permanent marker with surface disinfectant by applying 10% bleach solution with a paper towel, allowing it to remain damp for 2 minutes, and then wiping away any remaining disinfectant with a dry paper towel. Throw the used paper towels in the trash.
Step 4. Prepare for inoculating tool disinfection by filling a small, disposable, plastic container (8 ounce or larger plastic cup or empty water bottle) half full with isopropyl alcohol. Prepare for culture disinfection by filling a large, disposable, plastic container two thirds of the way with surface disinfectant (10% bleach solution).
Disinfection and Disposal Video
Step 5. In this lab exercise, we will be using an E. coli culture that has been lyophilized (freeze-dried) to prolong its shelf life. You will rehydrate the lyophilized culture with medium with nutrient broth, and then incubate the rehydrated culture to allow the bacteria to increase in number via binary fission. Retrieve two tryptic soy broth tubes from the refrigerator. Place the tubes in the disinfected tube rack on the disinfected work surface. Allow the tubes to sit 60 minutes at room temperature prior to use.
Step 6. Using the grease pencil or permanent marker, label one of the tryptic soy broths with the name of the organism (E. coli) and the date.
Step 7. Carefully remove the metal band from the E. coli culture vial by lifting the metal circle in the center and then pulling to one side. There is an arrow on the top of the metal band, lift there. The metal band may be discarded in the trash.
Step 8. Remove the sterile pipette from its wrapping by the bulb end. DO NOT set the pipette down; instead, hold it in your dominant hand.
Handling Sterile Inoculation Tools Video
Step 9. Using the pinky finger of your dominant hand (or your pinky and ring fingers), remove the cap from the tryptic soy broth. DO NOT set the cap down. Hold it with your pinky while the tube is open.
Holding the Culture Tube Cap Video
Step 10. Holding the tube at an angle, insert the pipette tip to obtain 1 ml of tryptic soy broth (there are markings on the stem of the pipette to measure 1ml). Replace the cap. Set the nutrient broth tube in the tube rack.
Step 11. Using your non-dominant hand, remove the rubber stopper from the lyophilized E. coli culture vial.
Step 12. Dispense 1 ml of tryptic soy broth into the lyophilized E. coli. Use the transfer pipette to stir the contents of the vial, breaking up the lyophilized pellet. Replace the rubber stopper and wait for 1 minute. Place the used transfer pipette in the inoculating tools disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 13. Remove the cap from the tryptic soy broth, do not set the cap down.
Step 14. Use a new sterile transfer pipette to transfer the rehydrated E. coli from the vial to the tube of tryptic soy broth and replace the cap. Set the tube in the tube rack. Screw the cap to the point of finger tightness, then backwards about one quarter of a turn. Set the newly inoculated tryptic soy broth tube in the tube rack for incubation. This will become your Escherichia coli tryptic soy broth culture after it is incubated.
Step 15. Place the used transfer pipette in the inoculating tools disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 16. Place the E. coli vial and rubber cap into the culture disposal container. Allow them to soak at least 24 hours before placing them in a sealed plastic bag and disposing of them in the trash. Pour the 10% bleach down a drain and flush with excess water for at least 30 seconds to dilute the bleach.
Step 17.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the rehydrated E. coli culture in tryptic soy broth. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the rehydrated E. coli culture in tryptic soy broth. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Step 18. Incubate the tube for 3 days in a consistently warm location (not to exceed 37 °C or 100 °F) out of direct sunlight.
Step 19. DO NOT STOP! You also need to subculture Serratia Marcescens now!
subculturing serratia marcescens procedure
PLEASE NOTE THE CONTENTS OF THE LAB KIT HAVE CHANGED. IN THE DEMONSTRATION VIDEO BELOW NUTRIENT BROTH AND PLATES ARE USED. YOU WILL USE TRYPTIC SOY BROTH AND PLATES INSTEAD OF NUTRIENT BROTH AND PLATES.
