10.6 Nuclear Energy
Jeff Simpson and Carolina Londono Michel
Learning Objectives – By the end of this chapter, you should be able to do the following.
- Explain the process by which nuclear power can be used to create electricity.
- List two advantages and two disadvantages of nuclear power.
- Explain why very few nuclear power plants are being built around the world.
Figure 10.6.1 – Nuclear 101 (2:56)
.
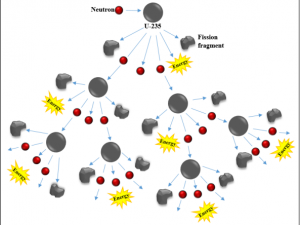
Nuclear energy is energy stored in the nucleus (core) of an atom. Strong forces hold protons and neutrons together [6]. When the nucleus of an atom splits, it releases energy in a process known as nuclear fission. During nuclear fission, a small atomic particle, a neutron, hits the nucleus of uranium atom with just enough energy to split the nucleus, releasing heat, radiation. and more neutrons. These newly-released neutrons bombard other uranium atoms, and the process repeats. This is the chain reaction used by nuclear power plants to produce heat energy and transform that heat energy into electricity. Scientists and engineers have learned to split nuclei of some large unstable elements and control the release of energy to use as a power source. (In a nuclear bomb, the chain reaction is not controlled and the concentration of nuclear material in a bomb is ~20X higher than in a power plant.)

Uranium
Uranium is a grey, metallic chemical element. It was discovered in 1789 by German physicist M.H. Klaproth. Its chemical symbol is U and its atomic number is 92. It is a heavy metal, the heaviest natural element, 70% heavier than lead, about 19X as heavy as water. This means that while a gallon of water will weight 8 pounds, a gallon of uranium will weight 152 pounds. It also is a naturally radioactive element that decays into daughter isotopes, releasing radiation energy. Uranium is a mixture of three different weights of atoms: three isotopes: 99.27 % uranium-238 (U238); the remainder consists of U-235 (0.72 %), and U-234 (0.006 %). U-235 is the preferred nuclear fuel because when its atoms are split (fissioned), they not only emit heat and high energy radiation but also enough neutrons to maintain a chain reaction and provide energy to power a nuclear power plant. Uranium is found in rocks all over the world but is relatively rare and the supply is finite making it a nonrenewable energy source.

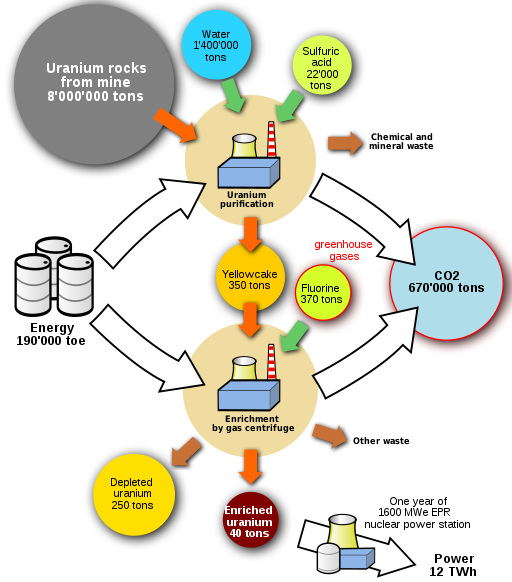
Uranium does not occur naturally in pure form. Instead, it usually occurs in combination with small amounts of other elements. Once mined, the U-235 must be extracted and processed before it can be used as a fuel in a nuclear power plant to generate electricity. Getting the uranium begins with exploration and the development of mines to extract the concentrated ore. Mining is either conventional (underground or open-pit) or unconventional, such as in-place solution mining or heap leaching which uses liquid solvents to dissolve and extract the ore. Mined uranium ore typically yields one to four pounds of uranium concentrate per ton of uranium ore (0.05% to 0.20%) [6].
