4.7 Thriving Near Volcanoes
Charlene Estrada
“Every act of creation is, first of all, an act of destruction.” -Pablo Picasso
Volcanic eruptions are deadly; molten lava destroys the surrounding land and vegetation, and unpredictable lahars will bury other regions downslope of the volcano. Even if a community is fortunate to survive a violent eruption accompanied by these and other hazards such as ash, toxic gases, and pyroclastic flows, these hazards can still cause fatalities, the death of livestock, and the immeasurable destruction of infrastructure such as buildings, homes, and farmlands.
As terrible as a volcanic eruption may be for our society, we also must acknowledge that without volcanism, life as we know it may never have begun on Earth! Volcanic activity is not limited to eruptions of lava, gases, or ash. Most active volcanoes es are continuous sources of heat and chemicals. For our earliest ancestor on the planet (which was likely bacteria), which sought its energy from heat or chemicals, areas of volcanic activity were a gold mine!
Literal gold mines are also sourced from volcanic activity, as are many other metals. Humans have had a long history of using igneous rocks and precious minerals to build industries and economies. Below, we will explore how volcanoes have transformed life on our planet, and how we have learned to harness the benefits of volcanic activity.
Hydrothermal Vents
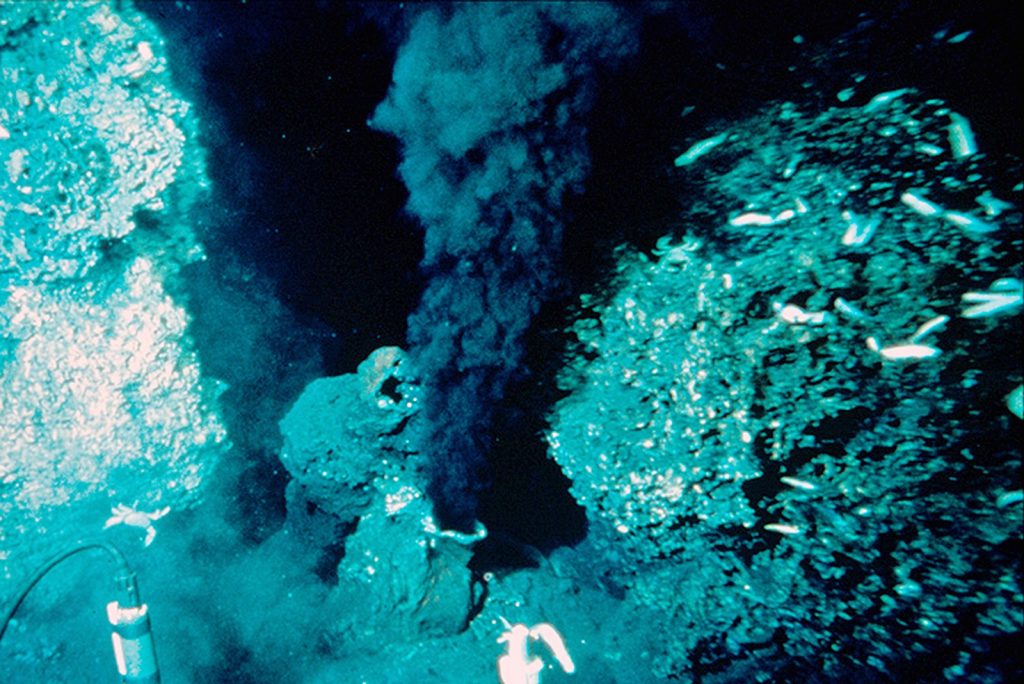
An intriguing consequence of volcanism at mid-ocean ridges are areas along the divergent boundary that heat the seawater. This water reaches temperatures up to 380°C (716°F!). At such hot temperatures, the water can dissolve metallic elements from the igneous rocks. When that water circulates up to the rest of the ocean, it carries a surprise: the water is dark black!