Step 1. You need to subculture (add a sample from one of your stock cultures to fresh media) one of your Serratia marcescens (S. marcescens) stock cultures stored in the refrigerator. You will use either your S. marcescens stock plate or stock slant to obtain a sample for subculturing.
Step 2. Using the grease pencil or permanent marker, label the other tryptic soy broth you took out of the refrigerator with the name of the organism S. marcescens and the date.
Step 3.
If you obtaining an inoculum (sample) from your S. marcescens tryptic soy stock slant stock culture:
Remove the cap from your S. marcescens tryptic soy slant stock. Remember do not set the cap down. Hold it in the pinky of your dominant hand while holding the tube in your non-dominant hand.
Holding the tube at an angle, insert the inoculating loop to obtain an inoculum (a sample) about the size of a pinhead of your S. marcescens tryptic soy slant stock, then withdraw the loop. Do not set the loop down. Replace the cap of your S. marcescens tryptic soy slant stock and set it aside in the tube rack.
If you are obtaining an inoculum (sample) from your S. marcescens tryptic soy stock plate:
Lift the lid of the nutrient agar plate slightly. Do not remove the lid completely, and do not set the lid down. Use the lid as a shield to protect the agar from contamination by airborne microorganisms.
Insert the inoculating loop to obtain an inoculum (sample) about the size of a pinhead of your S. marcesens tryptic soy agar stock plate. Withdraw the loop, do not set the loop down. Replace the lid. Set the plate aside.
Step 4. Remove the cap from the sterile tryptic soy broth tube. Do not set the cap down.
Step 5. While holding the tube at an angle, insert the inoculating loop and stir gently. Remove the loop.
Step 6. Place the used inoculating loop in the inoculating tools disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 7. Screw the cap of the newly inoculated tryptic soy broth to the point of finger tightness, then backwards about one quarter of a turn. Set the tube in the tube rack for incubation. Incubate the tube for 3 days in a consistently warm location (not to exceed 37 °C or 100 °F) out of direct sunlight.
Step 8.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the rehydrated S. marcesens subculture in tryptic soy broth. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the rehydrated S. marcesens subculture in tryptic soy broth. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Step 9.
If you subcultured from your S. marcescens tryptic soy stock slant:
Screw the cap of your S. marcescens tryptic soy slant stock to the point of finger tightness, then backwards about one quarter of a turn. Store your S. marcescens tryptic soy slant stock in the 250 ml beaker or a cup in the refrigerator.
If you subcultured from your S. marcescens tryptic soy agar stock plate:
Store your S. marcescens stock plate lid side down in a sealed plastic bag and store it in the refrigerator.
Step 10. Disinfect your work area with 10% bleach solution. Wash your lab bench with soap and water to remove the bleach residue. wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Dry your hands with paper towel.
AFTER 3 DAY INCUBATION
Read all instructions carefully before you start the experiment. Wear proper attire when performing laboratory experiments.
Step 1. After the 3 day incubation, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Dry your hands with paper towels. Put on your PPE (gloves, safety goggles, apron).
Step 2. Prepare your surface disinfectant. Add 180 ml of tap water to the 250 ml beaker. Now add 20 ml of bleach to the 250 ml beaker. Your surface disinfectant (10% bleach solution) is now ready to use.
Step 3. Disinfect the work surface, tube rack, and grease pencil or permanent marker with surface disinfectant by applying 10% bleach solution with a paper towel, allowing it to remain damp for 2 minutes, and then wiping away any remaining disinfectant with a dry paper towel. Throw the used paper towels in the trash.
Step 4.  Take a photo with your photo ID of your E. coli tryptic soy broth culture. The growth must be clearly visible in the photos. Do not remove the caps to take photos. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of your E. coli tryptic soy broth culture. The growth must be clearly visible in the photos. Do not remove the caps to take photos. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Step 5.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the S. marcescens tryptic soy broth subculture. The growth must be clearly visible in the photos. Do not remove the caps to take photos. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the S. marcescens tryptic soy broth subculture. The growth must be clearly visible in the photos. Do not remove the caps to take photos. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
6. DO NOT dispose of your E. coli culture or S. marcescens tryptic soy broth subculture! You will use them to for PART TWO of this lab exercise.