Uranium Ore Deposits
The Colorado Plateau of the southwest United States contains uranium ore deposits with different origins. Notably, the area surrounding Arizona’s Grand Canyon contains uranium accumulated in brecciated (fragmental sedimentary) rocks. This occurred when the flow of groundwater dissolved parts of the Red Limestone formation, creating underground sinkholes and caves. Sometimes, the hollowing out of the limestone moves upwards, generating hollow columns that can collapse because of the weight of the overlying rock. The result is a “pipe” filled with breccia, thus the name for this deposit type is “breccia pipe” The fractured material acts as a trap for the uranium, which is deposited by groundwater. The breccia pipes may also contain copper, gold, silver, vanadium and other minerals. Uranium ore deposits from different ages also occur in sedimentary rocks and are associated with water flows that transport the uranium.
Uranium Processing
Once mined, the raw uranium ore must be refined into uranium concentrate in a process referred to as milling. The ore is crushed and ground into a fine powder then reacted with chemicals to separate from other minerals. The concentrated uranium product is typically a bright yellow or orange powder called yellowcake (U3O8). Milling operations produce tailings, which are an environmental liability. The yellowcake then undergoes conversion into uranium hexafluoride (UF6) gas. This step enables the atomic segregation of the three naturally occurring uranium isotopes into individual components. In the UF6 gas, the original concentrations of uranium isotopes are still unchanged. This gas is then sent to an enrichment plant where the isotope separation takes place and the concentration of U-235 is increased to about 4% to 5% (compared to 0.72% original concentration). The enriched UF6 is sealed in canisters and allowed to cool and solidify before it is transported to a fuel assembly plant. The next step in the production of nuclear fuel takes place at fuel fabrication facilities. Here, the enriched UF6 is reacted to form a black uranium dioxide (UO2) powder. The powder is compressed and formed into the shape of small ceramic fuel pellets. Each ceramic pellet produces roughly the same amount of energy as 150 gallons of oil. The pellets are stacked and sealed into long metal tubes that are about 1 centimeter in diameter to form fuel rods. Fuel rods then are bundled together to make up a fuel assembly. Depending on the reactor type, there are about 179 to 264 fuel rods in each fuel assembly. A typical reactor core holds 121 to 193 fuel assemblies [6].
Uses of Nuclear Energy
Nuclear power plants, such as Arizona’s Palo Verde Nuclear Generation Station (PVNGS) in Arizona 3-5% uranium in pellets, rods, and, cores. PVNGS can produce 3,937 megawatts of power and has operating over 90% of the time – the capacity factor – making it the largest net generator of electricity in the US. (Grand Coulee Dam in Washington can produce more power but operates at only a 35% capacity factor. (LINK)
Nuclear power, natural gas, and coal, met 83% of electricity needs in Arizona in 2022, though these figures do not include distributed or rooftop solar.

Benefits of Nuclear Energy
Unlike fossil fuel power plants, nuclear power plants generate electricity without emitting air pollution. This means that financial costs related to chronic health problems caused by air pollutants such as particulate material, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and ozone among others are significantly reduced. Nuclear reactors do not produce carbon dioxide while operating, so nuclear energy does not contribute to the global warming problem. Uranium is more efficient, generating far more power per unit weight or volume than coal [6]. Nuclear Energy is clean, but “there’s no such thing as a free lunch,” and the cost for nuclear power can be very high, especially for the communities where the uranium is found and processed.
The Drawbacks of Nuclear Energy
Radioactive Waste
The creation and disposal of radioactive wastes is a major environmental concern. Waste includes both tailings (leftover material) from mining and from processing as well as used or spent reactor fuel, dust, and other radioactive waste. These materials remain dangerous to human health for thousands of years. Radioactive wastes are classified as low-level or high radioactivity levels. By volume, most of the waste related to the nuclear power industry has a relatively low-level of radioactivity. Uranium mill tailings contain the radioactive element radium Ra, which decays to produce radon Rn, a radioactive gas. Most uranium mill tailings are placed near the processing facility or mill where they come from. Miners covered uranium mill tailings with a barrier of material such as clay to prevent radon from escaping into the atmosphere, topped by a layer of soil, rocks, or other materials to prevent erosion of the sealing barrier [6]. However, these solutions are only temporary in the face of Earth’s dynamic processes. Currently, there is no long-term solution for storing this waste.