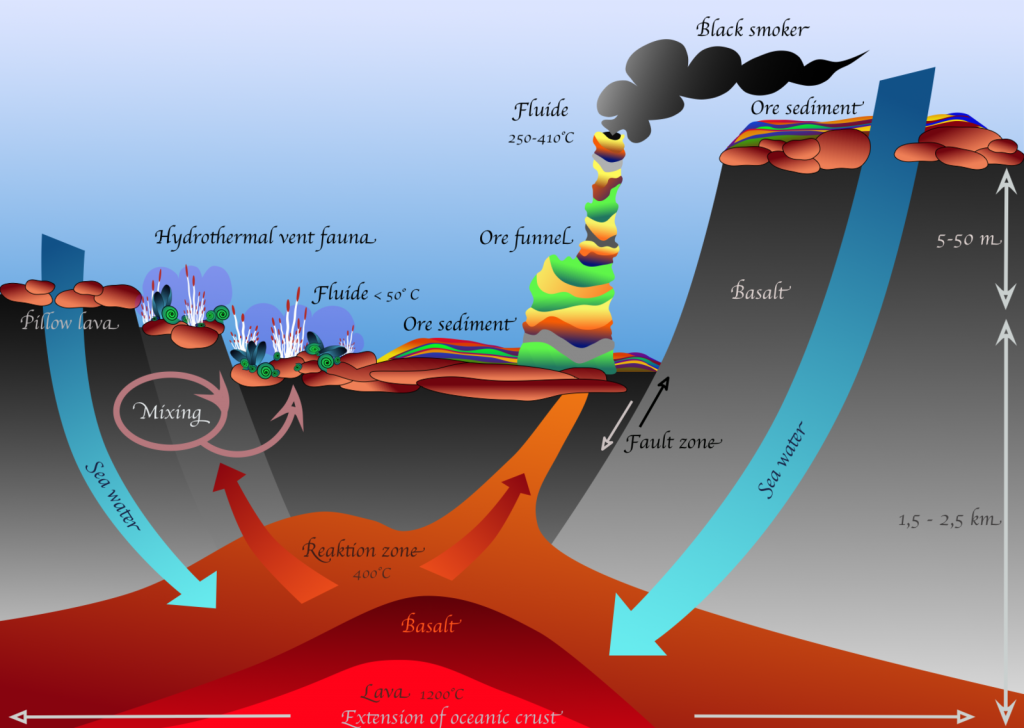
These areas of very hot, mineral-rich water are called deep-sea hydrothermal vents. They are sites for economic and precious mineral deposition, but they are also areas where diverse ecosystems can thrive deep beyond the reach of sunlight. Hydrothermal vents that belch out dark plumes of minerals along with hot water are usually called “black smokers”.
Scientists are very interested in hydrothermal vents because there is a strong indication that some of the earliest lifeforms on Earth preferred very high temperatures of over 80°C. We do not know much about the very first life on Earth, except that it had to be very similar to a single-celled bacterium, and that it did not have the capability to make its energy through photosynthesis. Some scientists suggest that the first life on Earth lived close to a hydrothermal vent, where it could keep warm and make its energy through an alternative method of eating the chemicals that are released through this volcanic process.
Hot Springs and Geysers
Water and high-temperature rock do not just encounter one another deep in the ocean at mid-oceanic ridges. This process also regularly occurs on land. Volcanic activity keeps rock beneath our surface very hot; therefore, when water meets this rock at depth, it too becomes superheated. This overly hot water will find a way to rise to the surface, often through cracks in the layers of rock, and the end result is often exciting! We will observe that hot water shoots upward from underground as a geyser.
Video 4.7.1. A large geyser, known as Old Faithful, continuously erupts hot water and steam up around 130 feet into the air, goes back down into the ground and then erupts more to the cheers of surrounding tourists at Yellowstone National Park. (2:22)
Perhaps the most famous geyser in the United States is Old Faithful, at Yellowstone National Park. This region is affected by hot spot volcanism, and the geyser itself predictably erupts about 17 times each day [15].
A hot spring describes hot or warm water that has quietly pooled at the surface. As you might expect from the presence of Old Faithful, there are thousands of hot springs at Yellowstone! Like hydrothermal vents, hot springs provide a wealth of chemical and heat energy for microbes to thrive, which can lead to a wide range of differently colored springs, such as the Grand Prismatic Spring in Yellowstone.
