6.2 Plastic Deformation
Plastic Deformation at Depth
When there is sufficiently high temperature and pressure deep in the Earth’s crust, solid rock exposed to stress can undergo folding, stretching, compression, and bending. This is called plastic deformation. In the previous section, we studied two types of stress, confining and differential. Let’s quickly review that again.
In plastic deformation, stretching and bending do not just occur on the scale of individual rocks! You can see folds in the rock layers themselves! This is something that you might have even seen driving around on road trips across America! There are two main types of folds that you learned about already in the video on the previous page: Anticlines and Synclines.
Anticlines tend to arch upward and Synclines arch downward. This isn’t all there is to them, however!
The OLDEST beds are found at the core of an anticline. The best way to remember that you are looking at an anticline is that it has an “A” shape in its arch.
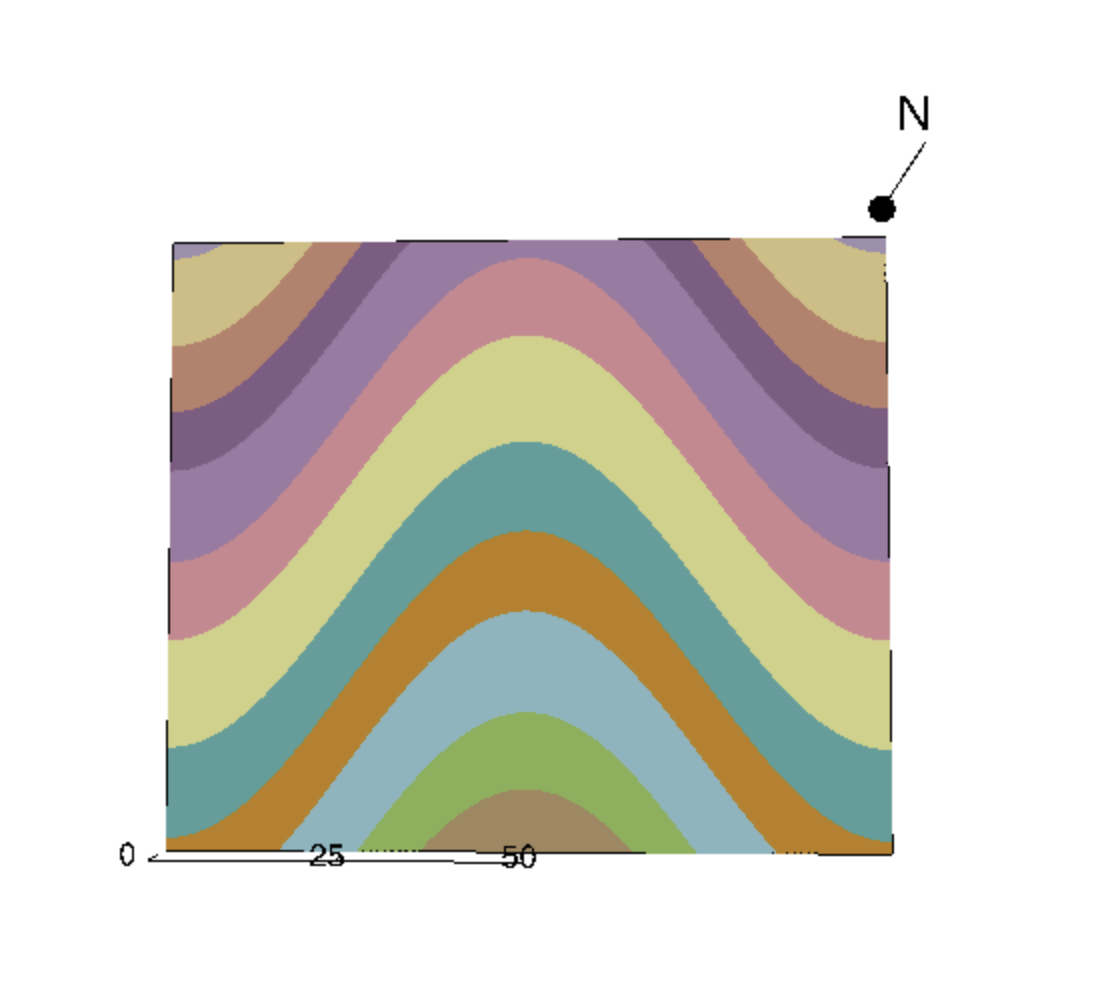
Click this link to interact with the model of an anticline! http://app.visiblegeology.com/model.html#ahFzfnZpc2libGUtZ2VvbG9neXIPCxIFTW9kZWwYu4eA4AEM
The YOUNGEST beds are found at the core of a syncline. The best way to remember that you are looking at a syncline is that it is “Smiling”, or has a U-shape (remember “S” for “Smile”)
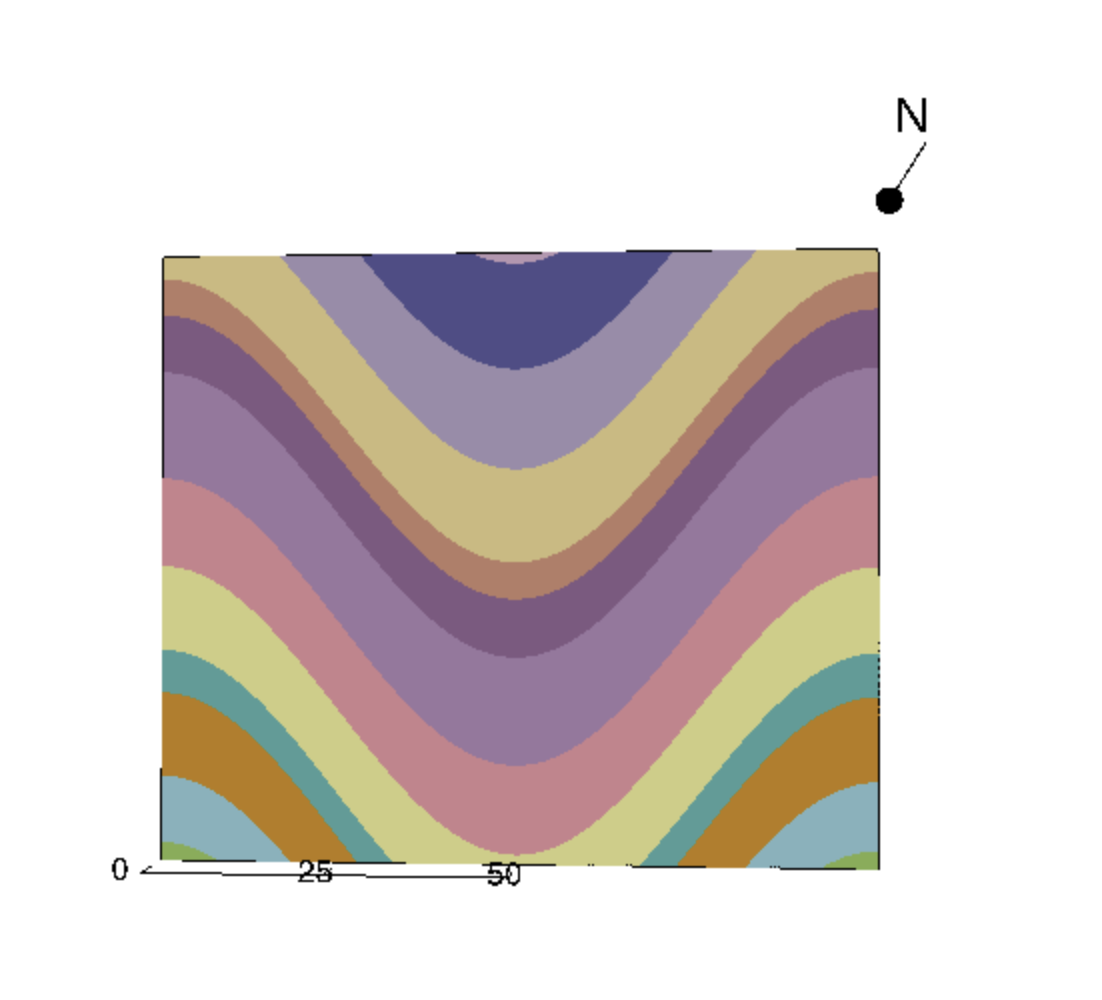
Click this link to interact with the model of a syncline! http://app.visiblegeology.com/model.html#ahFzfnZpc2libGUtZ2VvbG9neXIPCxIFTW9kZWwYi67y7wEM
A partial fold where only one side is bent in a different direction is called a monocline. These have an s-like shape.