Other types of low-level radioactive waste are tools, protective clothing, wiping cloths, and other disposable items that get contaminated with small amounts of radioactive dust or particles at nuclear fuel processing facilities and power plants. These materials are subject to special regulations that govern their handling, storage, and disposal so they will not come in contact with the outside environment. High-level radioactive waste consists of spent nuclear reactor fuel (i.e., fuel that is no longer useful for producing electricity). The spent reactor fuel is solid small fuel pellets in long metal tubes called rods (Fig 10.14). Spent reactor fuel assemblies are initially stored in specially designed pools of water, where the water cools the fuel and acts as a radiation shield. Spent reactor fuel assemblies can also be stored in specially designed dry storage containers. An increasing number of reactor operators now store their older spent fuel in dry storage facilities using special outdoor concrete or steel containers with air cooling. There is currently no permanent disposal facility in the United States for high-level nuclear waste.
The processes for mining and refining uranium ore and making reactor fuel require large amounts of energy. Nuclear power plants have large amounts of metal and concrete, which also require large amounts of energy to manufacture. If fossil fuels are used for mining and refining uranium ore or in constructing the nuclear plant, then the emissions from burning those fuels could be associated with the electricity that nuclear power plants generate. (Fig. 10.6.7)
It is possible to reprocess some fission products and unused uranium from spent nuclear fuel into new fuel. Reprocessed uranium can in principle also be re-used as fuel, but that is only economical when world’s uranium supply is low and prices are high. A breeder reactor is not restricted to using recycled plutonium and uranium. It can employ all the actinides, closing the nuclear fuel cycle and potentially multiplying the energy extracted from natural uranium by about 60 times. The process of extracting and concentrating spent fuel is both expensive and poses contamination risks. Once the fuel is reprocessed, the volume is decreased. Nuclear fuel reprocessing is performed Europe, Russia and Japan but not in the US where the Obama administration stepped back from President Bush’s plans for commercial-scale reprocessing and reverted to a program focused on reprocessing-related scientific research. LINK
Is Nuclear Power Really Cleaner?
The process of enriching the uranium used in a nuclear power plant requires vast amounts of electricity over years. This often is not included in the carbon calculations for nuclear power as shown below. Additionally, the mining and enrichment processes create their own waste products which are rarely mentioned when referring to nuclear power as “clean”.
Health Impacts
Uranium enters the body via ingestion, inhalation, and through the skin. Infrequent exposure to low levels of U is not considered problematic. In fact, the Colorado Plateau water contains natural low levels of uranium that are considered “safe”. However, mine workers and people living around processing facilities are continuously exposed to high levels of uranium and byproducts. Uranium contaminates soil, water, and air. Under this chronic exposure condition, uranium can accumulate in the kidneys, liver, muscles, bones, and the digestive tract, and it will flow through the blood to reach the brain and interfere with other systems. U produces kidney damage, genetic damage, cancer, and developmental problems.
Plant Failure
A nuclear meltdown, or uncontrolled nuclear reaction in a nuclear reactor, can result in widespread contamination of air and water. Some serious nuclear and radiation accidents have occurred worldwide. The most severe accident was the 1986 Chernobyl accident in the former Soviet Union (now Ukraine) which killed 31 people directly and sickened or caused cancer in thousands more. The 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in Japan was caused by a 9.0 magnitude earthquake that flooded the plant’s emergency power supply, causing the nuclear material to overheat. This resulted in the release of radioactivity although it did not directly result in any deaths at the time of the disaster. In 1979 the Three Mile Island accident (PA, USA) resulted in a near-disastrous core meltdown due to human error and mechanical failure. It did not result in any deaths. While there are potentially devastating consequences to a nuclear meltdown, the likelihood of one occurring is extremely small. After every meltdown, including the Fukushima disaster, new regulations have been put in place to prevent such an event from occurring again.
