4.1 Molten Materials
Charlene Estrada
We may receive all the heat we need on the Earth’s surface from sunlight, but if you dig a hole just a few feet deep, you might notice that the surrounding soil is much cooler. This happens because much of the sediment is insulated from the sun’s energy. But, if you could dig miles and miles into the crust, you would find that the temperature of the rock would increase!

This increase in temperature with depth in the Earth’s crust is called the geothermal gradient. We can expect temperatures to increase about 25°C for each kilometer of depth. This sounds like a significant increase in heat, but once we pass the 100 km mark, temperatures really take off!
As we learned in the second chapter, the Earth’s iron core is wickedly hot! Such heat powers plate tectonics, and when combined with other factors, it can lead to partial melting in the upper mantle. This melted, molten rock occasionally rises to the Earth’s surface and when it does, watch out!
Is it Magma or is it Lava?
You may have heard both magma and lava used to refer to molten rock. This can confuse, especially since both terms apply to hot, melted rock. So what’s the difference, anyway? It comes down to the location. Magma is hot, molten rock that exists beneath the Earth’s surface. It can be found in the crust right below a volcano or within the mantle. For a volcano to erupt, it must have a source of magma.
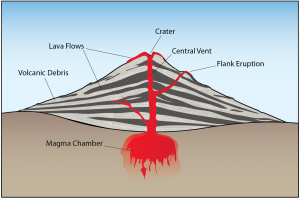
Lava, on the other hand, is only observed at the surface following a volcanic eruption. It will have the same composition as the magma from which it originated. Besides erupting only at the surface, lava cools quickly because it is exposed to the comparatively cold Earth’s atmosphere (or sometimes water!), and we see different igneous rock textures as a result. Igneous rocks from magma that solidified at depth are coarse-grained or intrusive because they cool slowly, but those from lava are fine-grained, or extrusive.

Melting Solid Rock. How does magma form?
Magma and lava contain three components—melt, solids, and volatiles (dissolved gases). The liquid part, called melt, is made of ions from molten minerals.
All you need to melt a solid rock is heat, right? Wrong! It may be counterintuitive, but most geological processes that melt rock do not involve increasing the temperature. Most lava at volcanoes is around 700 to 1300°C, which is the typical temperature of our upper mantle. However, our mantle as a whole is solid, so something else is required to cause rock to melt. That “something else” can be a sudden decrease in pressure or introducing liquid water, which will lower the melting point of rocks in the mantle. The two main mechanisms through which rocks melt are decompression melting and flux melting.
Decompression Melting
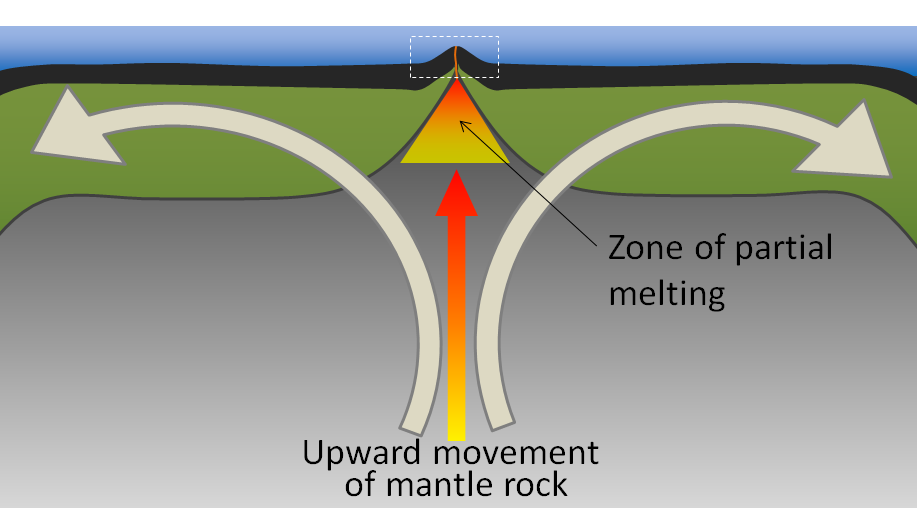
Our mantle is solid, but under high temperatures and pressures, it flows over very long timescales in a process known as convection. Convection forms circular cells of movement for the rock within the mantle, and sometimes leads to the upwelling of hot mantle material at divergent plate boundaries and hot spots.