Step 6. Begin PART TWO Now!
part two-streak plates and escherichia coli stocks
| REQUIRED SUPPLIES FROM THE LAB KIT |
|---|
| Sterile swab (4) Do not remove the swabs from the package!
|
| Loops (4) Do not remove the loops from the package!
|
| Transfer pipettes (2) Do not open the package!
|
| Tryptic soy agar plate (3) (stored in the refrigerator) Do not remove the lid!
PLEASE USE A TRYPTIC AGAR PLATE. DO NOT USE ONE OF THE OTHER AGAR PLATES! Allow media that have been stored in the refrigerator to sit at room temperature for 60 minutes prior to use Opening and Closing a Sleeve of Plates Video
|
| Tryptic soy slant (1) (stored in the refrigerator) Do not remove the cap!
DO NOT USE A TRIPLE SUGAR IRON AGAR SLANT. PLEASE MAKE SURE YOU ARE USING TRYPTIC SOY AGAR SLANT!! Allow media that have been stored in the refrigerator to sit at room temperature in the tube rack for 60 minutes prior to use
|
| Tube rack
|
| Grease pencil
|
| REQUIRED SUPPLIES YOU PROVIDE |
|---|
| Escherichia coli and Serratia marcescens tryptic soy broth cultures from PART ONE of this lab exercise |
| Bleach |
| Isopropyl alcohol |
| Paper towels |
| Small disposable plastic container (plastic cup or empty water bottle) filled half way with isopropyl alcohol for disinfect inoculating tools (for lab use only)
|
| Large disposable plastic container filled half way with 10% bleach solution for disinfecting cultures (for lab use only)
Prepare after 3 day incubation
|
| Resealable plastic bag (sandwich or quart size) |
| Timer or stopwatch, or resealable plastic bag to protect your cell phone if using it as a timer |
| Cell phone or digital camera to take digital photos |
| Fine tip permanent marker to be used instead of grease pencil (optional) |
Serratia marcescens streak plate procedure
Read all instructions carefully before you start the experiment. Wear proper attire when performing laboratory experiments. Allow media that have been stored in the refrigerator to sit at room temperature for 60 minutes prior to use. Read each step carefully and watch any accompanying video. Think about what you are going to do before you do it. Once you begin, move with purpose and focus.
Streak Plate Tips
- Hold the inoculating loop like a pencil instead of a hammer. The motion of moving the inoculating loop comes from the action of your fingers and wrist, rather than from the elbow.
- Rest your inoculating loop flat at a 45-degree angle, rather than perpendicular to the agar. This helps avoid digging into the agar which inhibits good isolation.
- Reflect light on the surface of the agar to see where you have already streaked the agar. As you finish streaking each section, this will enable you to better position your subsequent streaking.
- Keep the lid on the Petri plate when you are not actually streaking the agar surface. This minimizes the chance of contamination.
Step 1. Prepare for inoculating tool disinfection by filling a small, disposable, plastic container (8 ounce or larger plastic cup or empty water bottle) half way with isopropyl alcohol. Prepare for culture disinfection by filling a large, disposable, plastic container two thirds of the way with surface disinfectant (10% bleach solution). Prepare for culture disinfection by filling a large, disposable, plastic container half way with 10% bleach solution.
Disinfection and Disposal Video
Step 2. Using the grease pencil or permanent marker, label the outside of the bottom half (the half that contains the media) of one of the tryptic soy agar plates with S. marcescens and the date.
Step 3. Use the grease pencil or permanent marker. Divide the plate into 3 sections by drawing a “T” on the bottom (not the lid) of the plate where the media is.
