Enculturation Agents
Think back to an emotional event you experienced as a child. How did your parents react to you? Did your parents get frustrated or criticize you? Did they act patiently and provide support and guidance? Did your parents provide lots of rules for you or let you make decisions on your own? Why do you think your parents behaved the way they did? Enculturation agents are individuals and institutions that serve a role in shaping individual adaptations to a specific culture to better ensure growth and effectiveness.
Parents and caretakers are a primary enculturation agent for their young. Psychologists have attempted to answer questions about the influences on parents and understand why parents behave the way they do. Because parents are critical to a child’s development, a great deal of research has been focused on the impact that parents have on children. Parenting is a complex process in which parents and children influence one another. There are many reasons that parents behave the way they do.
The multiple influences on parenting are still being explored. Both caretakers and their children bring unique personality traits, characteristics, and habits to the parent-child dynamic that ultimately impacts the child’s development. Culture also influences parenting behaviors in fundamental ways. Although promoting the development of skills necessary to function effectively in one’s community is a universal goal of parenting, the specific skills necessary vary widely from culture to culture. Parents have different goals for their children that partially depend on their culture (Tamis-LeMonda et al., 2008).
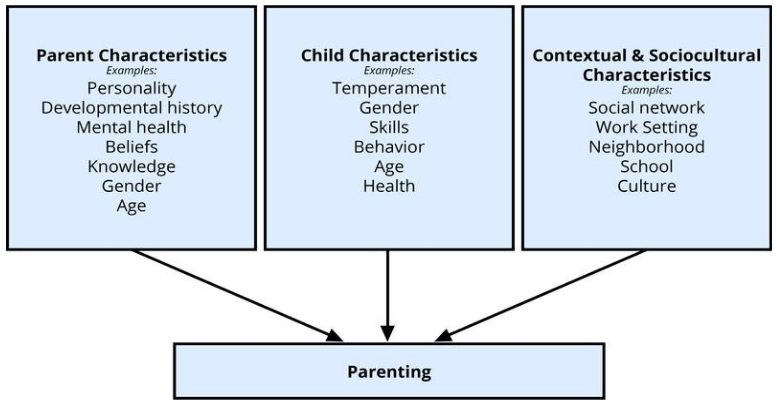
Differences in caretaking reflect differences in parenting goals, values, resources, and experiences. As previously stated, culture is learned. Regardless of the specific choices parents make, it can be said that caretakers play a pivotal role in exposing a child to early cultural learning. In fact, many researchers believe that parents/caretakers serve as the single, most important enculturation agent in any child’s life.
While some parenting priorities are culturally universal (parents are expected to play a role in nurturing and raising their young), many more childrearing values and habits are culture-specific. Culture-specific influences on caretaking choices can be subtle or overt, and promote a narrative of what parents “ought” to do in order to successfully raise their children. For example, American parents are encouraged to enculturate a sense of independence and assertiveness in children, while Japanese parents prioritize self-control, emotional maturity, and interdependence (Bornstein, 2012). Undoubtedly, every society places expectations on caretakers as enculturation agents to raise their young in ways that promote culture-specific goals and expectations. This chapter will focus on four areas of child development:
- Temperament
- Attachment
- Parenting Styles
- Cognition