Rock is a poor heat conductor, so as rock in the mantle rises with upwelling or convection, its temperature does not significantly change. Nevertheless, when that rock rises, the pressure of the rock decreases. This happens because the depth decreases, meaning that the weight of the column of rock above it decreases. It is the decrease in lithostatic pressure that causes the rock to melt. This process of the rock melting due to a sudden change in pressure is called decompression melting, and it typically occurs at hot spots and divergent boundaries, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge [1].
Flux Melting
At subduction zones along the Earth’s lithosphere, the descending slab is always made of oceanic lithosphere. This slab contains some hydrated minerals that, when exposed to elevated temperatures and pressures during subduction, will become released as volatile gases such as water vapor.
These volatile gases rise and interact with the overlying plate in the subduction zone. The addition of the volatiles does not change the pressure or temperature of the rock, but it does lower a property called the melting point. The decrease in melting point with those added volatiles suddenly makes it possible for the rocks in the subduction zone to melt at the same pressures and temperatures they have been experiencing, which is why we observe volcanoes at this type of plate boundary. Magmas producing the volcanoes of the Ring of Fire, associated with the subduction zones bordering the Pacific Ocean, are a result of flux melting [1].
Magma Composition
In 1980, Mount St. Helens blew up in the costliest and deadliest volcanic eruption in United States history. The eruption killed 57 people, destroyed 250 homes, and swept away 47 bridges. Mount St. Helens today still has minor earthquakes and eruptions and now has a horseshoe-shaped crater with a lava dome inside. The dome is made of pb_glossary id=”1812″]viscous[/pb_glossary] lava that oozes into place [1].
Video 4.1.1 Geologists from the US Geological Survey explained the main eruption event as well as the signs that announced it and the aftermath (7:00).
Volcanoes do not always erupt in the same way. Each volcanic eruption is unique, differing in magnitude, style, and composition of the erupted material. One key to what makes the eruption unique is the chemical composition of the magma that feeds a volcano, which determines (1) the eruption style, (2) the type of volcanic cone that forms, and (3) the composition of rocks that are found at the volcano.
The words that we use to describe the composition of igneous rocks (Ch. 3), also the ones we use to describe the composition of the magma. Mafic magmas are low in silica and have darker magnesium (Mg), and iron (Fe)-rich minerals, such as olivine and pyroxene. Felsic magmas are higher in silica and have lighter-colored minerals such as quartz and orthoclase feldspar.
The higher the amount of silica in the magma, the higher its viscosity. Viscosity is a liquid’s resistance to flow or movement within the Earth or on its surface. Viscosity determines what the magma will do. Mafic magma is not very viscous and will flow smoothly to the surface.
Video 4.1.2 Review the impacts of viscosity on magmas, lavas and the igneous rocks derived (4:57).
Volcanoes with a mafic composition will typically not have very explosive eruptions, but the lava will be fast moving. This mafic lava often moves down mountainsides and cools rapidly into unique textures that are either ropey called “Pahoehoe” or rough called “A’a“.

Felsic magma is very viscous, and it does not flow smoothly. Most felsic magma will stay deeper in the crust and will cool to form intrusive igneous rocks such as granite and diorite. If felsic magma rises into a magma chamber, it may be too viscous to move, so it tends to get stuck.
However, intermediate magma is also highly viscous, and it contains dissolved volatile gases. These gases become trapped by the magma, and the magma chamber begins to build in pressure. When the magma finally can erupt as lava, it does so very violently and explosively, as we have seen at Mount St. Helens.