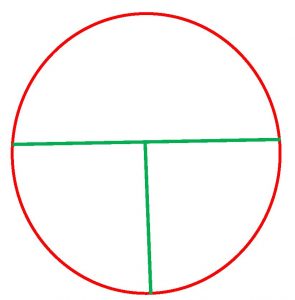
Step 4. Completely close the cap of the S. marcescens tryptic soy broth culture and resuspend by tapping or rolling gently between your palms.
PLEASE NOTE THE CONTENTS OF THE LAB KIT HAVE CHANGED. IN THE DEMONSTRATION VIDEO BELOW NUTRIENT AGAR IS USED. YOU WILL USE TRYPTIC SOY AGAR INSTEAD OF NUTRIENT AGAR.
Step 5. Using the pinky finger of your dominant hand (or your pinky and ring fingers), remove the cap from your S. marcescens tryptic soy broth. DO NOT set the cap down. Hold it with your pinky while the tube is open.
Holding the Culture Tube Cap Video
Step 6. Remove one sterile swab from its packaging. Peel the paper cover from the wooden end of the swab. Handle ONLY the wooden end of the swab to maintain the sterility of the cotton end. Insert a sterile swab into the S. marcescens tryptic soy broth. Recap the S. marcescens tryptic soy broth and place it in the tube rack.
Handling the Sterile Inoculation Tools Video
Step 7. Lift one side of the lid of the Petri plate up just enough to fit the swab in, swab the inoculum in a zigzag pattern onto the largest section of the agar. Replace the lid.

Step 8. Place the used swab in the inoculating tools disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 9. You will use loops for the rest of the streak plate procedure.
Step 10. Lift one side of the lid of the Petri plate up just enough the fit the loop in. Place the loop in the center of the first section and gently drag the loop one time into the second section. Lightly drag the tip of the loop from side to side in a back-and-forth motion to spread the inoculum to fill the second section. Take care not to gouge the agar. Replace the lid.
Step 11. Place the used inoculating loop in the disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 12. Lift one side of the lid of the Petri plate up just enough the fit the loop in. Place the loop in the center of the second section and gently drag the loop one time into the third section. Lightly drag the tip of the loop from side to side in a back-and-forth motion to spread the inoculum to fill the third section. Take care not to gouge the agar. Replace the lid.
Step 13. Place the used inoculating loop in the disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 14.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the S. marcescens streak plate. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the S. marcescens streak plate. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Step 15. Invert the plate (turn it lid side down) for incubation. This will prevent condensation from disrupting microbial growth. Incubate the plate for 3 days in a consistently warm location (not to exceed 37 °C or 100 °F) out of direct sunlight.
Step 16. Immerse the S. marcescens tryptic soy broth culture into the culture disinfection container and remove the cap. Allow the culture to soak in the bleach for at least 24 hours. After the culture has soaked for at least 24 hours while wearing your PPE, pour the 10% bleach down the drain with the faucet running. Let the faucet continue to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the bleach. Place the disinfected tube in a sealed plastic bag, and discard in the trash. Be sure to wash your hands after removing your gloves.
Escherichia coli streak plate procedure
Step 1. Using the grease pencil or permanent marker, label the outside of the bottom half (the half that contains the media) of one of the tryptic soy agar plates with E. coli and the date.
Step 2. Use the grease pencil or permanent marker. Divide the plate into 3 sections by drawing a “T” on the bottom (not the lid) of the plate where the media is.

Step 3. Completely close the cap of the E. coli nutrient broth culture and resuspend by tapping or rolling gently between your palms.
PLEASE NOTE THE CONTENTS OF THE LAB KIT HAVE CHANGED. IN THE DEMONSTRATION VIDEO BELOW NUTRIENT AGAR IS USED. YOU WILL USE TRYPTIC SOY AGAR INSTEAD OF NUTRIENT AGAR.
Step 4. Using the pinky finger of your dominant hand (or your pinky and ring fingers), remove the cap from your E. coli tryptic soy broth. DO NOT set the cap down. Hold it with your pinky while the tube is open.