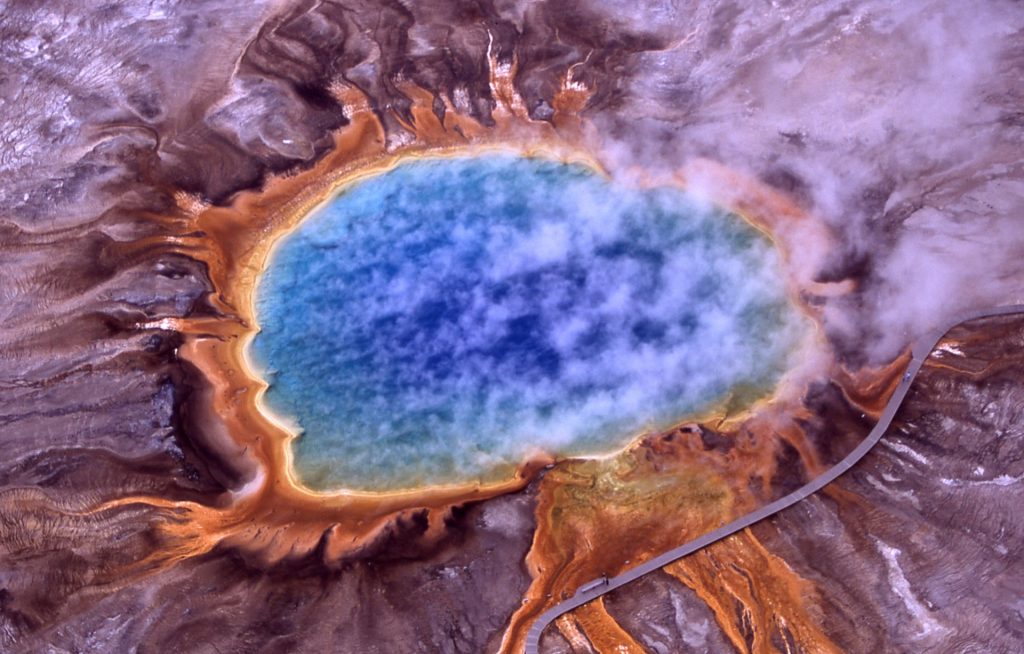
Most hot springs are known in the media for their warm water that humans (and animals!) can soak in comfortably. Japan, which sits along a subduction zone with significant volcanic activity, has built a rich culture surrounding hot springs. Some hot springs contain unique concentrations of dissolved elements and minerals that have softened skin and (reportedly) relaxed tired muscles.

Nevertheless, if you encounter a hot spring, DO NOT step into it, unless it has been approved as safe for human use! A lot of hot springs are extremely acidic, or extremely alkaline, both will burn you. Others are boiling hot or contain toxic gases and chemicals. Nearly every year, there is a report of a tourist death or severe injury at Yellowstone National Park due to attempted bathing in the hot springs. In some of these unfortunate circumstances, the bodies of these individuals are dissolved in acidic, boiling water within a day.

BACKYARD GEOLOGY: HOT SPRINGS IN ARIZONA
There are many hot springs throughout the United States, and Arizona is no exception! Although most of our Northern Arizona volcanoes are extinct, hot springs can also be created by a high geothermal gradient. When that warm water rises, it can have the same therapeutic benefits as springs in Japan. Two popular destinations are Castle Hot Springs (60 miles from Phoenix) and Verde Hot Springs (100 miles away from Phoenix, Fig. 4.7.6). The hot springs in our state were traditionally believed by the Apache and Yavapai to hold healing properties [16], and should you experience an Arizona hot spring (maybe not in the summer) it will be easy to understand why!

A Wealth of Resources
Most volcanic activity is great for business. Pompeii and Mount Vesuvius. The Hawaiian Islands. Arequipa and El Misti. Tokyo and Fuji-san. Historically, there have been many civilizations around volcanoes, and this was not bad luck or coincidence. When lava cools, it becomes igneous rock. When igneous rock is eventually weathered, it provides the land with fertile soil for agriculture.
Volcanoes also leave deposits of precious minerals such as gold, silver, copper, lead, zinc, iron, and nickel. Many of these are precipitated by the “black-smoker” hydrothermal vents. Volcanoes more commonly deposit igneous rocks such as granite that have been used as sturdy building materials.

Some of the most amazing landscapes are near volcanoes because volcanic activity builds land and creates breathtaking scenery. The volcanoes themselves are economically vital for many regions because of the recreational activity and tourism they bring [1]. As terrifying as an eruption at Yellowstone may be, this region is one of the most frequented parks by international tourists in the United States!