The thin, outermost layer of Earth composed of rigid rock, which is home to all known life on the planet.
a pattern in which temperatures in the crust increase by about 25 degrees Celsius per kilometer (km) of depth.
The extremely hot center layer within Earth, which is composed mainly of iron and nickel.
The theory that the outer layer of the Earth (the lithosphere) is broken in several plates, and these plates move relative to one another, causing the major topographic features of Earth (e.g. mountains, oceans) and most earthquakes and volcanoes.
The outermost layer of the Earth's mantle, which contains both the lower lithosphere and upper asthenosphere. This layer is susceptible to convection currents and plastic flow.
molten rock that can be found beneath the Earth's surface.
molten rock that has erupted at the Earth's surface due to volcanic processes.
an area on the Earth's surface where lava, ash, and/or volatile gases erupt and eventually solidify into rock.
A hot interior layer of solid rock between the crust and core that is capable of plastic flow. The mantle is the largest layer of Earth.
Rocks that crystallize from molten materials beneath the Earth surface or from volcanic processes.
coarse-grained igneous rock texture with visible crystals within the matrix.
Fine-grained, or microcrystalline, igneous rock texture.
The liquid portion of molten rock found in both lava and magma.
A charged atom or molecule.
a solid, inorganic, and crystalline substance that has a predictable chemical composition and form by natural processes.
the temperature and pressure required for a solid material to melt into a liquid.
movement driven by density and heat in which low-density hot materials move upward and dense, cold materials sink downward.
A region along Earth's lithosphere where at least two tectonic plates move apart from one another.
A type of volcanic activity, that occurs independent of plate boundaries, in which a plume of molten magma from deep within the mantle upwells at the Earths surface.
The vertical pressure at a point in the Earth's crust, equal to the pressure caused by the weight of a column of the overlying rock or soil.
The process in which solid rock melts upon experiencing a sudden decrease in pressure, but not temperature.
The world's longest mountain chain found beneath the Atlantic ocean between North America, South America and Europe and Africa. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an example of a mid-ocean ridge, or MOR.
The process in which the older, denser tectonic plate at a convergent boundary will buckle and sink into the lithosphere. This plate will always be composed of oceanic lithosphere.
The outer, relatively rigid layer of the Earth that is composed of crust and upper mantle.
The tectonic plate descending within a subduction zone into the asthenosphere, and beyond toward the deep mantle.
Gases dissolved within magma or lava.
A region extending along the islands and coastlines bordering the Pacific ocean that is affected by convergent and transform plate boundaries. These boundaries cause a higher incidence of earthquakes and volcanoes.
a process in which solid rock melts because volatiles such as water vapor have caused its melting point to decrease.
A round, hill-like protrusion formed by oozing, viscous lava found atop of a volcano.
Originating from an iron and magnesium-rich magma/lava composition.
a compound composed of silicon and oxygen in the formula SiO2.
(Mg,Fe)SiO4
A class of silicate mineral that forms at high temperatures and can have a magnesium (Mg) or iron (Fe) rich composition.
(Mg,Ca,Fe)SiO3
A class of dark-colored silicate minerals that form under high temperatures and/or pressures. These form in igneous and metamorphic rocks.
originating from a feldspar and silica-rich magma/lava composition.
A very common rock-forming silicate mineral with formula SiO2.
A type of potassium feldspar that is orange-pink in color. It is more abundant of the K-Feldspars and often found in granite.
a liquid's resistance to flow or movement
A felsic, intrusive rock with coarse-grained texture. Granite composes mountain cores and can be found on and within the continental crust.
An intermediate, extrusive igneous rock that is coarse-grained. The presence of large black and white crystals on the rock have a "dalmation"-like appearance.
A composition of igneous rocks, magma, and lava that is between felsic and mafic.