Holding the Culture Tube Cap Video
Step 5. Remove one sterile swab from its packaging. Peel the paper cover from the wooden end of the swab. Handle ONLY the wooden end of the swab to maintain the sterility of the cotton end. Insert a sterile swab into the E. coli tryptic soy broth. Recap the E. coli tryptic soy broth and place it in the tube rack.
Handling Sterile Inoculation Tools Video
Step 6. Lift one side of the lid of the Petri plate up just enough to fit the swab in, swab the inoculum in a zigzag pattern onto the largest section of the agar. Replace the lid.


Step 7. Place the used swab in the inoculating tools disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 8. You will use loops to complete the rest of the streak plate procedure.
Step 9. Lift one side of the lid of the Petri plate up just enough the fit the loop in. Place the loop in the center of the first section and gently drag the loop one time into the second section. Lightly drag the tip of the loop from side to side in a back-and-forth motion to spread the inoculum to fill the second section. Take care not to gouge the agar. Replace the lid.
Step 10. Place the used inoculating loop in the disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 11. Lift one side of the lid of the Petri plate up just enough the fit the loop in. Place the loop in the center of the second section and gently drag the loop one time into the third section. Lightly drag the tip of the loop from side to side in a back-and-forth motion to spread the inoculum to fill the third section. Take care not to gouge the agar. Replace the lid.
Step 12. Place the used inoculating loop in the disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 13.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the E. coli streak plate. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the E. coli streak plate. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Step 14. Invert the plate (turn it lid side down) for incubation. This will prevent condensation from disrupting microbial growth. Incubate the plate for 3 days in a consistently warm location (not to exceed 37 °C or 100 °F) out of direct sunlight.
KEEP GOING!!! MAKING STOCKS IS PART OF PART TWO OF THE LAB EXERCISE
ESCHERICHIA COLI STOCK slant PROCEDURE
PLEASE NOTE THE CONTENTS OF THE LAB KIT HAVE CHANGED. IN THE DEMONSTRATION VIDEO BELOW NUTRIENT AGAR IS USED. YOU WILL USE TRYPTIC SOY AGAR INSTEAD OF NUTRIENT AGAR.
Step 1. Using the grease pencil or permanent marker, label the tryptic soy slant with the name of the organism (E. coli), stock, and the date.
Step 2. Peel the paper cover from the wooden end of the swab. Peel the paper cover from the wooden end of the swab. Handle ONLY the wooden end of the swab to maintain the sterility of the cotton end. Remove one sterile swab from its packaging. Do not set the swab down. Hold it in your dominant hand.
Handling Sterile Inoculation Tools Video
Step 3. Remove the cap from your E. coli tryptic soy broth culture. Remember, do not set the cap down. Hold it in the pinky of your dominant hand while holding the tube in your non-dominant hand.
Holding the Culture Tube Cap Video
Step 4. Holding the tub at an angle, insert the sterile swab to obtain an inoculum of your Escherichia coli tryptic soy broth culture. Withdraw the swab, do not set the swab down. Replace the cap. Set your E. coli tryptic soy broth culture aside in the tube rack.
Step 5. Remove the cap from the tryptic soy slant. Do not set the cap down.
Step 6. Hold the swab like a pencil instead of a hammer. The motion of moving the swab comes from the action of your fingers and wrist, rather than from the elbow. While holding the tube at an angle, insert the swab and touch it to the bottom of the slant. Do not gouge the swab into the agar. Draw the swab back out of the tube, dragging it from side to side across the entire surface of the agar. This is known as “fishtail” inoculation because the way the swab is moved side to side is reminiscent of the tail movements of s swimming fish. Remove the swab.
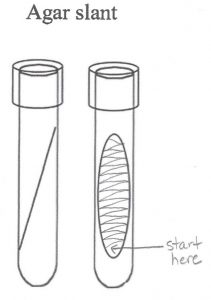
Step 7. Screw the cap to the point of finger tightness, then backwards about one quarter of a turn. Set the newly inoculated tryptic soy slant in the tube rack for incubation.