Such accidents raised concerns about the dangers of harnessing nuclear power. Since the early 1980s, the number of projects has dropped off except in China and India, both which have growing populations and are using more electricity. In China, nuclear power generates ~5% of the electricity compared to ~19% in the US. But even in China, ambitious plans to build more nuclear power plants have been scaled back due to concern from the public. Most nuclear power plants in China are located on the east coast where most of the population lives and where there is an ample supply of water to cool the reactors as the western part of the country is arid. [LINK]
Why then is the Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station in the Arizona desert? For its cooling water, Palo Verde uses treated effluent (sewage) from the Phoenix area. What was waste now is a resource.
Cost
Despite early predictions that nuclear energy would produce electricity too cheap to meter, electricity from nuclear power is one of there most expensive sources of electricity. [LINK]
Units 3 and 4 of the Vogtle Electric Generating Plant in Georgia was in 2023 after a decade of building. The original cost of $14,000,000,000 cost has ballooned to >$30,000,000,000 dollars. [Link] The Hinkley Point C Nuclear Power Plant in England is many years behind schedule and billions of dollars over budget. It is slated to begin generation in June 2027 and has a projected lifetime of 60 years.
Backyard Geology: Uranium in the Grand Canyon

Producing electricity from nuclear energy does not contribute directly to climate change, but it comes at a high cost that is not evenly shared. Uranium mining and processing in Arizona have affected the lives and homes of the Native Americans. The Cold War-era provoked a uranium rush in the arms race between the US and the Soviet Union. To supply the enriched U, many mines opened in Northern Arizona, without regulations and without minimum safety measures to protect the workers. The war ended. Over 500 mines were abandoned but the contamination, environmental damage, and health problems did not leave and residents of the area cannot forget because they live in the contamination. Navajos have higher rates of cancer, larger than the rest of the population.
In the mid- 2000’s a spike in the price of uranium ore brought back miners to the Colorado Plateau. Thousands filed claims near the Grand Canyon National Park. Because of health and environmental risks, Secretary of Interior, Ken Salazar, halted all claims in an area of one million acres of land for two years to allow time for more research. In 2012, Salazar extended the moratorium 20 more years as a precaution.
However, in 2018, the Trump administration expressed interest in nuclear weapons and listed uranium as a critical mineral for national security even though only non-fuel minerals should be listed. With this impulse, the mining sector pushed again to overturn the ban. However, preliminary results from the U.S. Geological Survey showed that the risk to the groundwater supply could be too high. An estimated 30 million people would have their water source contaminated. The Redwall Limestone aquifer which underlies the Colorado Plateau and connects to the Colorado River would be irreversibly contaminated. The Havasupai tribe in the Grand Canyon relies on this aquifer as their only source of water; the impact for them would be devastating. More research is needed to understand and measure the risk of uranium mining. So far, the research has been largely underfunded.
The Grand Canyon is one of the wonders of Earth. People from all over the world come to admire it. The relentless erosion of the Colorado River has exposed its vast richness and wealth. Should we risk that to get the uranium for a few decades of power? Should we fund the research to learn more? So far, mining companies are rarely accountable for the messes they leave behind.
Cameron, Arizona still is dealing with the legacy of uranium tailings.
One of two or more species of the same chemical element, i.e., having the same number of protons in the nucleus, but differing from one another by having a different number of neturons
Valuable material in the Earth, typically used for metallic mineral resources.
A type of clastic sedimentary rock that consists of angular pebble or cobble-sized clasts that are cemented together with finer-grained sediments.