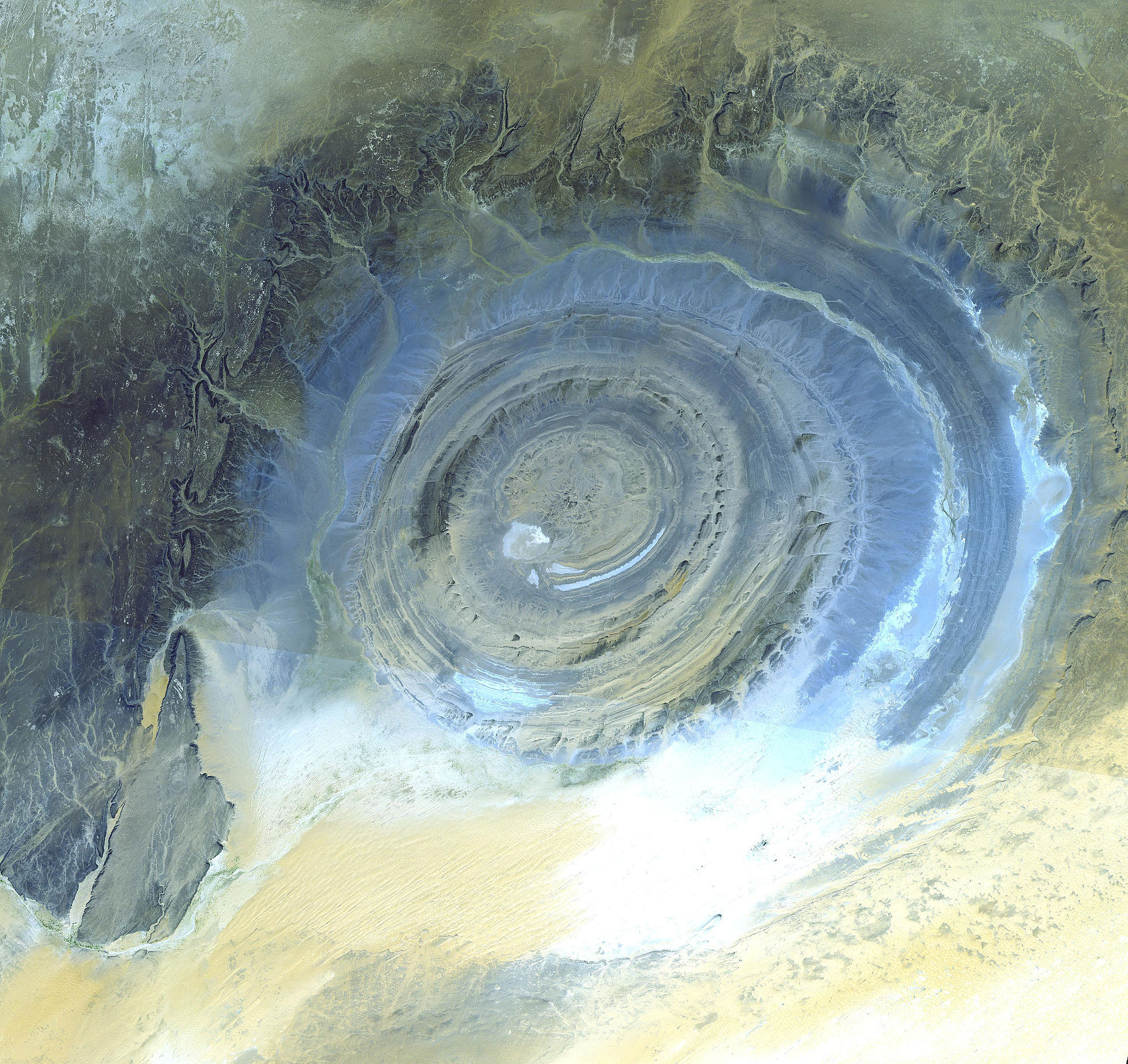
Another geologic feature that forms due to plastic deformation is called a dome. These are like architectural domes in buildings – unlike anticlines, they are rounded and arched from all directions, so they are different from a simple fold.
Let’s Review!
In the section below, review the terminology and apply the concepts.
Structure 1

Structure 2

Structure 3