Step 8. Place the used swab in the disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 9.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the inoculated E. coli tryptic soy slant. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the inoculated E. coli tryptic soy slant. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
ESCHERICHIA COLI Stock Plate procedure
Step 1. Using the grease pencil or permanent marker, label the outside of the bottom half (the half that contains the media) of the tryptic soy agar plate with the name of the organism (E. coli), stock, and the date.
Step 2. Peel the paper cover from the wooden end of the swab. Peel the paper cover from the wooden end of the swab. Handle ONLY the wooden end of the swab to maintain the sterility of the cotton end. Remove one sterile swab from its packaging. Do not set the swab down. Hold it in your dominant hand.
Step 3. Remove the cap from your E. coli tryptic soy broth culture. Remember, do not set the cap down. Hold it in the pinky of your dominant hand while holding the tube in your non-dominant hand.
Step 4. Holding the tub at an angle, insert the sterile swab to obtain an inoculum (sample) of your E. coli culture. Withdraw the swab, do not set the swab down. Set your E. coli tryptic soy broth culture aside in the tube rack.
Step 5. Lift the lid of the nutrient agar plate slightly. Do not remove the lid completely, and do not set the lid down. Use the lid as a shield to protect the agar from contamination by airborne microorganisms.

Step 6. Touch the swab gently to the surface of the agar. Drag the swab over the surface of the agar in a zigzag pattern. Take care not to gouge the agar. Close the lid immediately after you inoculate the plate. Invert the plate (turn it lid side down) for incubation. This will prevent condensation from disrupting microbial growth.
Step 7. Place the used swab in the disposal cup/bottle and let it soak for at least 30 minutes before discarding it in the trash. Used alcohol can be poured down the drain. Allow the water to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the alcohol.
Step 8.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the inoculated E. coli nutrient agar plate. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the inoculated E. coli nutrient agar plate. This photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Step 9. Incubate the E. coli stock slant and E. coli stock plate for 3 days in a consistently warm location (not to exceed 37 °C or 100 °F) out of direct sunlight.
Step 10. Screw the cap of your E. coli tryptic soy broth culture to the point of finger tightness, then backwards about one quarter of a turn. Store your E. coli tryptic soy broth culture in the 250 ml beaker or a cup in the refrigerator.
Step 11. Disinfect your work area with 10% bleach solution. Wash your lab bench with soap and water to remove the bleach residue. wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Dry your hands with paper towel.
AFTER 3 DAY INCUBATION
Step 1. After the 3 day incubation, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Dry your hands with paper towels. Put on your PPE (gloves, safety goggles, apron).
Step 2. Prepare your surface disinfectant. Add 180 ml of tap water to the 250 ml beaker. Now add 20 ml of bleach to the 250 ml beaker. Your surface disinfectant (10% bleach solution) is now ready to use.
Step 3. Disinfect the work surface, tube rack, and grease pencil or permanent marker with surface disinfectant by applying 10% bleach solution with a paper towel, allowing it to remain damp for 2 minutes, and then wiping away any remaining disinfectant with a dry paper towel. Throw the used paper towels in the trash.
Step 4. Prepare for culture disinfection by filling a large, disposable, plastic container half way with 10% bleach solution.