Geothermal Energy
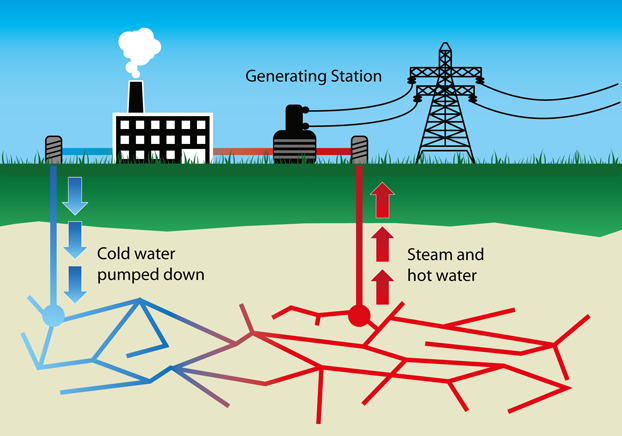
Geothermal energy is becoming a rising alternative source of energy. “Geothermal” references the fact that heat is being sources from the Earth, or in this situation, volcanic activity at depth. Volcanic activity generates heat, which can be harnessed to create electricity [1]. In some regions, there is enough geothermal power to completely replace our more traditional methods of generating electricity such as burning fossil fuels, and this method does not produce additional greenhouse gases.
Which regions would benefit most from geothermal energy? Follow the volcanoes. Hawaii, particularly at the world’s most active volcano of Kilauea, is an excellent source of American geothermal energy. Iceland also significantly benefits from this natural resource since it sits along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Around 85% of the homes in that country are already powered by geothermal energy [17].

molten rock that has erupted at the Earth's surface due to volcanic processes.
A mudflow, or type of mass movement, that is a mixture of water, ash, rock, sediment, and debris that rapidly and suddenly moves downslope. Lahars are a commonly associated hazard with volcanic eruptions.
an extreme natural event that is a threat to life and property
volcanically ejected rock fragments or particles that are less than 2 mm.
A mixture of super-heated gas, ash, volcanic glass, and rock fragments that rapidly moves downslope from 60 to over 400 mph.
A volcano that has erupted at least once over the past 10,000 years and has the possibility of erupting in the future.
a metallic, brassy-yellow mineral made only of the element gold (Au). It is a precious metal in the world economy.
Rocks that crystallize from molten materials beneath the Earth surface or from volcanic processes.
(sometimes abbreviated as "MORs" by scientists) an underwater mountain ridge in the middle of the ocean that is formed by seafloor spreading centers at divergent boundaries.
A region along Earth's lithosphere where at least two tectonic plates move apart from one another.
A type of volcanic activity, that occurs independent of plate boundaries, in which a plume of molten magma from deep within the mantle upwells at the Earths surface.
The process in which the older, denser tectonic plate at a convergent boundary will buckle and sink into the lithosphere. This plate will always be composed of oceanic lithosphere.
A pure substance that is not composed of any other ingredients found in the Periodic Table of Elements. One atom can be composed of only one element and form bonds with other elements.
a solid, inorganic, and crystalline substance that has a predictable chemical composition and form by natural processes.
a pattern in which temperatures in the crust increase by about 25 degrees Celsius per kilometer (km) of depth.
The process of physically or chemically breaking down, transforming, or dissolving existing rock with contact by water, the atmosphere, or biosphere.
a grayish-white metallic mineral composed only of the element silver (Ag). It is a precious metal used by the global economy.
A metallic, brownish-red mineral composed only of the element copper (Cu). It is used widely in the global economy in industry and technology.
A felsic, intrusive rock with coarse-grained texture. Granite composes mountain cores and can be found on and within the continental crust.
An alternative and renewable fuel source in which electricity is generated from the Earth's heat from volcanic activity below the surface.
A type of fuel source that has formed on the planet from natural processes.
A category of gas molecules that can absorb infrared radiation from sunlight and cause heat to remain trapped within a planet's atmosphere.
The world's longest mountain chain found beneath the Atlantic ocean between North America, South America and Europe and Africa. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an example of a mid-ocean ridge, or MOR.