Disinfection and Disposal Video
Step 5.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the S. marcescens streak plate. The growth must be clearly visible in the photo. Do not remove the lid of the Petri dish to take the photo. Avoid the use of the flash, which will simply be reflected off of the lid. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the S. marcescens streak plate. The growth must be clearly visible in the photo. Do not remove the lid of the Petri dish to take the photo. Avoid the use of the flash, which will simply be reflected off of the lid. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Step 6.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the E. coli streak plate. The growth must be clearly visible in the photo. Do not remove the lid of the Petri dish to take the photo. Avoid the use of the flash, which will simply be reflected off of the lid. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the E. coli streak plate. The growth must be clearly visible in the photo. Do not remove the lid of the Petri dish to take the photo. Avoid the use of the flash, which will simply be reflected off of the lid. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Step 7.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the E. coli stock slant culture. The growth must be clearly visible in the photo. Do not remove the cap from the slant to take the photo. Avoid the use of the flash, which will simply be reflected off of the lid. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the E. coli stock slant culture. The growth must be clearly visible in the photo. Do not remove the cap from the slant to take the photo. Avoid the use of the flash, which will simply be reflected off of the lid. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Step 8.  Take a photo with your photo ID of the E. coli stock plate culture. The growth must be clearly visible in the photo. Do not remove the lid of the Petri dish to take the photo. Avoid the use of the flash, which will simply be reflected off of the lid. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Take a photo with your photo ID of the E. coli stock plate culture. The growth must be clearly visible in the photo. Do not remove the lid of the Petri dish to take the photo. Avoid the use of the flash, which will simply be reflected off of the lid. You may need to experiment with lighting conditions and camera angles to get the best pictures in your work space. The photo will be pasted into the Streak Plate Questions Document.
Step 9. Describe the colony morphology of an isolated, individual S. marcescens colony on your streak plate using the terms in the Colony Characteristics figure in the Streak Plate Questions Document.
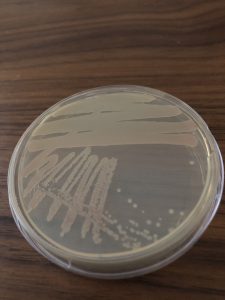
Step 10. Place your S. marcescens streak plate lid side down in a sealed plastic bag and store it in the refrigerator. We will keep this streak plate as an additional stock plate. We will take samples from the stock cultures in future lab exercises.
Step 11. Describe the colony morphology of an isolated, individual E. coli colony on your streak plate using the terms in the Colony Characteristics figure in the Streak Plate Questions Document.
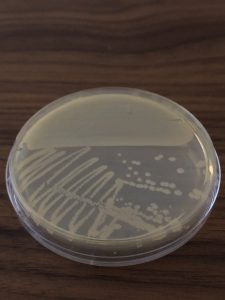
Step 12. Place your E. coli streak plate lid side down in a sealed plastic bag and store it in the refrigerator. We will keep this streak plate as an additional stock plate. We will take samples from the stock cultures in future lab exercises.
Step 13. Place your E. coli stock plate lid side down in a sealed plastic bag and store it in the refrigerator.
Step 14. Screw the cap of your E. coli tryptic soy slant stock to the point of finger tightness, then backwards about one quarter of a turn. This will leave the cap just loose enough that air (but not contaminants) can enter the tube. Store your E. coli stock slant in the 250 ml beaker or a cup in the refrigerator.

If you do not have growth on your E. coli stock slant or E. coli stock plate, please email your professor for guidance, do not dispose of the E. coli tryptic soy broth cultures at this time.
Step 15. If you have growth on the E. coli stock slant and E. coli stock plate, immerse the E. coli tryptic soy broth culture stored in the refrigerator into the culture disinfection container and remove the cap. Allow the culture to soak in the bleach for at least 24 hours. After the culture has soaked for at least 24 hours while wearing your PPE, pour the 10% bleach down the drain with the faucet running. Let the faucet continue to run for at least 30 seconds to dilute the bleach. Place the disinfected tube in a sealed plastic bag, and discard in the trash. Be sure to wash your hands after removing your gloves.
Step 16. Disinfect your work area with 10% bleach solution. Wash your lab bench with soap and water to remove the bleach residue. wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Dry your hands with paper towel.
DISCOVERIES IN MICROBIOLOGY
DR. JULIUS PETRI
German microbiologist Dr. Petri worked in Robert Koch’s lab in Germany. At the time, media was poured into an open dish and placed under a jar. The plate was exposed to the air each time the culture was viewed under a microscope or with the naked eye. In 1887 Petri had the idea of placing a slightly larger glass lid on top of the glass dish that contained the culture media. Petri’s dish was simple and reduced contamination. The design of the dish has not changed since it was invented.